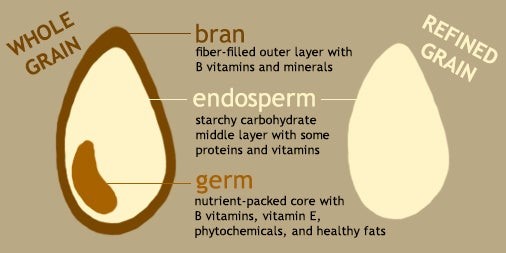
Grain-processing of millets raises new concerns in the consumption of millets.
|
Millet Variety |
Rich in |
|
Pearl millet |
Higher protein content than rice, maize, and sorghum |
|
Foxtail millet |
Amino acid lysine |
|
Finger millet |
More crude fibre than wheat and rice |
|
Proso millet |
Amino acids leucine, isoleucine, and methionine |
References
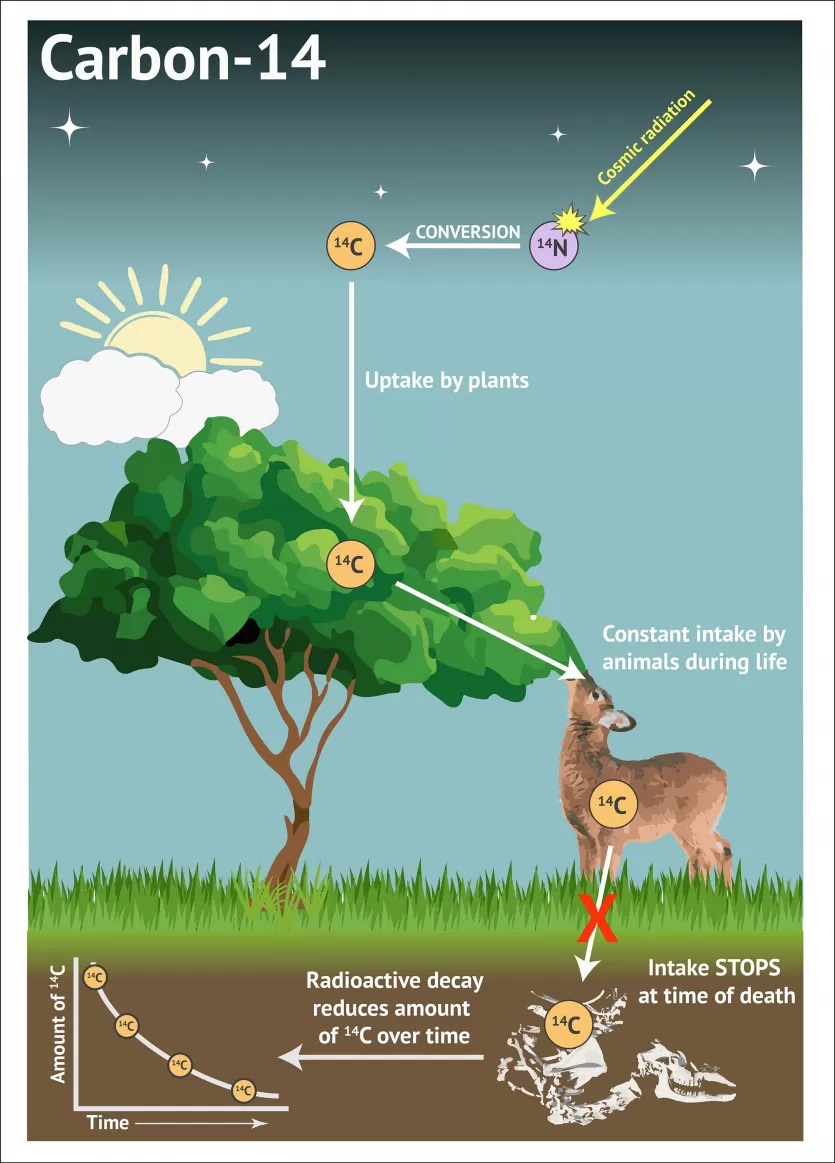
The Allahabad High Court ordered a ‘scientific survey’, including carbon dating, of a ‘Shivling’ said to have been found at the Gyanvapi mosque complex in Varanasi.
References
SDGs Localisation
Bhopal becomes the first city in India to adopt the localisation of the United Nations-mandated sustainable development goals (SDG).
References
The Election Commission denies Congress’ claim on EVMs being brought from South Africa for Karnataka elections.
References
UNFF18 held in New York, discussed the contributions of SFM to energy, livelihoods and the SDGs.
References