7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
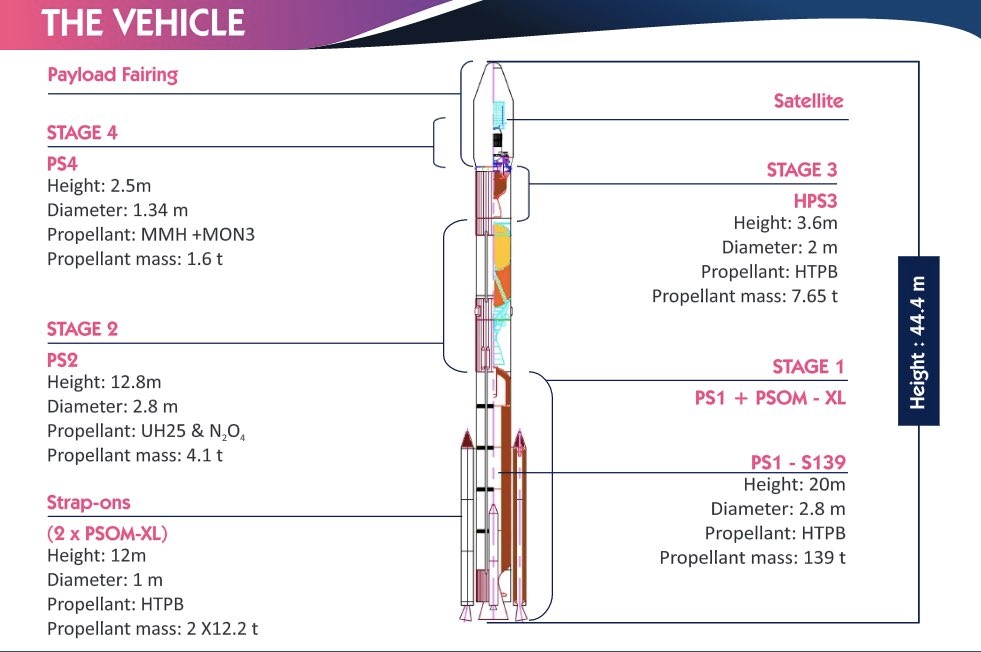
MICROSAT-R and KALAMSAT
INS Kohassa
National Girl Child Day
E-Court Service
Biojet fuel for Aircraft
Source: PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express