7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Rising dengue cases in Mumbai
NVBDCP
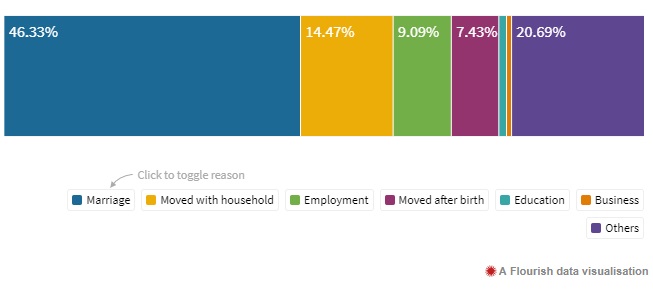
Census data on Migrations
Van Dhan Vikas Kendras
Poshan Abhiyaan
Source: PIB, The Indian Express