7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Iconic Tourist Sites
Adopt a Heritage Scheme (Apni Dharohar, Apni Pehchaan)
Cryptocurrency
Distributed Ledger Technologies
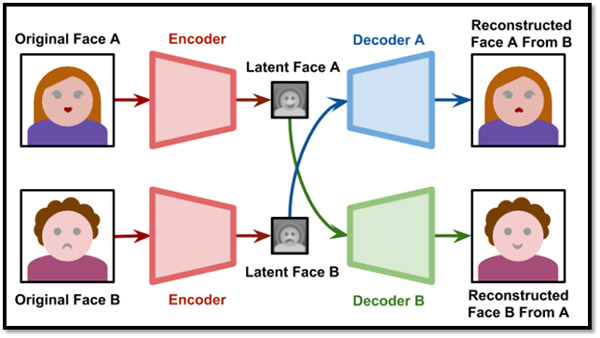
Deepfakes
Source: Indian Express, PIB, IDSA