Footballer Lionel Messi’s signing on fee at Ligue 1 French club Paris St Germain (PSG) includes some of the PSG’s cryptocurrency ‘fan tokens’.
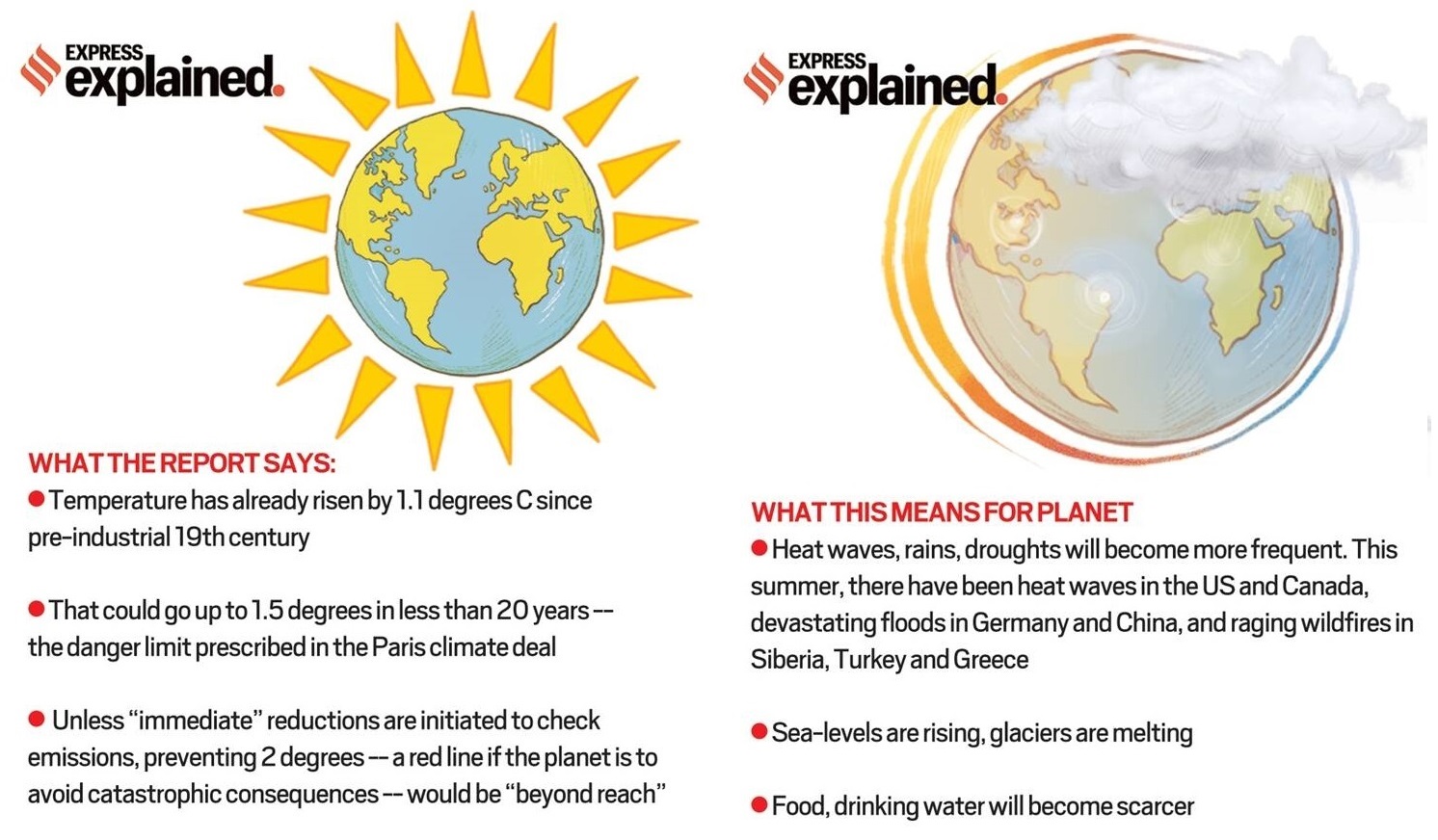
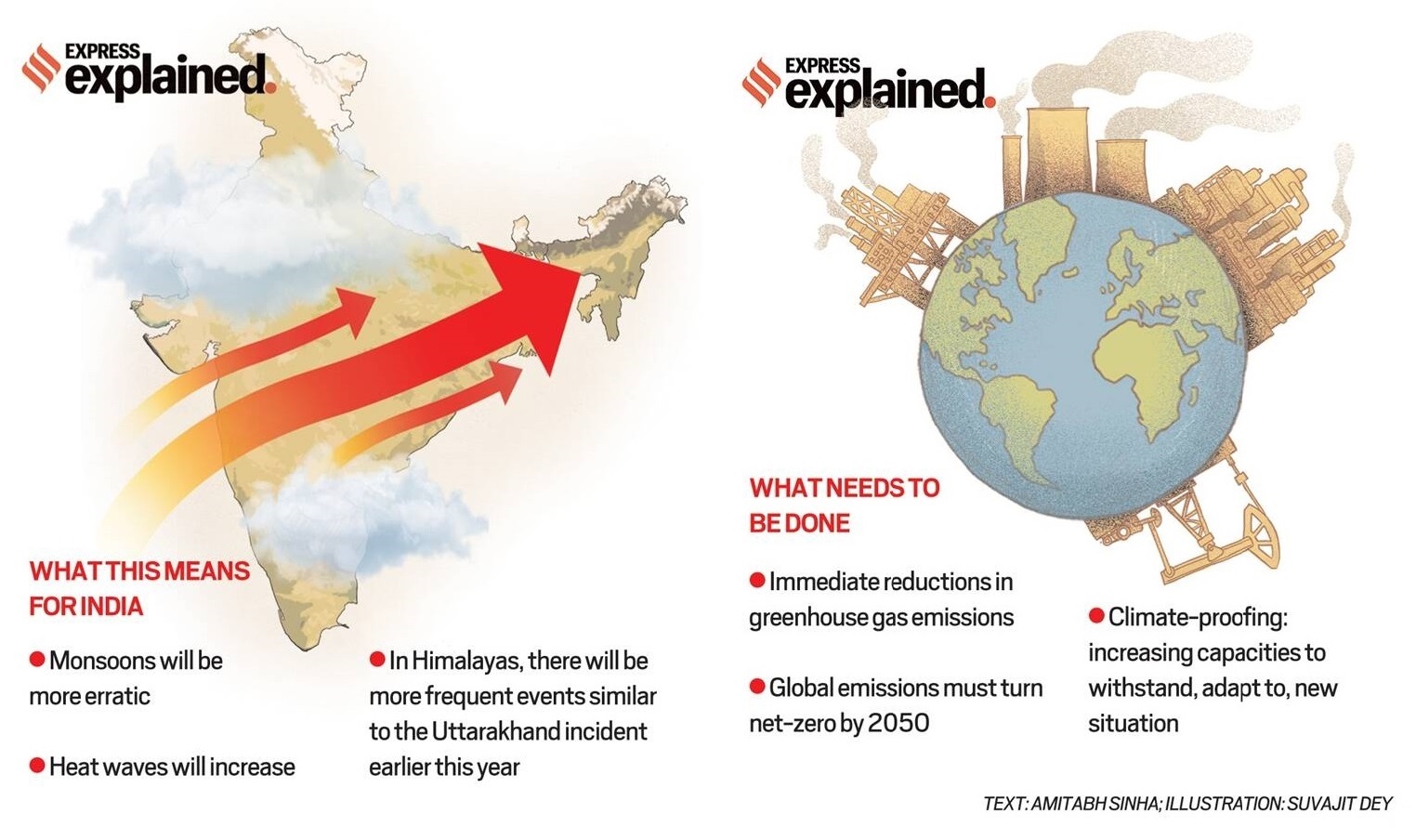
Inter-governmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has released the 6th Assessment Report titled ‘Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis’.
Researchers have developed a protein-based vaccine that mimics shape of coronavirus. This can be used to create immunity that lasts for long time.
The following are the result of the Government’s initiatives for controlling the Population.
TFR is the average number of children born to a woman in her life time. TFR of 2.1 is set by the Government as the replacement level fertility rate (target) at which population stability is achieved.
|
Particulars |
Goals |
|
Maternal Mortality Rate |
Reduce MMR to 1/1000 live births |
|
Infant Mortality Rate |
Reduce IMR to 25/1000 live births |
|
Total Fertility Rate |
Reduce TFR to 2.1 |
|
Anaemia |
Prevention and reduction of anaemia in women aged 15-49 years |
|
Diseases |
Prevent and reduce mortality & morbidity from communicable, non-communicable; injuries and emerging diseases |
|
Tuberculosis |
Reduce annual incidence and mortality from Tuberculosis by half |
|
Leprosy |
Reduce the prevalence of Leprosy to <1/10000 population and incidence to zero in all districts |
|
Malaria |
Annual Malaria Incidence to be <1/1000 |
|
Microfilaria |
Less than 1% microfilaria prevalence in all districts |
|
Kala-azar |
Elimination by 2015, <1 case/10000 population in all blocks |
|
Expenditure |
Reduce household out-of-pocket expenditure on total health care expenditure |
Source: PIB, The Indian Express, First Post