7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Doctrine of Essentiality
Arrokoth
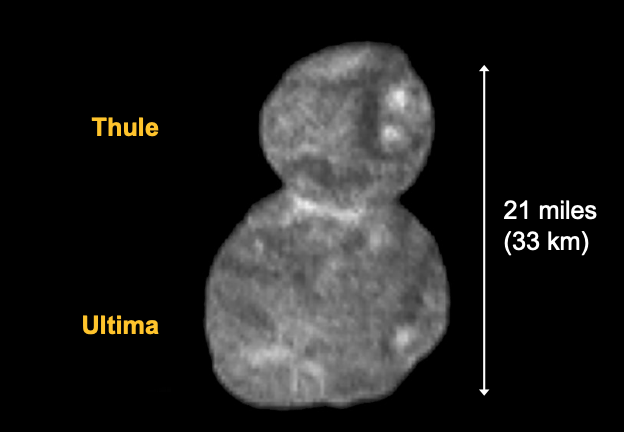
New Horizons Spacecraft
International Astronomical Union
World Gold Council
North East Convention Centre
Source: The Hindu, PIB, Indian Express