Day and Night Microphysics
Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) has been issuing alerts with maps from various weather monitoring satellites.
|
Day and Night Microphysics RGB Imager
|
- It is image created by combination of Red, Green and Blue colours.
- Aim – To study various atmospheric characteristics.
- Radiometer – A device that measures the properties of radiation by studying the radiation’s interaction with matter.
- Atmospheric sounders – A devices that measure temperature, humidity and study water vapour as a function of their heights from the ground.
- Factors determining RGB imager – Solar reflectance and brightness temperature.
- Applications - It helps in analysis of different cloud types, initial stages of convection, maturing stages of a thunderstorm, identification of snow area, and the detection of fires.
- It also helps in tracking the formation, evolution and depletion of cyclones and other weather events.
|
Solar reflectance is a ratio of the amount of solar energy reflected by a surface and the amount of solar energy incident on it.
Brightness temperature is the relationship between the temperature of an object and the corresponding brightness of its surface.
- Daytime Microphysics (DtMicro) RGB – It is the data formed by combining information about the cloud brightness, cloud particle phase and size, and cloud top temperature.
- Aim – To distinguish ice from water phase and to monitor the development of convection, fog and low clouds.
|
Solar Reflectance Recorded by INSAT 3D
|
|
Wavelength
|
Colour beam
|
Relates to
|
|
0.5 µm (visible radiation)
|
Red colour
|
Cloud thickness and
amount of cloud water and ice
|
|
1.6 µm (shortwave IR radiation)
|
Green colour
|
Cloud particle size and phase
|
|
10.8 µm (thermal IR radiation)
|
Blue colour
|
Temperature
|
- Observations – Water cloud is more reflective than ice cloud and have a stronger red beam, smaller water or ice particles have a higher reflectivity, resulting in a stronger green beam and warm surface corresponds to strong blue beam component.
- Night microphysics – It is designed for monitoring the evolution of night time fog and stratus clouds.
|
Colour band
|
Determining factors
|
|
Red
|
Difference between 2 Thermal IR
|
|
Green
|
Difference between Thermal IR and a middle IR
|
|
Blue
|
Strength of 1 Thermal IR signal
|
- Observations – A strong red beam for thick clouds, strong green beam for water clouds with small droplets and a strong blue beam for warm surfaces.
The Kalpana 1 and INSATs 3A, 3D, and 3DR satellites have bolstered India’s weather monitoring and warning services.
References
- The Hindu| IMD maps for weather alerts
- IMD| INSAT 3D’s Day and Night Microphysics
Pakke Paga Hornbill Festival
The 9th edition of the 3-day Pakke Paga Hornbill Festival (PPHF) commenced in Arunachal Pradesh in 2024.
Theme for 9th Edition is ‘Domutoh Domutoh, Paga hum Domutoh’, translates to ‘Let Our Hornbills Remain’ in Nyishi, emphasising the critical need to preserve the iconic birds.
- 1st Edition – In 2015
- In 2019, it was declared as a state festival of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Aim – To recognise the role played by the Nyishi community in conserving hornbills in Pakke Tiger Reserve (PTR).
- To raise alternative sources of income for the region and to create awareness in the rest of India about the wonders of PTR and its surrounding areas.
Nyishi is the largest tribal group in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Pakke Tiger Reserve – It is home to 4 species of hornbills namely Wreathed, Great Indian, Oriental Pied and the endangered Rufous-necked.
- Activities – It includes bird-watching, butterfly walks, bear walks, hornbill roost site visits, cultural programs, food stalls, sightseeing tours, river walks, as well as displays of local tribal sports and dances
- Positive Impact – It unites people from diverse backgrounds to combat pollution, protect wildlife, and address environmental degradation.
Hornbill festival in Nagaland is also called as ‘festival of festivals.
Reference
Down To Earth| 9th Edition of Pakke Paga Hornbill Festival
Prehistoric Rock Paintings in Tamil Nadu
The Tamil Nadu government has planned to declare the entire hillocks of Alampadi, Melvalai, and Sethavarai a protected monument.
- All 3 sites are located in Villupuram district of Tamil Nadu.
- Melvalai – A nondescript village whose paintings dates back to 3000 B.C. and majority of etchings was in red ochre.
The word, Rattapparai, has become synonymous with the rock art painted in red ochre.
- There are 4 sets of paintings that includes human figurines, animals, and symbols.
- 1st set – There are 3 persons, with a man mounted on a horse; another is pulling the horse with a rope fastened to the animal, while the 3rd man is depicted with hands stretched, welcoming others.
- 4th set – 6 men standing and a few others with hands stretched out.
- Link with IVC – Painting depicting a group of men rowing a boat, indicates a link between the Indus Valley and the southern region.
|
Alampadi
|
Sethavarai
|
- The paintings are in red and white ochre.
|
- It has paintings of animals, especially a deer and a fish.
- The outlines are in red ochre, while the inner portion is filled with white ochre.
|
- Challenges – There have been instances of unregulated entry of people and they also face threats from quarrying and vandalism.
- Measures – Tamil Nadu Ancient and Historical Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1966 and Tamil Nadu Ancient and Historical Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Rules, 1971.
References
The Hindu| Prehistoric Rock Paintings in Villupuram District
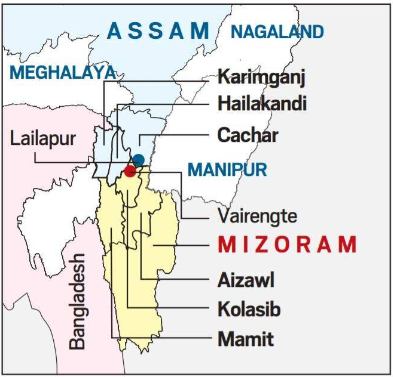
Boundary Committee in Mizoram
Mizoram forms panel to resolve border dispute with Assam.
Mizoram, once was part of Assam became a union territory in 1972 and later became a full-fledged state in 1987.
- Boundary Committee – It has been constituted by the Zoram People’s Movement (ZPM) government of Mizoram.
- Aim – To resolve the 165-km border disputes between Mizoram and Assam shared across 3 districts on each side.
- Panel members – It will have the Minister for Environment, Forests and Climate Change, the state Home Department Commissioner, the advisor to the Chief Minister, the Chief Secretary and the state DGP along with 1 member each from the recognised parties in the state.
- Mizoram’s Border – It shares boundaries with Assam, Manipur and Tripura in India and also share border with Bangladesh.
|
Assam-Mizoram Border Dispute
|
- Historical background – It dates back to colonial era when inner lines where demarcated as per administrative needs of British Raj.
- 1875 notification – It differentiated Lushai hills (Mizoram) from the plains of Cachar.
- 1933 notification – It demarcated a boundary between Lushai hills and Manipur.
- Dispute – While Mizoram follows 1875 notification, Assam follows 1933 notification.
- Recent issue – It turned violent in 2021 when 6 Assam cops were killed after the forces of the 2 states clashed.
|
Reference
The Indian Express| Mizoram forms a Boundary Committee
Global Carbon Project (GCP) Report
The Global Carbon Project report for 2023 was released during the recent COP28 summit held in Dubai, UAE.
- It is a Global Research Project of Future Earth and a research partner of the World Climate Research Programme.
- Established in – 2001
- It is prepared every year by a global consortium of scientists.
- Aim – To develop a complete picture of the global carbon cycle, including both its biophysical and human dimensions together with the interactions and feedbacks between them.
- Focus – On the global biogeochemical cycles which govern 3 greenhouse gases (GHGs) like carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), including their natural and human drivers, and opportunities for low carbon pathways.
- Significance – It produces Global Carbon Budget annually which provides an in-depth look at the amount of fossil fuels that nations around the world burn and where it ends up.
- 2023 report – It projects fossil CO2 emissions of 36.8 billion tonnes in 2023, up 1.1% from 2022.
- Global emissions from coal, oil and gas are all projected to increase with most steep increase from oil.
- Atmospheric CO2 levels are projected to average 419.3 ppm in 2023, 51% above pre-industrial levels.
- In India – CO2 emissions will cross 3 gigatons (gt) by the end of 2023, about 8% higher than the figure of 2022.
- India’s per capita emissions is only about 1.9 tonnes (against a world average of almost 5 tons) and its cumulative emissions is only 3% (as against 25% for US) of the global emissions.
|
India’s Third National Communication (2023) Report
|
- India’s total greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs) was 3.1 gt of CO2eq (2019).
- Almost 76% of GHGs were emitted by the energy sector followed by agriculture and industrial process sectors.
- About 92% of the CO2 emissions is from the energy sector.
- Among energy sectors, power generation contributes about 39% in the total CO2 emissions followed by transport and iron and steel.
|
References
- Down To Earth| Global Carbon Project Report 2023
- The Indian Express| India’s GHG Emission Scenario
- GCP| Global Carbon Project