Mercury pollution
In a recent research, scientists studied the levels of mercury in Antarctic seals and whales to determine the source of its contamination and the transmission link across the food chain in Antarctica.
Mercury (hydrargyrum) is toxic heavy metal, also known as quick silver. It was previously observed in the feathers of chinstrap penguins on King George Island.
- Findings of the study – Some 9,000 tons of the toxic substance are released into the atmosphere every year.
- Mercury is believed to reach the ocean through rivers or rain, after it evaporates into air.
- Its pollution appears to extend south to Livingston Island and the Gerlache Strait, a natural channel off Antarctica.
- Sources – Artisanal mining is the main source of emissions, where it is used to collect gold by binding to it.
- Coal combustion is another major source and is also present in products like batteries, some lightbulbs and even mascara.
- Vulnerability – Marine mammals being at the top of the food chain, are particularly susceptible to mercury contamination.
- Humpback whales consume large quantities of krill, small crustaceans susceptible to contamination.
Leopard seal (Hydrurga leptonyx), the marine mammal is one of the largest predators in Antarctica after the orca. It is protected by Antarctic Treaty and the Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Seals.
- Impact – According to UNEP, if an animal consumes mercury, it may suffer reproductive failure, behavioural changes and may even (die).
UNEP Global Mercury Partnership initiated in 2005, to protect human health and the environment from the releases of mercury to air, water and land. It supports for timely and effective implementation of the Minamata Convention on Mercury, which was signed in 2013 by 140 countries to reduce the use of mercury.
References
- Hindustan Times| Mercury Contamination in Antarctic Mammals
- UNEP| Global Mercury Partnership
Kilkari Programme
Recently, Indian government had launched a mobile health service 'Kilkari' and mobile academy in Maharashtra and Gujarat to strengthen public health infrastructure.
Mobile Academy is a free audio training course to expand and refresh the knowledge of ASHAs and improve their communication skills via their mobile phones. It is currently implemented in 17 States/ UTs.
- Kilkari means ‘a baby’s gurgle’, is a centralized interactive voice response (IVR) based mobile health (m-health) initiative.
- Aim – To offer weekly services, time appropriate 72 audio messages about reproductive maternal, neonatal and child health care (RMNCH).
- Hosted by – Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoHFW).
- No further investment in the technology, telephony infrastructure or operational costs is required to be borne by States/UTs.
- Implemented in – 18 States / UTs, in 6 languages (Hindi, Bhojpuri, Oriya, Assamese, Bengali & Telugu version).
Kilkari programmes was designed and launched originally in Bihar in 2013, was adopted by the Government of India in 2014, and scaled up nationally.
- Free of cost – For both States/UTs and beneficiaries.
- Data Source – Centralized Reproductive Child Health (RCH) portal of MoHFW.
- Beneficiaries – Maternal mothers from the 2nd trimester of pregnancy until the child is 1 year old.
- Working – Women registered in RCH portal, will receive a weekly call with pre-recorded audio content directly to their mobiles based on their last menstrual period or the child’s Date of Birth.
- Audio messages are in the form of voice of a fictitious doctor character called Dr. Anita.
- Significance – It strengthens public health infrastructure and citizen-centric health services by leveraging India's expanding mobile phone penetration.
As of March 2019, Kilkari had reached almost 10 million users across 13 states in the country.
References
- PIB| Launch of Kilkari in Gujarat and Maharashtra
- Vikaspedia| Kilkari Programme
Speaker of State Legislative Assemblies
Recently, Speaker of Bihar State Legislative Assembly had refused to resign until floor test in Assembly citing constitutional provisions.
- SLA – State Legislative Assembly is the legislative wing of the government, the lower house in Bicameral States and the sole house in unicameral states and are also called as Vidhan Sabha.
- Speaker of SLA – Article 178 of Indian constitution provides for speaker to preside over the sessions of SLA.
- It is modelled on the basis of Office of Speaker in Britain.
Article 93 provides for speaker to preside over the session in Lok Sabha.
- Election – After every general election, the SLA at its 1st session shall elect Speaker and Deputy Speaker from amongst its members.
- Term – He remains in office till the next speaker sworn in.
- Independence – The salary of speaker is charged on the Consolidated Fund of the State.
- His resignation from the party does not account for defection and thereby upholds his independence.
- Vacancy – According to Article 179, it arises, if he resigns or removed from office by a resolution of SLA or ceases to be a member of the house or he dies.
Article 180 says that, while the office of Speaker is vacant, the duties of the office shall be performed by the Deputy Speaker or, if it is also vacant, by such member of the SLA as the Governor may appoint for the purpose.
- Removal – A no-confidence motion can be brought against the Speaker after 14 days of giving notice to the Secretary.
- Article 181 says that, when a motion for his removal is discussed in the house, he does not preside over the SLA.
- Powers and Functions – He ensures quorum, order and discipline in the house and may adjourn or suspend the sitting to maintain this.
- He does not participate in the debate and casts a vote only if there is tie in voting.
- He may even suspend or expel members of the house for unruly behaviour.
- He decides whether a bill is money bill or not and his decisions cannot be challenged in the court of law.
Unlike Speaker of Lok Sabha, Speaker of SLA does not preside over Joint Session of the 2 houses as there is no provision of joint session in bicameral states.
References
- The Hindu| No Confidence Motion on Bihar’s SLA Speaker
- Indian Constitution| Speaker of State Legislative Assemblies
World Sustainable Development Summit 2024
Vice-President of India inaugurated the World Sustainable Development Summit in Delhi in February 2024.
|
World Sustainable Development Summit (WSDS)
|
- It is an annual flagship multistakeholder convening, which was previously called as Delhi Sustainable Development Summit.
- Instituted in – 2001.
- Organized by – The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI).
- Main Partners – Ministries of Earth Sciences, New and Renewable Energy and Environment, Forests, and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Aim – To mobilize opinion-makers to address issues concerning sustainable development and climate change.
- It created a new knowledge outputs through Act4Earth, launched during WSDS 2022.
|
The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI), an independent, research institute headquartered in New Delhi with 6 regional centres. Its aims for an equitable and sustainable future through conservation and efficient use of energy and other resources.
- WSDS 2024 – 23rd edition of WSDS.
- Umbrella theme – Leadership for Sustainable Development and Climate Justice.
- Deliberating topics – Integrating SD, nature-based solutions, adaptation and resilience, sustainable consumption and lifestyles, addressing the energy trilemma, and climate action.
- Vasundhara Magazine – Its 14th edition titled ‘EquiClimate’, based on the theme ‘Climate Injustice: Vulnerabilities of the Vulnerable’ will be introduced.
- Cool it for the climate – As a behaviour change campaign, it organises a poster-making competition for school students aimed to promote simple sustainable practices.
World Sustainable Development Summit (WSDS) is only independent international Summit on sustainable development and environment, based in the Global South.
References
- News on AIR| Inauguration of WSDS 2024 in New Delhi
- WSDS| World Sustainable Development Summit
Deep Tech
The recent Interim Budget 2024 announced Rs. 1 lakh crore for Research and Development (R&D) and have proposed to launch a new scheme to strengthen deep-tech capabilities in defence sectors.
- Deep tech – It refers to advanced and disruptive technologies, many of which are still under development.
- Domains – Nanotechnology, biotechnology, material sciences, quantum technologies, semiconductors, artificial intelligence, data sciences, robotics, 3D printing, etc.
- Converging approaches
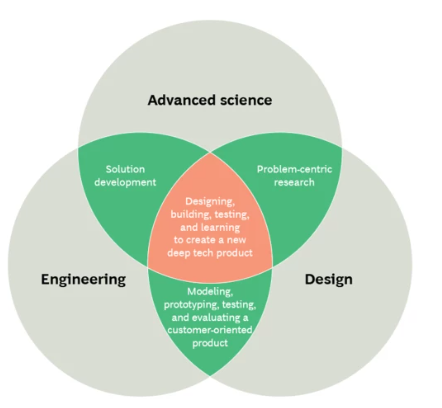
- Address global challenges – Climate change, hunger, epidemics, energy access, mobility, physical and digital infrastructure, and cyber security.
- Economic significance – It can enhance productivity, drive economic growth, create jobs in coming years.
- India’s status – It has large base of relatively high-quality science and engineering manpower and a fairly well-established technology culture.
- More than 10,000 startups working in these technology domains.
- Challenges – Most deep tech projects are time- and money-intensive, with relatively high funding requirements.
- India’s expenditure on R&D is far below the global average.
India’s stated objective has been to allocate at least 2% of GDP for R&D. But India currently spends just about 0.65% of its national GDP on R&D while the global average is about 1.8%.
The National Deep Tech Startup Policy (NDTSP)
- It was finalised in 2023, is currently awaiting government approval.
- Piloted by – Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade and the Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser.
- Objectives – To create a deep tech startup ecosystem by offering the right incentives to companies that invest time and money in innovation and research.
Reference
The Indian Express| Development of Deep-tech in India
|
Other Important Topics
|
|
Sub schemes of PRITHvi VIgyan (PRITHVI) Scheme
|
- The PRITHVI Scheme is a government initiative that aims to improve long-term observations of the Earth's atmosphere, ocean, geosphere, cryosphere, and solid earth.
- The scheme will be implemented from 2021–2026 and includes 5 sub-schemes namely-
- Atmosphere & Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems & Services (ACROSS).
- Ocean Services, Modelling Application, Resources and Technology (O-SMART).
- Polar Science and Cryosphere Research (PACER).
- Seismology and Geosciences (SAGE).
- Research, Education, Training and Outreach (REACHOUT).
|
|
SVAMITVA Scheme
|
- The Survey of Villages and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas (SVAMITVA) scheme is a central government initiative.
- It was launched in April, 2020 to promote socio-economic empowerment and a more self-reliant rural India.
- The Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR) is the Nodal Ministry for implementation of the scheme.
|
|
Hypervelocity Expansion Tunnel
|
- India’s 1st Hypervelocity Expansion Tunnel Test Facility successfully established and tested by Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur (IITK) recently.
- It is capable of generating flight speeds between 3-10 km/s, simulating the hypersonic condition.
- It was named as S2, indigenously designed and developed and is a valuable test facility for ongoing missions of ISRO and DRDO including Gaganyaan, RLV and hypersonic cruise missiles.
|
|
Centre for Bear Rehabilitation and Conservation (CBRC)
|
|
The Centre for Bear Rehabilitation and Conservation rehabilitates 60 bear cubs in two decades.
- The Centre for Bear Rehabilitation and Conservation (CBRC) is located in the Pakke Wildlife Sanctuary on the West Bank of the Pakke River in Arunachal Pradesh.
- It is a joint venture of the State’s Environment, Forest, and Climate Change Department and the Wildlife Trust of India.
- The CBRC's mission is to rehabilitate displaced Asiatic black bear cubs back and is the only facility for Asiatic bears in India.
|
|
World Cancer Day
|
- World Cancer Day is an international day that takes place every year on February 4.
- It is to raise awareness about cancer, and to encourage its prevention, detection, and treatment.
- It also aims to prevent millions of deaths each year by pressing governments and individuals across the world to take action against the disease.
- In 2023, the global cancer community commemorates World Cancer Day with the slogan "Close the care gap" and the focus of 2022 and 2024 is to help “Close the cancer gap”.
|
|
iOncology ai
|
- The All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Delhi, in collaboration with the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing, Pune, has launched iOncology.ai. recently.
- It is an Artificial Intelligence (AI) platform designed for the early detection of breast and ovarian cancer.
|
|
Raman Research Institute (RRI)
|
|
A research group at the Raman Research Institute (RRI) have designed a new image-correction technique capable of getting better images during the study of cold atoms or atoms at absolute zero temperature.
- The Raman Research Institute (RRI) is an autonomous research university in Bengaluru, India.
- It was founded in 1948 by Sir C.V. Raman, an Indian physicist and Nobel laureate, to continue his research after he retired from the Indian Institute of Science.
- The institute's main activity is basic research in specific areas of physics that interest Raman.
|
|
Mahmudia Wetland
|
- The Mahmudia wetland is a part of the Danube Delta ecosystem in Romania, Europe.
- 8 years ago, the EU restored the wetland, transforming the area and providing livelihoods and climate resilience for locals.
- World Wildlife Fund (WWF) has urged the Romanian government to classify Mahmudia wetland as a ‘national interest ecological restoration area’ to protect its natural progress.
|
|
EU Emission Targets
|
- The European Commission published a detailed impact assessment that set a goal of 90% reduction in net greenhouse gas emissions by 2024.
- The new target is part of the European Union’s push to become the 1st continent to be carbon-neutral by 2050.
- According to the commission, the energy sector in Europe is set to achieve full decarbonisation shortly after 2040.
- The Fit for 55 package aimed to reform the EU emissions trading system a carbon market based on emission allowances by making it more ambitious.
|
|
Fencing Indo - Myanmar Border
|
|
Union Home Minister Amit Shah recently said the government has decided to construct a fence along the entire Indo-Myanmar border to facilitate better surveillance.
- The border between India and Myanmar runs along 4 states - Mizoram, Manipur, Nagaland, and Arunachal Pradesh.
|
