The Attukal Pongala festival in Kerala will be a muted affair this year with strict Covid-19 protocols limiting rituals to the temple and homes.
Attukal Bhagavathi is believed to be an incarnation of Kannaki, the central character of the Tamil epic 'Silappathikaaram'.
Reference
Reference
India has lashed out at the Organisation of the Islamic Cooperation for being "communal minded" amid the Karnataka hijab row.
Reference
Ministry of Education (MoE) has approved the ‘New India Literacy Programme’ for the period FYs 2022-2027, to cover all the aspects of Adult Education to align with the National Education Policy (NEP).
Instead of ‘Adult Education,’ the ministry has decided to use ‘Education for All’ as the previous term did not represent all non-literates in the age group of 15 years and above across all state and union territories.
Reference
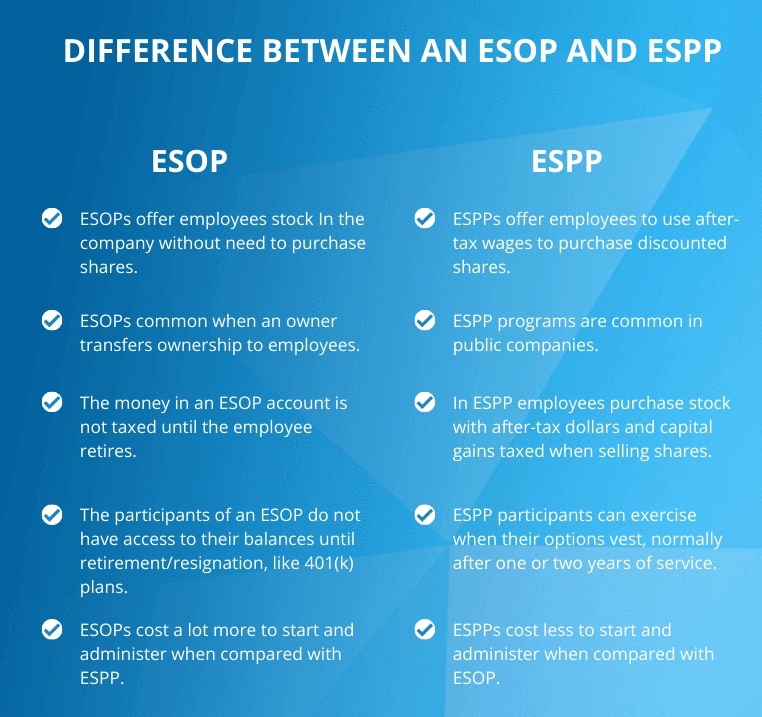
Udaan, a B2B e-commerce platform, has announced an employee stock option plan (ESOP) policy covering all its employees with significant changes including the removal of ‘cliff’ vesting period for all ESOPs.
The one year ‘cliff’ period is a widely prevalent industry practice that requires employees to wait for one year for their ESOPs to start vesting.
Reference