7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Biennial Update Report (BUR)
UNFCC
Coastal Regulation Zone
eBuzz K9
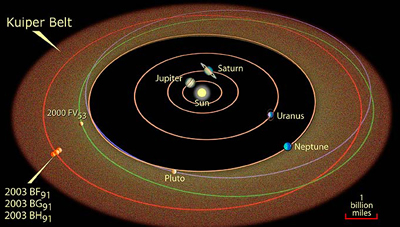
NASA’s New Horizons
Kuiper Belt
Measuring Earthquakes
Source: Indian Express, the Hindu