Extrajudicial Divorces
The Kerala High Court will reconsider its 2021 ruling on whether Muslim women lost their right to extrajudicial divorce by a way of Khula after the passage of the Dissolution of Muslim Marriages Act, 1939.
Khula
- Khula refers to the right of a Muslim woman to unilaterally divorce her husband.
- This is similar to the right of talaq conferred upon Muslim men under Sharia law.
- The recognition of khula as a form of divorce stems directly from the Holy Qur’an.
In 1972, the case of K.C. Moyin vs. Nafeesa negated the right of Muslim women to invoke extra-judicial divorce in light of the Dissolution of Muslim Marriages Act, 1939.
Shariat Act
- The Muslim Personal Law (Shariat) Application Act, 1937, recognizes both judicial and extrajudicial divorce.
- Section 2 - Recognizes all forms of extrajudicial divorce except faskh.
- Section 5 - Allows the dissolution of marriage by court in certain circumstances and allows a district judge to dissolve a marriage based on the woman’s plea.
1939 Act
- The 1939 Act was passed to clarify and consolidate the provisions of the law relating to the dissolution of marriage by Muslim women.
- The 1939 Act recognised the faskh route of extrajudicial divorce.
|
Quick Facts
|
|
Other forms of extrajudicial divorce available to Muslim women
|
|
Illa
- Illa is when a husband takes an oath not to have sexual intercourse with his wife.
- After the expiry of 4 months of such abstinence, a marriage is dissolved according to Hanafi law.
Zihar
- In zihar, the husband swears that his wife is like his mother, which was regarded as an insult in Arab society, and a wife could obtain divorce on this ground.
- In India, illa and zihar are of no practical importance.
Ithna Ashari
- Ithna Ashari (predominant within the Shia sect) and Shafi law (Sunni Sect), legal proceedings are necessary for dissolution after 4 months of abstinence.
Lian
- Lian (mutual imprecation) is when a husband accuses his wife of infidelity, and is liable to punishment for defamation (qadhf) unless he proves his allegation.
- In case of failure to prove such an allegation, the wife can file a suit for dissolution of marriage.
Talaq-e-Bidat
- Talaq-e-Bidat (instant triple talaq) having been criminalized now, talaq-e-Ahsan and talaq-e-Hasan are recognized forms of divorce for Muslim men under Indian Law.
Nikah halala also known as tahleel marriage, is a practice in which a woman, after being divorced by triple talaq, marries another man, consummates the marriage, and gets divorced again in order to be able to remarry her former husband.
Talaq-e-Tafwiz
- This is contract-based divorce and the parties are free to choose the terms of their contract and decide how their marital lives will be regulated.
Mubara’at
- This is a form of separation by mutual consent.
- Both Shi’a and Sunni sects deem this form of divorce to be irrevocable.
Faskh
- This is divorce through a third party or external authority like an arbitrator, mediator, judge or an authority like a qazi.
|
References
- The Indian Express – Muslim women’s right to divorce
- The Leaflet – Muslim Women’s Right to Extra-Judicial Divorce
- Deccan Herald – Will examine validity of extrajudicial divorce: SC
Portals for Modernized Media Landscape
Union minister launched four transformative portals aimed at fostering a more conducive business environment and enhancing transparency in government communication.
Press Sewa Portal
- It is developed under the Press and Registration of Periodicals Act, 2023 (PRP Act, 2023).
- It automates the process for newspaper registration and related procedures.
- Key features - Online application filing, real-time tracking, and a dedicated module for District Magistrates to manage applications.
|
Press and Registration of Periodicals Act, 2023
|
- The Act provides for the registration of newspapers, periodicals, and books and also provides for the cataloguing of books.
- Periodicals do not include books or scientific and academic journals.
- Books as a subject are administered by the Ministry of Education.
|
Transparent Empanelment Media Planning and eBilling System
- It was introduced for the Central Bureau of Communication (CBC).
- It streamlines media planning processes and provides an end-to-end ERP solution for the media industry.
- Features - automated empanelment, media planning, billing, and a mobile app for partners.
|
Central Bureau of Communication (CBC)
|
- CBC was set up in 2017 by integration of erstwhile Directorate of Advertising and Visual Publicity (DAVP), Directorate of Field Publicity (DFP) and Song & Drama Division (S&DD).
- It is the nodal agency of the Government of India for advertising by various Ministries and organisations of Government of India, including public sector undertakings and autonomous bodies.
- It works under the administrative control of Ministry of Information and broadcasting, with its headquarters at New Delhi.
|
NaViGate Bharat Portal
- It is developed by the New Media Wing of the Information & Broadcasting ministry.
- It serves as a unified bilingual platform hosting videos on the government's development and citizen welfare measures.
- It offers easy navigation, categorization, seamless video playback, and advanced search functionality.
National Register for LCOs
- It aims to bring registration of Local Cable Operators (LCOs) under a centralized system, promising a more organized cable sector.
References
- Hindustan Times – Government launches 4 transformatory portals
- The Indian Express – New media-related portals to streamline services
- PIB – Transformative Portals for a Modernized Media Landscape
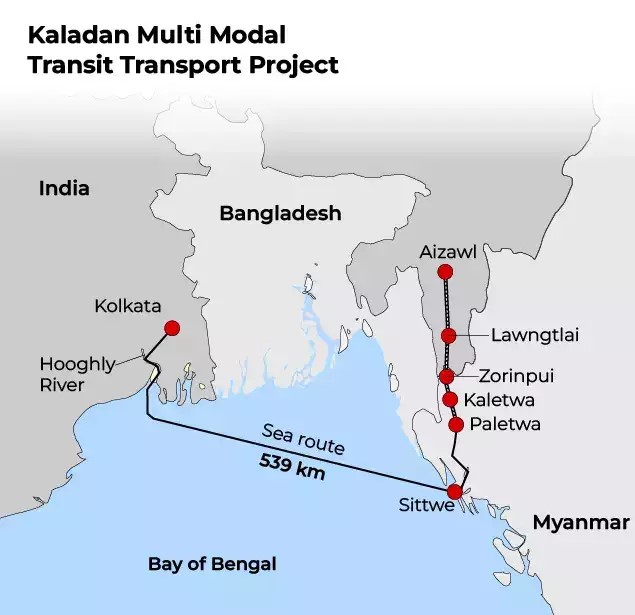
Sittwe Port
Advances by Myanmar’s anti-junta forces mount pressure on port developed by India.
Kaladan is a transboundary river flowing in India (Mizoram) and Myanmar.
Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project (KMTTP)
- The project aims to provide connectivity between India and Myanmar by connecting the port of Kolkata with the port of Sittwe in Rakhine.
- The Kaladan project has 2 major components -Waterways component and road component.
References
- Hindustan Times – Pressure on Sittwe Port
- India Today – India-financed Sittwe in Myanmar
- The Economic Times – India monitors battle near Sittwe
Purple Revolution & Aroma Mission
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that India’s demand for medicinal plants will increase from the current $14 billion per year to $5 trillion by 2050.
Aroma Mission
- Launch - In 2016 by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
- Aim - To deliver technological and infrastructure aid for value-addition and distillation to agriculturalists or growers all over India.
- The Aroma Mission through the Purple Revolution aims to bring about a revolutionary change in the fragrance industry.
- It is popularly known as the Lavender or Purple Revolution.
- Lavender has been designated by the central government as a "Doda brand product" to promote the rare aromatic plant under One District, One Product.
Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia) is an evergreen plant native to the Mediterranean.
The Purple Revolution
- Launched by - Ministry of Science and Technology
- Aim - To promote the indigenous aromatic crop-based agro economy through the ‘aroma mission’.
- To increase the income of the farmers and promote lavender cultivation on commercial scale.
- Jammu and Kashmir’s climatic conditions are conducive to lavender cultivation, since lavender can withstand both chilly winters and pleasant summers.
"Marc" is the leftover residue from lavender flower steam distillation for oil extraction.
Hydrosol is a scented lavender-infused water produced from the steam distillation process which offers versatility in products like room sprays and bodymists.
References
- Invest India – India’s Purple Revolution
- The Economic Times – The purple revolution
- PIB – J&K to be a heritage town and aroma start-up destination
Upper Yamuna River Board (UYRB)
Union Minster of Jal Shakti has inaugurated the Upper Yamuna River Board (UYRB) building at Noida.
- A memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signed by Chief Ministers of Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan and National Capital Territory of Delhi in 1994 provides for creation of a board called Upper Yamuna River Board (UYRB).
Upper Yamuna refers to the stretch of Yamuna from its origin upto and including the Okhla Barrage at Delhi.
- UYRB is a sub-ordinate office under the Department of Water Resources, Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- Chairman - Union Minister / Minister of State for Water Resources
- Members - Chief Ministers of basin
- Secretary - Chairman, UYRB
- Functions - Regulation and supply of water from all storages and barrages upto and including Okhla barrage.
- Maintenance of minimum flow in Yamuna from ecological considerations.
- Monitoring return flows from the waters withdrawn:
- By Delhi for domestic use.
- By the States of Uttar Pradesh and Haryana for the purpose of silt exclusion.
- For Khara hydel station.
Basin States includes Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Rajasthan and Delhi.
- Barrages - Tajewala/Hathnikund; Wazirabad; Okhla.
- Canal Networks - Western Yamuna Canal; Eastern Yamuna Canal; Agra Canal/Gurgaon Canal.
|
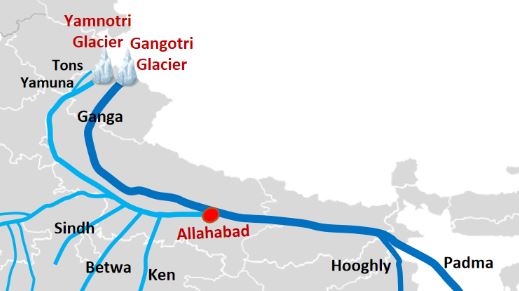
Yamuna River
|
- The Yamuna rises on the slopes of the Bandarpunch massif in the Great Himalayas near Yamnotri (Jamnotri) in western Uttarakhand.
- Near Prayagraj (Allahabad), the Yamuna joins the Ganges (Ganga) River.
- The confluence of the two rivers is an especially sacred place to Hindus and is the site of annual festivals as well as the Kumbh Mela.
- The important tributaries of the Yamuna River are Tons, Chambal, Hindon, Betwa and Ken.
- Other small tributaries of the Yamuna River include the Giri, Sind, Uttangan, Sengar and the Rind.
|
References
- Jalshakti – Upper Yamuna River Board (UYRB)
- Britannica – Yamuna River
