Tamil Nadu was the first State to create the role of Director General of Audit to oversee all audit departments.
The Nyingma sect has identified a boy from Spiti in Himachal Pradesh as the reincarnation of the late Taklung Setrung Rinpoche.
The 4 schools of Tibetan Buddhism are Nyingma, Kagyu, Sakya, and Gelug or Gelugpa.
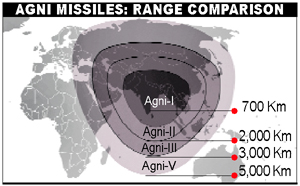
India successfully test-fires intermediate range ballistic Agni-3 missile.
Strategic Forces Command is part of India’s Nuclear Command Authority (NCA) of India, which is responsible for all command, control, and operational decisions relating to its nuclear-weapons capability.
According to The Lancet study, five bacteria types caused nearly 6.8 lakh deaths in India in 2019.
E. coli, S. pneumoniae, K. pneumoniae, S. aureus and A. baumanii are the top 5 deadliest bacterial pathogens.
Common bacterial infections were the second-leading cause of death in 2019, and were linked to one in eight deaths globally.
|
Bacteria |
Normal Presence |
Disease |
|
Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
The gram-negative bacteria is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. |
Most E.coli strains are harmless, but some strains such as Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC) can cause can cause severe foodborne disease. |
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae |
It is an encapsulated gram-negative bacteria with a polysaccharide capsule an essential factor in virulence. |
Serious pneumococcal infections include pneumonia, meningitis and febrile bacteraemia |
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae |
Occurs in soil and water and on plants, and some strains are found in human gastrointestinal tract. |
A pathogen of the human respiratory system that causes lethal pneumonia in persons with underlying medical problems. |
|
Staphylococcus aureus |
The gram-positive bacteria frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. |
It may lead to abscessing infections of the skin, eyes and genital tract and can become life threatening to immunocompromised or immunodeficient individuals. |
|
Acinetobacter baumannii |
The opportunistic gram-negative pathogen are found in soil, water and sometimes on the skin of healthy people. They are generally harmless to healthy individuals but can cause serious infections in critically ill hospital patients. |
It infiltrates open wounds, catheters, and ventilation tubes and causes fatal meningitis, bacteraemia and pneumonia. |
The Reserve Bank of India data shows that banks wrote off more than Rs 10 lakh crore in loans over the last five years.
If the principal or interest payment for a loan has not been paid for over 3 months, the loan account is termed as Non-Performing Asset.
Loan waive-off would mean that the loan is considered to be completely cancelled and the borrower no longer holds the liability of the loan.