7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
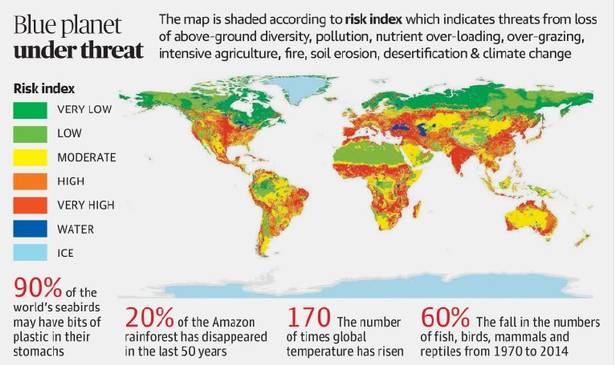
Global Soil Biodiversity Atlas
Financial Stability and Development Council
i. the heads of financial sector regulators (RBI, SEBI, PFRDA, and IRDA)
ii. Finance Secretary, Department of Economic Affairs
iii. Secretary, Department of Financial Services
iv. Chief Economic Adviser
v. Chairman of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board
i. to perform as an apex level forum to strengthen and institutionalize the mechanism for maintaining financial stability
ii. to enhance inter-regulatory coordination and promote financial sector development in the country
Commercial Paper
Dal-Nageen Lake
Multidimensional Poverty Index
Source: The Hindu