The OECD/G20 Inclusive Framework on Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (IF) has agreed a two-Pillar Solution to address the tax challenges arising from the digitalization of the Economy.
Reference
Recently, India and the USA agreed on a transition from India's charge of 2% Equalisation Levy 2020 on e-commerce supplies & the US’ trade action regarding the said Equalisation Levy under the 2-Pillar Solution.
Reference
Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare released the findings of Phase-II of the 2019-21 National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5).
|
Child Nutrition indicators |
All-India level data |
|
Stunting |
Declined from 38% to 36% |
|
Wasting |
Declined from 21% to 19% |
|
Underweight |
Declined from 36% to 32% |
|
NFHS |
Year |
|
NFHS-1 |
1992-93 |
|
NFHS-2 |
1998-99 |
|
NFHS-3 |
2005-2006 |
|
NFHS-4 |
2015-2016 |
|
NFHS-5 |
2019-2021 |
Reference
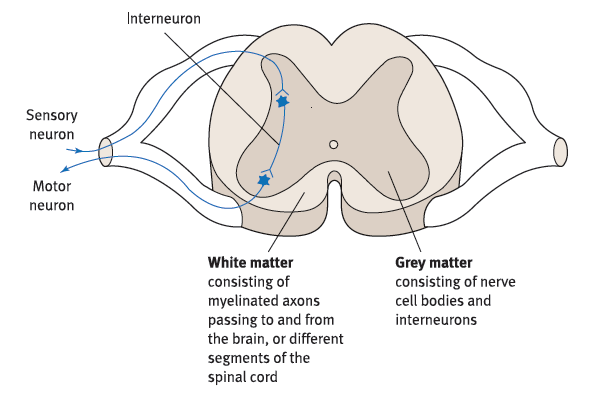
A research supported under the SATYAM program by Department of Science & Technology has found that daily home-based meditation can increase the amount of grey matter in brains of patients with mild Alzheimer’s disease.
White matter consists of fibres of the tracts covered with the myelin sheath, which gives an opaque white appearance to the layer.

Reference
The participants from 16 States signed the Mysuru Declaration and resolved to roll out the Common Minimum Service delivery by Panchayats across the country from April 1, 2022.
Reference
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1774310
Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying organises a National Stakeholder Workshop on the National Action Plan to Combat Anti-Microbial Resistance.
Reference