Hampi and Khajuraho Temples
The Government plans to include Hampi, Khajuraho as venues to host meetings as part of G20 ‘culture track’ and India’s G20 Presidency.
India is the Chairman of G20 for 2022-23 and is to host the 18th G20 summit 2023.
Hampi
- The group of monuments at Hampi is located in the Tungabhadra river basin in Bellary District, Karnataka.
- Hampi is the Capital City of the Vijayanagara Empire (14th-16th Century CE).
Vijayanagara Empire was founded by Harihara and Bukka in 1336.
- Hampi is classified as a World Heritage Site by the UNESCO.
- Hampi is also known as the ‘World’s Largest Open-air Museum’.
- Hampi structures belong to the Dravidian architecture.

- Few important sites in Hampi ruins
- The Krishna temple complex,
- The Vitthala temple complex
- Virupaksha Temple
- Stone chariot Garuda shrine
- Pattabhirama temple complex
- Lotus Mahal complex
- The Battle of Talikota (1565 CE) led to a massive destruction of these structures in Hampi.
The recently released INR 50 currency note features the Stone Chariot of Humpi.
Khajuraho
- Khajuraho temple monuments are located in the Chattarpur district of Madhya Pradesh.
- Khajuraho temples were built by the Chandela Dynasty in Nagara-style of temple architecture.
- The 23 temples form the western, eastern, and southern clusters of the monument and belong to two different religions - Hinduism and Jainism.
- The temples are built in sandstone and has nagara-style structures like jagati (highly ornate terraced platform), jangha (the body) or shikhara (the tower).
- The famous erotic sculptures of khajuraho account for only 10% of all sculptures.
- Some of the famous temples are
- Kandariya Mahadeva Temple - It is the largest among the group. The chief deity is Lord Shiv
- Chitragupta Temple - dedicated to Lord Surya.
- Chaturbhuja Temple - This temple is the only temple in Khajuraho that does not have a single erotic sculpture.
- Parsvanatha Temple is a Jain temple built using sand-stone. It also holds images of Lord Vishnu.
- Adinatha Temple, Santinatha Temple, Ghantai Temple are the other famous Jain temples.
References
- https://indianexpress.com/article/india/hampi-khajuraho-on-list-for-g20-culture-track-8212864/
- https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/241/
- https://karnatakatourism.org/tour-item/hampi/
- https://www.mptourism.com/destination-khajuraho.php
Launch Vehicle Mark 3
ISRO’s launch vehicle LVM3 will launch 36 broadband communication satellites of the OneWeb and marks it entry into the global commercial launch service market.
The launch of the 36 satellites by the LVM3 into the Lower Earth Orbit (LEO) marks the first LVM3-dedicated commercial launch on demand through NewSpace India Limited (NSIL).
NSIL is a central public sector enterprise under the Department of Space and the commercial arm of the space agency.
- Launch Vehicle Mark 3 (LVM3) is the heaviest rocket of ISRO.
- LVM3 was earlier called Geosynchronous Launch Vehicle Mark III (GSLV Mk III).
- The name of the vehicle is changed from GSLV to LVM because the rocket will not deploy the satellites in the geosynchronous orbit.
- This is not the first time that ISRO has re-designated the vehicle to LVM-3.
- In 2014, the GSLV-Mk-III was also named LVM-3 as it launched with the Crew module Atmospheric Re-entry Experiment (CARE) into space.
GSLV Mk III
- GSLV Mk III is configured as a three stage vehicle with two solid strap-on motors, one liquid core stage and a cryogenic upper stage.
- It is a medium-lift launch vehicle primarily designed to launch communication satellites into geosynchronous orbit.
- GSLV Mk III has the capability to launch 4000 kg payload into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) and 8000 kg payload into LEO.
GSLV Mk III carried India’s second lunar mission Chandrayaan-2.
References
- https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/isros-lvm3-to-make-commercial-foray-with-launch-of-36-oneweb-satellites/article66013403.ece
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/business/india-business/isros-lvm3-to-make-commercial-foray-with-launch-of-36-oneweb-satellites-on-october-23/articleshow/94873095.cms
- https://www.isro.gov.in/lvmhtml
Next-Gen Launch Vehicle
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is developing a Next-Gen Launch Vehicle (NGLV), which will replace the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) in future.
- Next-Gen Launch Vehicle (NGLV) will feature a simple, robust design which allows bulk manufacturing and minimal turnaround time.
- It is a three-stage to orbit, reusable heavy-lift vehicle.
- The payload capability is comparatively lower than expendable launch vehicle.
- NGLV uses semi-cryogenic propulsion system which is both efficient and cost-effective.
A semi-cryogenic engine uses refined kerosene instead of liquid hydrogen and the liquid oxygen is used as an oxidiser.
- Potential areas of NGLV’s use –
- launching communication satellites
- deep space missions
- future human spaceflight
- cargo missions
Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle
- Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) is the third-generation four-stage launch vehicle of India.
- It is the first Indian launch vehicle to be equipped with liquid stages in its propulsion system.
- PSLV is an indigenously-developed expendable launch system of the ISRO.
The word ‘expendable’ means that the vehicle is designed for single use and not reusable.
- PSLVs are medium-lift launchers with multiple satellite launch capability and multiple orbit capability.
- They can reach up to various orbits, including the Geo Synchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO), Lower Earth Orbit (LEO), and Polar Sun Synchronous Orbit.
- PSLV earned its title 'the Workhorse of ISRO' through consistently delivering various satellites to Low Earth Orbits.
PSLV was used in missions like Chandrayaan-1, MOM, and IRNSS.
References
- https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/isros-next-gen-launch-vehicle-may-assume-pslvs-role/article66005152.ece
- https://www.newindianexpress.com/states/kerala/2022/oct/13/isro-developing-new-rocket-to-replace-pslv-250775html
- https://www.indiatoday.in/science/story/isro-oneweb-launch-gslv-mk-iii-lvm-3-rocket-2286187-2022-10-17
- https://www.isro.gov.in/GSLVmk3_CON.html
The Galápagos Islands
According to a new study, the cold, eastward equatorial ocean current has been gaining strength for decades.
- This is of great significant because the Galápagos Islands are protected from global warming in the Pacific Ocean Region by this cold, eastward equatorial ocean current.
- This cold ocean current creates a cooler, more stable environment for coral reefs and marine life and birds that often live much closer to the poles.
- The temperatures in waters along the west coast of the Galápagos have dropped by 0.5 degrees Celsius since the early 1990s due to this cold ocean current.
- Corals do not bleach and die in these waters off the west coast of Ecuador.
- However, El Niño poses a threat to the island group.
- It shuts down the cold current every couple of years, causing penguin populations to collapse.
El Niño is a climate pattern that causes unusual warming of surface waters in the eastern tropical Pacific Ocean.
Galapagos Islands
- The Galapagos Islands are a group of islands in the Pacific Ocean some 1,000 km from the South American continent.
- The islands lies on the equator and belong to the country Ecuador.
- It is located at the confluence of three ocean currents viz - Humboldt Current, Panama current and South Equatorial counter current (Cromwell current).
- This confluence of currents makes it one of the richest marine ecosystems in the world.
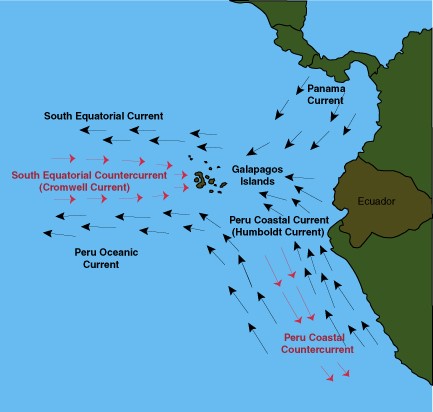
- The Galapagos Marine Reserve which surrounds the islands, is one of the largest marine reserves in the world.
- The island is a biodiverse ecosystem and home to several endangered species.
- Galápagos penguin
- Galápagos fur seal and
- Galápagos sea lion.
- Recognition - The Galapagos Islands is designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Ongoing seismic and volcanic activity reflects the processes that formed the islands.
- Hence, it is described by the UNESCO World Heritage Convention as a ‘living museum and showcase of evolution.’
References
- https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/wildlife-biodiversity/ocean-currents-protect-gal-pagos-islands-from-global-warming-but-are-they-safe-forever--85467
- https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1/
UNDRR-WMO Joint Report on MHEWS
The United Nations Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR) and the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) released a report on the International Day of Disaster Risk Reduction (13th October).
- The UNDRR-WMO joint report assesses the current global status of multi-hazard early warning systems (MHEWS) against Target G of the Sendai Framework.
- The analysis was made with data from the Sendai Framework Monitor (SFM).
- SFM is an online tool where member countries report their progress on the targets outlined in the Sendai Framework.
The Sendai Framework (2015-2030) is a global blueprint for disaster risk reduction and prevention.
Key Findings of the Report
- On average, at least 40% of countries in every region reported that they operate a multi-hazard early warning systems (MHEWS).
- Less than 50% of the Least Developing Countries (LDC) are equipped with MHEWS.
- Only 33% of Small Island Developing Countries (SIDS) are equipped with MHEWS.
- There are four items on the UNDRR checklist to ensure that an early warning system is up to the mark:
- Risk knowledge;
- Technical monitoring and warning service;
- Communication and dissemination of warnings;
- Community response capability
- Considerable progress has been made in all four areas, but considerable investments are still needed in MHEWS.
- National capacities in assessing MHEWS’ effectiveness, especially in LDCs and SIDS, need to be enhanced.
United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction
- United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR) is the United Nations focal point for disaster risk reduction.
- The mission of the UNDRR is to provide leadership and support to accelerate global efforts in disaster risk reduction
- To achieve inclusive sustainable development and
- To achieve the goal of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030.
- It oversees the implementation of the Sendai Framework.
- It supports countries in its implementation, monitoring and sharing what works in reducing existing risk and preventing the creation of new risk.
- Related Links - Global Platform for Disaster Risk Reduction,
References
- https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/natural-disasters/hazards-in-waiting-half-the-world-still-without-early-warning-systems-flags-un-report-85461
- https://vikaspedia.in/social-welfare/disaster-management-1/important-days/international-day-for-disaster-reduction
- https://www.undrr.org/publication/global-status-multi-hazard-early-warning-systems-target-g

