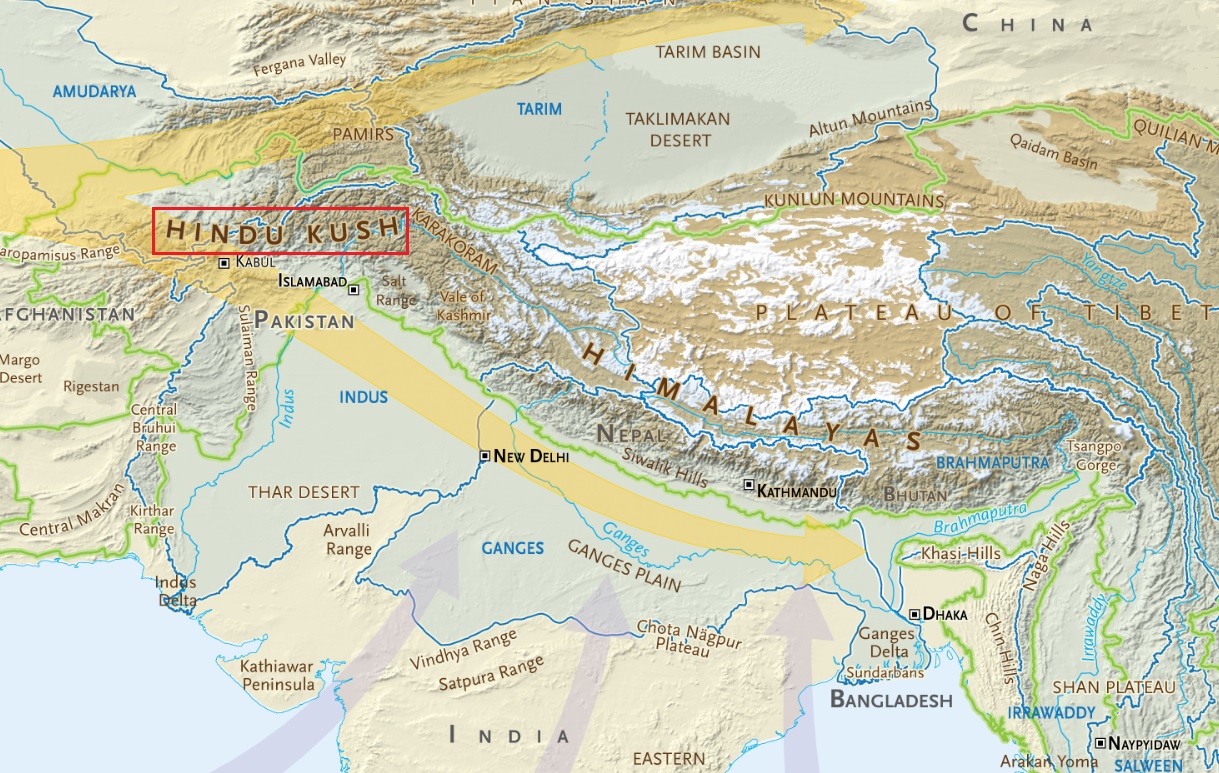
Hindu Kush Himalayan Mountain Ranges
A recent study shows that if global warming isn’t controlled Himalayan glaciers could lose 80% of their volume.
- Location - It is the great mountain system of Central Asia.
- It spreads across 8 countries – Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Nepal, Myanmar and Pakistan.
- Boundaries - It runs northeast to southwest and divides the valley of the Amu Darya to the north from the Indus River valley to the south.
- To the east the Hindu Kush supports the Pamir range near the point where the borders of China, Pakistani-controlled Kashmir, and Afghanistan meet.
- The eastern end of the Hindu Kush in the north merges with the Karakoram Range.
- It runs southwest through Pakistan and into Afghanistan, finally merging into minor ranges in western Afghanistan.
- Peaks and ranges - The highest peak is Mount Tirich Mir, which rises near the Pakistan-Afghanistan border.
- Towards its southern end, it connects with the Spin Ghar Range near the Kabul River.
- Water source - Hindu Kush Himalayas are the world’s most important ‘water tower’, being the source of 10 of Asia’s largest rivers.
- It is the Earth's 3rd Pole as it's the storehouse of the 3rd largest body of snow on our planet after the Antarctic and the Arctic.
- Other significance - The Hindu Kush Mountains were centers of Buddhism, including the Bamyan Buddha.
- It has also been a gateway for invasions into the Indian subcontinent, a growing region for the Taliban and al-Qaeda, and a theater of modern warfare in Afghanistan.
Reference
The Indian Express | Himalayan glaciers could lose 80% of their volume
Down to Earth | Climate change affecting biodiversity in Hindu Kush
Down to Earth | ICIMOD report warning for rivers of East, Northeast India
GEMCOVAC-OM
India’s first indigenous mRNA vaccine (GEMCOVAC-OM) for the Omicron variant, was approved under emergency use guidelines by the Drug Controller General of India.
- Developed by - Pune-based Gennova Biopharmaceuticals Ltd.
- Features – It is India's first mRNA vaccine developed to address the problems in the earlier approved mRNA vaccines.
- This mRNA-based vaccine uses spike protein of the omicron variant (BA.1) of the SARS- CoV-2 as an antigen.
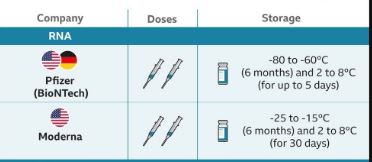
- It was stable in a 2-8 °C range and could therefore be stored in ordinary refrigerators.
- The vaccines could be administered as an intradermal (ID) injection only (into the skin) via a “needle-free” PharmaJet system.
- It is tested at the National Institute of Virology (NIV) against the newest (Omicron subvariant), XBB 1.16, and it is shown to be effective.
- It is indicated as a single booster dose in individuals aged more than 18 years administered at least 4 months after completion of primary vaccination with either Covishied or Covaxin.
mRNA is a molecule that contains the instructions or recipe that directs the cells to make a protein using its natural machinery.
m-RNA based vaccine technology
- mRNA vaccines work by introducing a piece of mRNA that instructs the cells to produce the viral protein.
- As part of a normal immune response, the immune system recognizes that the protein is foreign and produces specialized proteins called antibodies.
- Antibodies protect the body against infection by recognizing individual viruses or other pathogens, attaching to them, and marking the pathogens for destruction.
- Once produced, antibodies remain in the body, even after the body has rid itself of the pathogen.
- If a person is exposed to a virus after receiving mRNA vaccination for it, antibodies can quickly recognize it, attach to it, and mark it for destruction before it can cause serious illness.
- Individuals who get an mRNA vaccine are not exposed to the virus, nor can they become infected with the virus by the vaccine.
|
mRNA based vaccines
|
Developed by
|
|
GEMCOVAC™-19
|
India
|
|
Pfizer-BioNTech
|
USA
|
|
Moderna COVID-19
|
USA
|
References
The Hindu | Regulator approves first Omicron-specific mRNA vaccine
The Indian Express | India’s first mRNA-based Omicron-specific booster vaccine
Submersible vs Submarine
The Titan, one of the crewed submersibles operated by OceanGate, went missing in the area of the Titanic wreck in the North Atlantic.
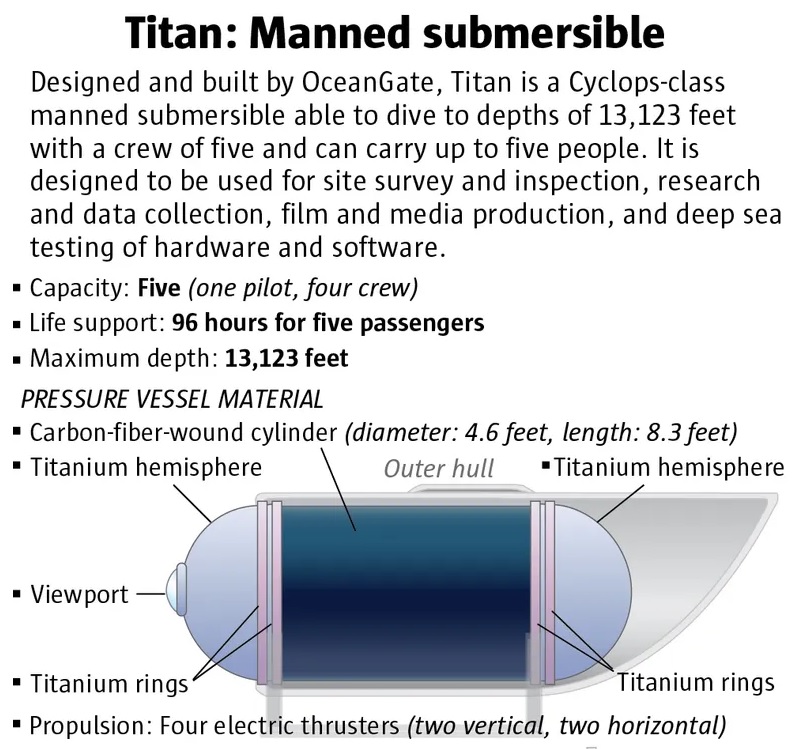
Titan
- Titan is the only crewed submersible in the world that can take 5 people as deep as 4,000 meters enabling it to reach almost 50% of the world’s oceans.
- It is made of carbon fiber and titanium.
- The submersible was part of an 8-day journey conducted by OceanGate Expeditions to reach the Titanic wreck site.
- The wreck site is about 900 miles off the coast of Cape Cod, Massachusetts.
- Once submerged, the platform uses a patented motion-dampening flotation system to remain coupled to the surface that provide a stable underwater platform.
- At the conclusion of each dive, the sub lands on the submerged platform and the entire system is brought to the surface in approximately 2 minutes by filling the ballast tanks with air.
Submersible
- A submersible is a small boat or other craft, designed especially for research and exploration.
- It does not function as an autonomous craft and needs a mother ship that can launch and recover it.
- The submersibles have a top speed of 3 knots (5.5 kmph).
- It can’t stay underwater for as long compared to submarines.
- Since there is no GPS underwater, the submersible is only guided by text messages from the surface ship.
- The pilot steers the sub using a video game controller but if that fails, a hard-wired system can control the propellers.
Submarines
- A submarine is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater.
- It refers to any naval vessel that is capable of propelling itself beneath the water as well as on the water’s surface.
- When submarine is to dive, water is filled in water tanks and it is made heavier.
- Since the average density of submarine becomes greater than the density of sea water, it sinks.
- To make the submarine rise to the surface of water, water tanks are emptied.
Reference
The Indian Express | Titanic tourist submersible missing
Lake Victoria Basin
A recent report shows that heavy rains, wind storms, and floods threaten the survival and water access of the communities living in the Lake Victoria Basin (LVB), East Africa.
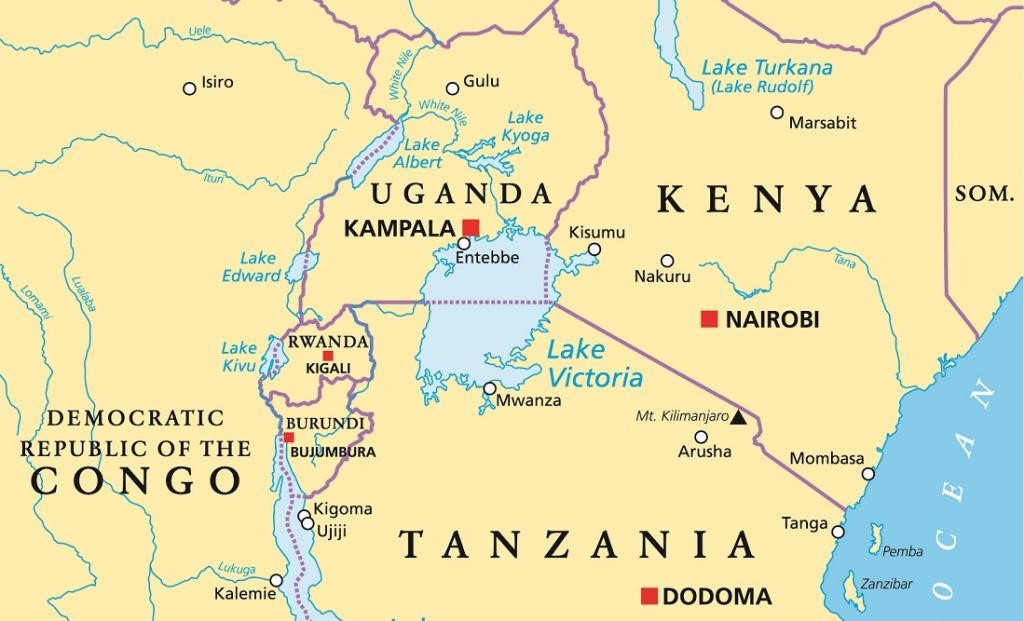
- Location - Lake Victoria Basin is situated at East Africa.
- Features - Lake Victoria is the
- Largest freshwater lake in Africa
- World’s largest tropical lake
- Second largest freshwater lake in the world, after Lake Superior in North America
- Largest inland water fishery sanctuary in East Africa
- Climate - It has modified equatorial climate, regional rainfall regulates the water levels in the lake.
- Most of the lake’s water comes from rainfall, while almost the same amount of water is lost through evaporation and carried out by the Nile.
- Associated countries - The basin’s catchment area traverses through 5 East African Countries - Tanzania (44%), Kenya (22%), Uganda (16%), Rwanda (11%) and Burundi (7%).
- This trans-boundary asset is shared by Tanzania (51%), Uganda (43%) and Kenya (6%).
- Rivers - A number of important rivers flow into Lake Victoria including the River Mara, Kagera, Yala, Nyando, Bukora and Katonga.
- The White Nile is the only river flowing out of the Lake.
- The Kagera (Akagera) River, which drains the mountains of Burundi and Rwanda, is considered as the source of the Nile.
Reference
Down to Earth | Measures needed to minimise disaster impact in Lake Victoria Basin
Multi-cap Funds
Multi-cap funds with equity exposure of 25% each in the large-, mid- and small-caps have delivered better returns in the last few years.
- Multi Cap Funds invest their corpus in a portfolio of equity and equity-related stocks of companies with varying market capitalizations.
- Their portfolio comprises of large cap, midcap and small cap stocks.
- Multi-cap funds allocate 75% of the fund assets to equities and related instruments, with at least 25% in each of the large, medium, and small capitalizations as per the SEBI mandate.
- They are relatively less risky compared to a pure mid cap or a small cap fund but are riskier than those of large cap funds.
- Types of Multi-Cap Funds
- Large cap – It refers to the top 100 publicly listed companies in India by full market capitalization
- Mid cap – It refers to the 101st to 250th company in terms of full market capitalization
- Small caps - 251st company onwards in terms of full market capitalization.
Market capitalization = No. of publicly listed shares x Price of each share
Advantages of Multi Cap Funds
- Exposure to all key sectors driving the Indian economy forward
- Ideal for an investment horizon of 5+ year
- Eliminates the need for buying different funds for comprehensive market coverage
- Provide a perfect blend of all capital markets that allows to earn good interest balancing the risks and returns.
Reference
The Hindu Businessline|multi-cap-funds-deliver-better-returns-in-volatile-times

