7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Repo-linked deposit and lending rates
Repo Rate
India’s economic slowdown
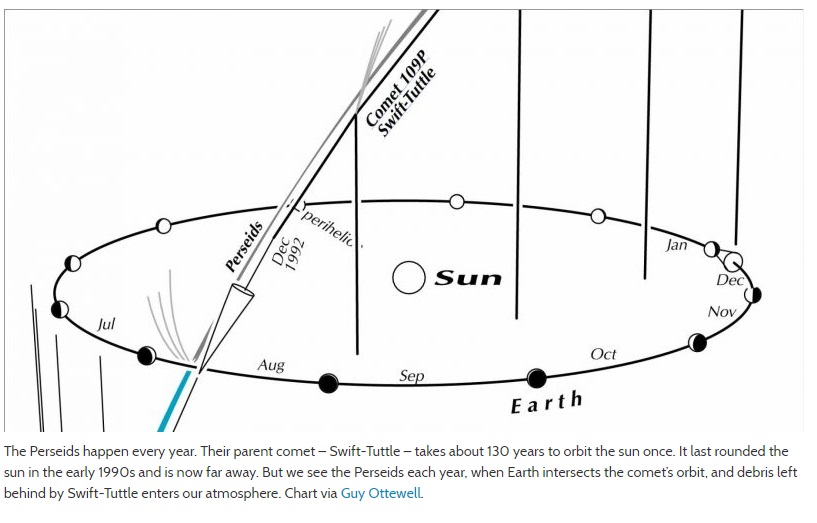
Perseid Meteor Shower
Increase of harmful Mercury level in fish
Source: PIB, The Indian Express