The World Health Organisation (WHO) released the Global TB Report 2022 highlighting the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on TB all over the world.
Key Findings
India Specific Findings
For Related Topics - BPal treatment, PM TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan, Ni-kshay Mitra, click here.
References
A farmer from Wayanad creates different patterns including Ashoka Chakra in his paddy field using Tambo art.
How Tambo art is made?
References
Drastic changes in climate patterns over the last few years have adversely impacted India’s coffee production and the quality of the crop.
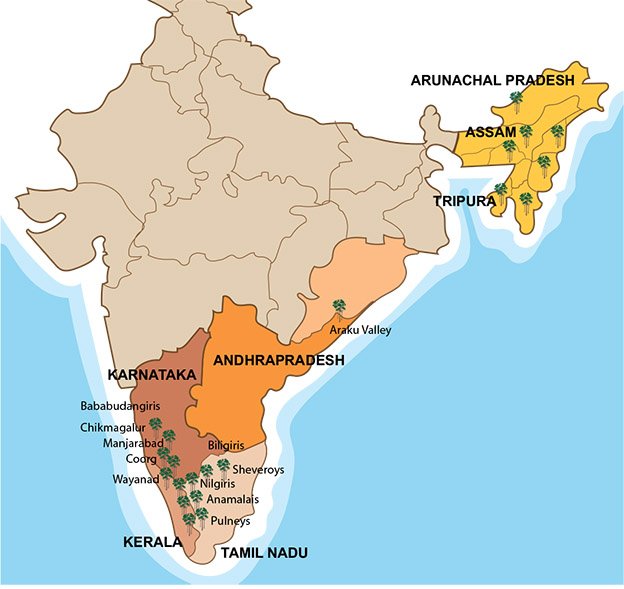
Issues in Coffee Production in India
Coffee Board of India
Coffee Crop
|
Factors |
Arabica |
Robusta |
|
Soils |
Deep, fertile, rich in organic matter, well drained and slightly acidic (Ph6.0-6.5) |
Same as Arabica |
|
Slopes |
Gentle to moderate slopes |
Gentle slopes to fairly level fields |
|
Elevation |
1000-1500m |
500-1000m |
|
Temperature |
150 C – 25 0 C ; cool, equable |
200 C – 300 C; hot, humid |
|
Annual rainfall |
1600-2500 mm |
1000-2000 mm |
References
NASA has formed a new team to investigate 'unidentified aerial phenomena' (UAPs) or 'unidentified flying objects' (UFOs).
References
The World Health Organisation (WHO) has released the first-ever fungal priority pathogen list to identify fungi which pose the greatest threat to public health.
World Health Organisation released first-ever priority pathogen list for bacteria in 2017.
References