Aral Sea
Recently NASA has reported that, the climate change is accelerating the demise of the Aral Sea.
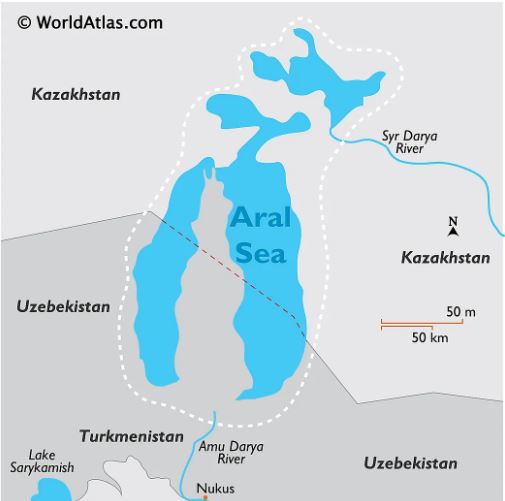
- Aral Sea – An endorheic lake, once the 4th largest saline lake in the world with a surface area of 66,900 square km.
Endorheic lakes do not have a natural outflow and lose water solely by evaporation or underground seepage or both. Caspian Sea, Great Salt Lake in Utah and Dead Sea are some of the endorheic lakes.
- Geographical location – Between Kazakhstan in the north and Uzbekistan in the south.
- Formation – It was made by waters from the Syr Darya and the Amu Darya rivers that were dependent on glacial melt.
- Catchment area – It is approximately 1.5 million square miles and drains Uzbekistan and portions of Kazakhstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Turkmenistan, Iran, and Kyrgyzstan.
- Threat – Climate change, human engineering & agricultural projects has shrunk about less than 25% of its former size.
- Water diversion project – In 1960, the Soviet Union diverted the Syr Darya and the Amu Darya rivers for irrigation that lead to gradual drying up of the lake.
- The North Aral Sea (called the Small Aral Sea) had separated from the South (Large) Aral Sea.
- Impacts – Its demise is the cause of land degradation and desertification, drinking water shortages, malnutrition, and deteriorating health conditions in the surrounding areas.
The United Nations Development Program (UNDP) calls the destruction of the Aral Sea ‘the most staggering disaster of the 20th century’. The salinity level of Aral Sea has risen from less than 10 grams/litre to over 100 g/l in the remnant lake. It has also now become the Aralkum Desert, a significant new source of sand and dust storms.
- Measures – 5 countries, Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Kyrgyzstan adopted the Aral Sea Basin Program in 1994 as part of the restoration strategy.
Reference
Hindustan Times| Accelerated drying up of Aral Sea
IUCN Red List of Ecosystems (RLE)
A recent research paper, examined the roles of the Red List of Ecosystems in achieving the goals of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) of the UN Convention on Biological Diversity, adopted in 2022, set the agenda for global aspirations and action to reverse biodiversity loss
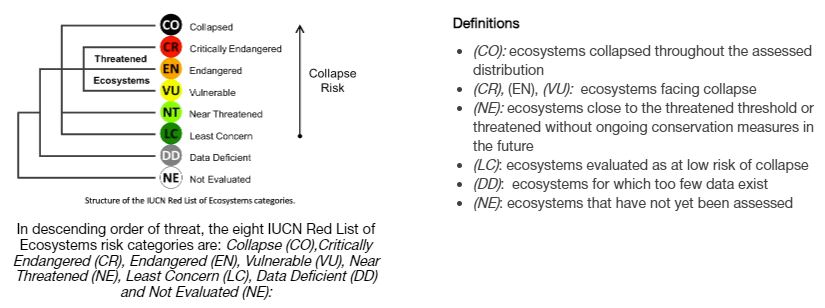
- IUCN RLE – An innovative tool for assessing and monitoring the status of ecosystems.
- Aim – To assess the health condition and threat levels faced by each ecosystem as well as to identify the most effective management pathways to reduce risks and loss of biodiversity.
- Coverage – Terrestrial, freshwater and marine ecosystems at subnational, national, regional and global scales.
- RLE Assessment – Define the target ecosystem, describe it, compile the available data, validate it and conduct the ecosystem risk assessment.
- Ecosystem status – It is assigned based on the risks identified within each criterion and the overall risk of ecosystem collapse.
- Uses – It provides key information to support ecosystem management, decision-making and adequate public policies.
- It supports territorial & protected areas planning and to prioritize & monitor restoration action.
- It complements other IUCN knowledge products like Red List of Threatened Species, the World Database on Protected Areas and the World Database on Biodiversity areas.
- It reports on progress and achievements of global conservation targets.
References
- IUCNRLE| IUCN Red List of Ecosystems
- IUCN| Ecosystem Risk Categories
High Altitude Pseudo Satellite Vehicle (HAPS)
Recently, the National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) has successfully completed the 1st test of high altitude pseudo satellite vehicle.
National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) in Bengaluru is one of the laboratories under the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
- HAPS – It is a solar-powered pseudo satellite, a new age unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) which is also called as stratospheric vehicle.
- Features – It can fly at altitudes of 18-20 km from the ground, almost double the heights attained by commercial airplanes.
- They move slowly, at just about 80-100 km per hour.
- Advantages of other existing vehicles
- Unlike drones, they can remain in air for months for being solar powered and can cover larger area.
- One can observe even over a 400 sq km area with a 5 metre resolution.
- Unlike satellites, it has lower operating cost as it does not require a rocket to get into space.
- Unlike geostationary satellites, can be easily redeployed over another location, or can be reequipped with a different payload.
- India’s prototype – A scaled-down version, one-third in size to the eventual aircraft had a wing-span of about 12 metres, remain in air for about 8 and a half hours, achieving an altitude of about 3 km.

NASA with its Pathfinder series of aircraft and other countries like China, South Korea, and the UK are also developing HAPS.
- The full-scale machine that NAL is trying to build, by 2027, would be aiming to remain in the air for 90 days at a stretch.
- Significance – It can significantly increase India’s surveillance and monitoring capabilities in the border areas.
- It can provide mobile communications networks in remote areas, if the normal networks get damaged due to any disasters or calamity.
- Challenges in Designing – To generate solar power continuously even in night, to build it extremely lightweight and to keep the electronics warmer to work well.
In December 2023, Bengaluru-based NewSpace Research and Technologies, a deep-tech start-up, flew a similar solar-powered UAV, through the Innovation of Defence Excellence initiative of the Defence Ministry.
References
- The Indian Express| India’s Successful test of HAPS Prototype
- The Indian Express| Features of HAPS
Pace Mission
The PACE mission lifted off from Earth by the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.
- PACE — Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, Ocean Ecosystem.
- Initiative of – NASA.
- Aim – To assess ocean health, by measuring distribution of marine food web (phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae).
- To give insights into the interactions between atmospheric aerosols and sea life forms (algae and plankton).
PACE Mission is the most advanced mission ever launched to study ocean biology.
- Uniqueness – Current Earth-observing satellites can see in 7 or 8 colours but Pace can see in 200 colours.
- It will allow scientists to identify the types of algae in the sea and types of particles in the air.
- Duration – At least 3 years (up to 10 years).
- Research – It will study the impact of tiny, microscopic life in water and microscopic particles in the air from 676 kms.
- It will scan the globe daily with 2 of the science instruments and a 3rd instrument will take monthly measurements.
- Hyperspectral Ocean Colour instrument – It measure oceans and other waterbodies across a spectrum of ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared light to track the distribution of phytoplankton.
- 2 Polarimeter instruments – Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter and Spectro-polarimeter, to detect how sunlight interacts with particles in the atmosphere.
- Significance – It will severe weather forecasts and detail Earth's changes as temperatures rise.
- It will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide and will reveal how aerosols might fuel phytoplankton growth in the surface ocean.
- It will benefit our economy and society.
- For example, it will help identify the extent and duration of harmful algal blooms.
NASA is collaborating with India on another advanced Earth-observing satellite, Nisar due to launch in 2024. It will use radar to measure the effect of rising temperatures on glaciers and other melting icy surfaces.
References
- The Hindu| PACE Mission lifts off from Earth
- NASA| PACE Mission
Supreme Court on Subcategorization of SCs
A 7-judge Constitution Bench headed by Chief Justice of India is examining the legality of individual States to sub-classify backward classes within the Scheduled Caste (SC) category.
- Issue – There are 23 petitions before the Supreme Court regarding subcategorization of SCs.
- The lead one is filed by the Punjab government challenging the 2010 verdict of High Court that struck down its provision 50% reservation within SCs to selected categories.
In 2004 ‘EV Chinnaiah vs. State of Andhra Pradesh' case, a 5-judge constitution bench held that SCs and STs are homogenous groups and any sub-classification of SCs would violate Article 14 (right to equality) of the Constitution. It had stated that only Parliament can exclude castes deemed to be SC from the Presidential List under Article 341 of the Constitution.
- Current observations of Supreme Court – Diverse groups, clubbed together in the Presidential list under Article 341 of the Constitution as “Scheduled Castes”, cannot be treated alike.
- They were heterogeneous in terms of their
- Pre-existing occupations, social status and social indicators of backwardness or development.
- It also said that among SCs, some may have advanced in society while other continue to remain “particularly underprivileged”.
- Social indicators like infant mortality, maternal mortality, and fertility rates would also broadly show whether there had been progress.
In central government-funded higher education institutions and in case of public employment, 22.5% of available seats are reserved for SC and 7.5% for ST students.
Punjab and Haryana don't have an ST population.
References
- The Hindu| Supreme Court on Subcategorization of SCs
- NDTV| 2004 EV Chinnaiah Case on Subcategorization of SCs
|
Other Important Topics
|
|
Bharat Ratna Awards, 2024
|
|
Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced recently that Bharat Ratna Awards will be conferred on 5 eminent personalities for 2024.
- Personalities
- Former Prime Ministers PV Narasimha Rao,
- Chaudhary Charan Singh,
- Agricultural scientist MS Swaminathan,
- Former Bihar chief minister Karpoori Thakur,
- Deputy prime minister Lal Krishna Advani.
- In 2024, 5 recipients marks the highest number of Bharat Ratnas awarded in a single year, eventhough it is restricted to 3 in particular year.
- Bharat Ratna Award is the highest civilian Award of the country, was instituted in the year 1954.
- Aim - It is awarded in recognition of exceptional service/performance of the highest order in any field of human endeavour.
|
|
Treasure of Villena
|
|
A recent study finds that a 3000-year-old ‘treasure’ ( treasure of villena) is made with extraterrestrial material.
- The Treasure of Villena is one of the greatest hoards of gold from the European Bronze Age (1400 and 1200 B.C.) ever discovered in 1963.
- It contains 59 objects made of gold, silver, iron, and amber.
- The treasure was discovered in a gravel pit in the province of Alicante.
- Researchers noticed that some of the iron pieces were made from a dark leaden metal.
|
|
Mimas
|
|
A recent analysis reveals that the Saturn’s Moon Mimas may host a huge ocean under its surface.
- Mimas is a natural satellite of Saturn, also known as Saturn I.
- It's the smallest and innermost of Saturn's major moons.
- Mimas was discovered in 1789 by William Herschel and named after a Giant from Greek mythology.
- A recent analysis reveals that a “young” ocean formed on the planet just 5 to 15 million years ago.
|
|
Trichoglossum Syamviswanathii
|
- Scientists have recently discovered a new fungus species, Trichoglossum syamviswanathii, from Kerala.
- The species is named after renowned scientist and former director of KFRI Syam Viswanath for his contribution to the field of forestry in India.
- It belongs to the family Geoglossaceae (Ascomycota) and it is commonly known as “hairy earth tongues” fungus that exhibits club-shaped apothecia in dark shades of black or brown.
- Trichoglossum species are globally distributed in tropical and temperate forests in at least 5 continents of the world and it plays a crucial role in the decomposition of organic matter.
|
|
Mauna Loa
|
|
The earthquake struck the world’s largest active volcano recently, Mauna Loa on the Big Island of Hawaii.
- Mauna Loa is the world's largest active volcano by volume and mass.
- It is located in the Pacific Ocean, on the island of Hawaii, and is one of 5 volcanoes that make up the island.
- Mauna Loa is above sea level and makes up about half of the island.
- The volcano's name means "long mountain" in Hawaiian, and it has broad, rounded slopes that are typical of a shield volcano.
|
|
Joint European Torus (JET)
|
|
Researchers have set a new nuclear fusion reaction record and produced more power using the technology (JET) than ever before.
- JET is a nuclear fusion reactor & the world's largest and most advanced tokamaka (machine that confines a plasma using magnetic fields in a donut shape that scientists call a torus).
- It is located at the Culham Centre for Fusion Energy in Oxfordshire, UK.
- It’s purpose was to explore fusion in conditions similar needed for a power plant and only experiment that can use the deuterium-tritium fuel mix used for commercial fusion power.
- It generated high fusion power for 5 seconds the amount of energy which is equivalent to 15 kilograms of TNT.
|
|
7th Indian Ocean Conference 2024
|
|
External Affairs Minister will address the inaugural session of the 7th Indian Ocean Conference in Perth, Australia recently.
- The Conference is a flagship consultative forum for countries in the Indian Ocean Region, organized annually by the Ministry of External Affairs since 2016, in association with India Foundation.
- The Indian Ocean Conference commences theme for 2024 - "Towards a Stable and Sustainable Indian Ocean”.
|
|
Olive Ridley turtles
|
- The olive ridley sea turtle (Lepidochelys olivacea) is one of the smallest sea turtles in the world.
- Olive ridley turtles are found in tropical regions of the Pacific, Indian, and Atlantic oceans.
- Threats - They are poached for their meat, eggs, and shell and leather.
- Conservation
- IUCN- Endangered
- CITES - Appendix I
- Schedule 1 - Wildlife Act of 1972
|
|
Repo rate of RBI
|
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently kept the main policy instrument, the repo rate, unchanged at 6.5%.
- RBI also retained the stance of the monetary policy as “withdrawal of accommodation”.
- A major reason for the continued pause in the repo rate is that retail inflation continues to remain above the 4% target of the RBI.
- Repo rate is the rate at which RBI lends money to banks to meet their short-term funding needs.
|
|
PVTG groups in A.P & Odisha
|
|
The Lok Sabha recently passed the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order Amendment Bill, 2024 and Constitution (Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes) Order Amendment Bill, 2024.
- It will add several new communities to the Scheduled Tribes list of Odisha and for the inclusion of synonyms and phonetic variations of existing tribes in the ST lists of Andhra Pradesh and Odisha.
- The Bill to amend Odisha’s ST list also shifted 2 entries — Tamadia and Tamudia from the Scheduled Castes list to the Scheduled Tribes list.
|