7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Lokmanya Bal Gangadhar birth anniversary (23 July 1856)
Swadesh Darshan Scheme
Sree Narayana Guru
Prevention and Management of Heat-Wave - Action Plan
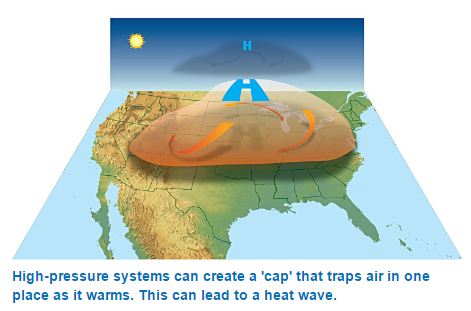
Source: PIB, The Indian Express