Fixed Rate Regime
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) allows switch from floating to fixed rate regime.
- The RBI asked all regulated entities (REs) including banks and NBFCs, to give personal loan borrowers an option to switch over from a floating rate to a fixed rate regime at the time of resetting interest rates.
Regulated entities include banks, primary co-operative banks, Non-Banking Financial Companies, Credit Information Companies and also institutions such as EXIM Bank, NABARD, NaBFID, National Housing Bank ('NHB') and Small Industries Development Bank of India ('SIDBI').
Floating & Fixed Rate
- Banks can change the interest rate by changing the internal benchmark rate and the spread during the term of the loan which could harm the interest of the borrower and also impair monetary transmission.
- A floating exchange rate is determined by the private market through supply and demand.
- A fixed, or pegged, rate is a rate the government (central bank) sets and maintains as the official exchange rate.
- The reasons to peg a currency are linked to stability.
- Especially in today's developing nations, a country may decide to peg its currency to create a stable atmosphere for foreign investment.
New Changes
- At the time of sanction, REs will have to clearly communicate to the borrowers about the possible impact of a change in benchmark interest rate on the loan leading to changes in EMI and/or tenor or both.
- Any increase in the EMI/ tenor or both will have to be communicated to the borrower immediately through appropriate channels.
- Switchcover – At the time of reset of interest rates, REs will have to give the option to borrowers to switch over to a fixed rate as per their board-approved policy.
- The policy will also specify the number of times a borrower will be allowed to switch during the tenor of the loan.
- REs will have to disclose all applicable charges for switching loans from floating to fixed rate.
- Elongation – The borrowers will also be given the choice to opt for enhancement in EMI or elongation of tenor or for a combination of both options.
- They also can prepay, either in part or in full, at any point during the tenor of the loan, with foreclosure charges.
References
- The Indian Express – RBI allows switch from floating to fixed rate regime
- Deccan Herald – Understanding RBI’s announcement on resetting floating rate loans
Penal Charge (vs) Penal Interest
RBI has directed lenders not to levy penal interest on borrowers.
- The RBI issued guidelines on Penal Charges in Loan Accounts under the Fair Lending Practice.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) directed lenders to levy penalty for default by borrowers as penal charges and not as penal interest.
- Applicable To – The new guidelines are applicable to banks, including small finance banks, regional rural banks.
- Not applicable – Payments banks, non-banking financial companies, housing finance companies, primary urban co-operative banks, all India Financial Institutions such as Exim Bank, Nabard, SIDBI and NaBFID.
The penal charges in case of loans sanctioned to individual borrowers, for purposes other than business, cannot be higher than the penal charges applicable to non-individual borrowers for similar non-compliance of loan contracts, according to the guidelines.
Penal Charge
- They are additional charges levied by the lender on a borrower.
- These are payable when the borrower delays in repaying a loan or the equated monthly instalment (EMI) on a loan and other financial instruments.
- The penal charge levied on a payment default vary from banks to NBFCs.
Penal Interest
- It is added to the rate of interest charged on the advances.
- It is a penalty interest levied by the loan provider if a borrower does not pay the loan EMI as per the repayment schedule of the loan.
- Irrespective of whether the individual pays monthly EMIs or make the payment quarterly or annually, if the lender does not receive the loan payment by the scheduled date, it is required to pay penal interest.
References
- The Indian Express – RBI has directed lenders not to levy penal interest on borrowers
- The Economic Times – RBI stops banks, NBFCs from compounding penal interest on loans
Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit
RBI announced a pilot programme for Public Tech Platform for Frictionless Credit, which would strive to deliver frictionless credit by facilitating seamless flow of required digital information to lenders.
- Digital delivery of credit (or delivering credit/loans though digital means) is preceded by a process of scrutiny known as credit appraisal.
- The process attempts to evaluate and accordingly predict the prospective borrowers ability for repayment of credit/loan and adhering to the credit agreement.
- The process rests on three important pillars, namely:
- The problem of adverse selection (that results from the asymmetry of information from either the borrower or lender)
- Measurement of exposure risk
- The assessment of default risk (the probability that the borrower may default in repayment).
- This pre-disbursal process is particularly important for banks since it would in turn determine their interest income and impact on the balance sheet.
- RBI observed that the data required for the process rest with different entities like central and state governments, account aggregators, banks, credit information companies, and digital identity authorities.
- Thus, being in separate systems, it creates hindrances in frictionless and timely delivery of rule-based lending.
- This new platform would bring all of it together in a single place.
- To facilitate frictionless and timely delivery of loans, the central banking regulator had instituted a pilot project for digitalisation of Kisan Credit Card (KCC) loans, of less than Rs 1.60 lakh.
- The pilot is currently ongoing in select districts of Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra.
- It provides for doorstep disbursement of loans in assisted or self-service mode without any paperwork.
References
- The Hindu – What is RBI’s pilot programme for facilitating ‘frictionless’ and ‘timely’ credit?
- India Today – RBI to launch pilot project for ‘frictionless credit’
Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH)
India and the WHO will launch the Global Initiative on Digital Health.
- The Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH) is a WHO managed network of stakeholders organized to facilitate the implementation of the Global Strategy on Digital Health.
- The Initiative will serve as a platform to enable a wide global ecosystem to work collectively to promote country capacity and strengthen international cooperation in digital health.
- The initiative aims to converge global efforts for digital health and scale up digital solutions with the use of cutting-edge technologies.
- In partnership with the WHO, the Global Initiative on Digital Health has been established, fostering collaboration among nations and organizations to realize this transformative vision.
The Global Initiative on Digital Health to be launched under India’s G20 Presidency, will support the WHO Strategy on Digital Health.
- This important initiative will support the WHO global strategy on digital health and amplify other initiatives including the WHO global digital health certification network.
India's national platform, e-Sanjeevani, facilitated 140 million telehealth consultations to date.
- The Global Initiative on Digital Health will bring together various digital health initiatives on a common platform.
- This initiative will allow countries in the Global South to close the gap in health-care delivery.
References
- WHO – Global Initiative on Digital Health
- Live Mint – India and WHO launch the Global Initiative on Digital Health
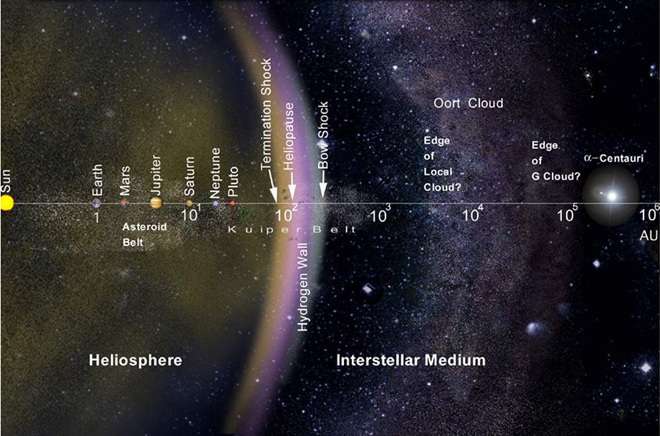
Oort Cloud
NASA’s Voyager 1 probe will take 300 years to reach the Oort cloud, the most distant region of our solar system.
- The Oort Cloud is the most distant region of our solar system.
- Even the nearest objects in the Oort Cloud are thought to be many times farther from the Sun than the outer reaches of the Kuiper Belt.
Kuiper Belt is the collection of millions of icy objects, collectively referred to as Kuiper Belt objects (KBOs) or trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs), in this distant region of our solar system.
- Unlike the orbits of the planets and the Kuiper Belt, which lie mostly in the same flat disk around the Sun, the Oort Cloud is believed to be a giant spherical shell surrounding the rest of the solar system.
- Because the orbits of long-period comets are so extremely long, scientists suspect that the Oort Cloud is the source of most of those comets.
- The distance from the Sun to the Oort Cloud is so enormous that it’s useful to describe it not in the more common units of miles or kilometers, but astronomical units.
One astronomical unit (or AU) is the distance between Earth and the Sun.
Voyager 1 and Voyager 2
- The twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are exploring where nothing from Earth has flown before.
- Continuing on their more-than-40-year journey since their 1977 launches, they each are much farther away from Earth and the sun than Pluto.
- In August 2012, Voyager 1 made the historic entry into interstellar space, the region between stars, filled with material ejected by the death of nearby stars millions of years ago.
- Voyager 2 entered interstellar space on November 5, 2018 and scientists hope to learn more about this region.
- Both spacecraft are still sending scientific information about their surroundings through the Deep Space Network, or DSN.
- The primary mission was the exploration of Jupiter and Saturn.
- After making a string of discoveries there, such as active volcanoes on Jupiter's moon Io and intricacies of Saturn's rings, the mission was extended.
- Voyager 2 went on to explore Uranus and Neptune, and is still the only spacecraft to have visited those outer planets.
- The adventurers' current mission, the Voyager Interstellar Mission (VIM), will explore the outermost edge of the Sun's domain.
References
- The Business Insider – It would take another 300 years for NASA's Voyager 1 to reach the Oort cloud
- NASA – Oort Cloud
