Fermentation
Fermentation can help make uniquely tangy healthy dishes while also reducing food waste at home.
- Definition – The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics defines fermented foods and beverages as “foods made through desired microbial growth and enzymatic conversions of food components”.
|
Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB)
|
- It consists of 16 genera, 12 of which are associated with food.
- Examples – Lactobacillus and Streptococcus among others.
- Significance – Used in fermentations of food products.
- These genera are amongst the very 1st bacteria studied.
|
In 1873, Joseph Lister isolated the 1st bacterial pure culture, which he called Bacterium lactis. This LAB is now called Lactococcus lactis and is used to ferment milk to produce hundreds of dairy products.
- Improves flavour – It gives distinct sour taste.
- Preserves food – LAB converts the starch in the food to lactic acid that inhibits growth of food-spoiling bacteria and fungi.
- Health Benefits – It can reduce the likelihood of developing cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- kimchi – It has anti-obesity and anti-diabetic effects.
- LAB fermented milk – It could help lower cholesterol and has anti-cancer properties.
- It could also reduce symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease and can improve in mood and cognitive function.
- Improves gut microbiota – LAB fermentates can beneficially modulate gut microbiota which can improve overall health.
- Reduce food wastage – By using them as fermented foods.
- Common examples of fermented food
- Curd – It is commonly prepared in Indian households.
- Kasundi – A spiced mustard sauce from West Bengal
- Dal vadis or dried lentil fritters – From Uttarakhand
- Sour and spicy kanji – Used in North India, prepared from black carrots by the action of Lactobacillus plantarum,
- Idli and dosa batter – In making traditional foods in India.
- Sauerkraut – A traditionally consumed food in eastern and central Europe, made from cabbage.
- Kimchi – A Korean vegetable dish.
|
|
Prebiotic
|
Probiotic
|
|
Content
|
Non-digestible, a form of carbohydrates or fibre
|
Live microorganisms
|
|
Role
|
It nourishes the bacteria that lives in intestine.
|
It fight the harmful gut bacterial species.
|
|
Vulnerability
|
It can survive heat, cold and acid action.
|
Vulnerable to heat, stomach acid and they may be killed over time.
|
|
Fermentation process
|
Can be controlled
|
Not controlled
|
|
Health benefits
|
Beneficial in irritable bowel movements, colon polyps and cancer
|
Improves gut health and protects against disease.
|
Reference
Down to Earth| Importance of Fermented foods
Lab Grown Fish
Recently, MoU was signed for CMFRI-Neat Meatt public private partnership project to accelerate development of lab grown fish meat.
Mark Post, the Dutch pharmacologist was the 1st to present a proof of concept for cultured meat in 2013. Currently lab-grown meat from cells including chicken, pork, lamb, fish and beef are underway.
- Cultivated fish meat – It is produced by isolating specific cells from fish and growing them in a laboratory setting using media that is free of animal components.
- It is expected to replicate the flavour, texture, and nutritional qualities of ‘real’ fish meat.
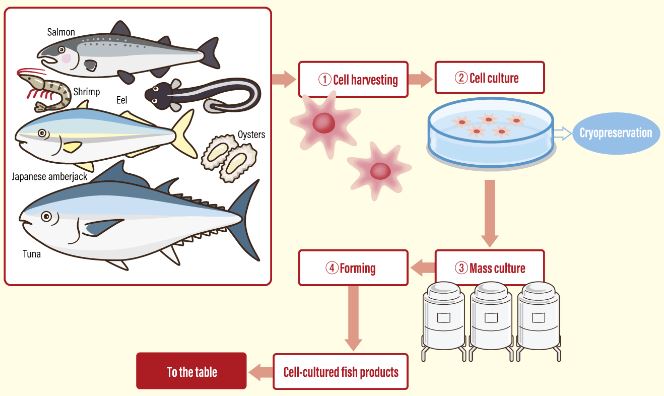
- Need – To address the ever growing demand for seafood, and reduce excessive pressure on wild resources.
- Countries engaged – Israel is the frontrunner, followed by Singapore, the United States and China.
In 2023, the US cleared the sale of lab grown chicken meat in the country. Previously Singapore have approved cell-based meat for consumption.
- Significance – It can ensure food security and environmental benefits.
- It will also be antibiotics- and environmental contamination-free, and will have no contact with microplastics or heavy metals in the polluted oceans.
Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI) was established in 1947, joined ICAR family in 1967 with its headquarters in Kochi.
Reference
The Indian Express| Lab Grown Fish Meat Production in India
AISHE 2021-22
All India Survey of Higher Education (AISHE) 2021–22 was made public on January 25, 2024.
- Initiated in – 2011.
- Aim – To give complete picture of Higher Education in the country.
- 3 Categories – Universities, Colleges and Stand-alone institutions.
- Data source – Voluntary uploading of data by institutions of Higher Education listed in www.aishe.gov.in portal.
- AISHE 2021-22 – It was the 11th Survey and 1st Survey conducted through Web Data Capture Format (DCF).
For the 1st time, all the major Stakeholders in Higher Education, such as UGC, AICTE, MCI as well as State Governments participated in the data collection exercise for AISHE 2021-22.
Key takeaways from AISHE 2021-22 Report
- Increase in enrolment – 4.33 crore students, up from 2020-21 level, captured in 8 different levels.
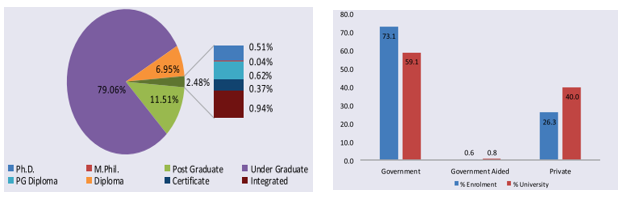
- Primacy of government institutions – 73.7% of all students attend government universities, where state public universities have the largest share of enrolment, accounting for around 31%.
- Higher enrolment of females – It has steadily increased to 2.07 crores in 2021-22, a 32% jump from 2014-15 levels with the highest numbers at the post graduate level, 55.4% are women.
- Gender Enrolment Ratio – It is 28.4 for the age group 18-23 years at all India level (population data from the 2011 census) and is in favour of women in 26 states and Union Territories.
- Chandigarh boasts of the highest GER (64.8%), followed by Puducherry, Delhi and Tamil Nadu.
Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) indicates how many students are part of the higher education system in a given population.
- Gender Parity Index – It is 1.01 at all-India level, and for SC and ST categories, it is 1.01 and 0.98 respectively.
Gender Parity Index (GPI) shows the ratio of the female GER to male GER. A GPI of 1 indicates parity between the two genders, GPI greater than 1 indicates a disparity in favour of females.
- Higher preferences for Arts – In UG, Bachelor of Arts (BA) and in PG, Master of Arts (MA) programme has the highest enrolment.
- Demographics of students graduating – Among the graduated students, roughly 50.8% are women and the graduation rate in arts and social sciences streams is higher than others.
- Category-wise, around 35% of the students belong to OBC, 13% are from SC and 5.7% are from ST community.
References
- The Indian Express| Key takeaways from AISHE 2020-21
- AISHE| AISHE 2020-21
UN Relief and Works Agency for Palestinian Refugees (UNRWA)
Recently, UN officials urged countries to reconsider their decision to suspend the funding for the United Nations agency for Palestinian refugees (UNRWA).
The US and 8 other Western countries, which together provided more than 50% of UNRWA’s 2022 budget, cut the money after Israel accused some of the agency’s staff members of involvement in Israel attack.
- UNRWA – UN Relief and Works Agency for Palestinian Refugees in the Near East.
- Founded in – 1949, mandated by the UN General Assembly to serve ‘Palestine refugees’.
- Objective – To provide aid to about 700,000 Palestinians who were forced to leave their homes during the 1948 Arab-Israeli war.
- To offer services to certain other persons who require humanitarian assistance, on an emergency basis in UNRWA fields of operations.
- Funded by – Voluntary contributions by donor states, and a limited subsidy for administrative costs from the UN.
- Areas covered – It operates in Gaza and the Israeli-occupied West Bank, as well as Lebanon, Syria, and Jordan, countries where the refugees took shelter after their expulsion.
- Activities – It runs education, health, relief and social services, microfinance and emergency assistance programmes inside and outside refugee camps.
- Beneficiaries - Currently, it is accessed by around 5.9 million Palestine refugees, most are descendants of original refugees.
The Associated Press reported that in Gaza, where some 85% of the enclave’s 2.3 million people have fled their homes after the latest Israel-Hamas conflict, over 1 million are sheltering in UNRWA schools and other facilities.
References
- The Indian Express| Pause of Funding for UNRWA
- UNRWA| UN Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees
Islamic Resistance of Iraq (IRI)
Recently, 3 US military servicemen were killed in a drone attack on their Tower 22 outpost in Jordan, which was claimed by Islamic Resistance of Iraq (IRI).
- Islamic Resistance of Iraq – IRI is an umbrella term to describe the operations of all Iran-backed militias in Iraq.
IRI is claimed to be a part of the ‘Axis of Resistance’, the multiple groups that Iran backs as part of its anti-Western and anti-USA stance.
|
Iran backed Militias in Middle East
|
|
Militant Group
|
Region
|
|
Hezbollah
|
Lebanon
|
|
Houthis
|
Yemen
|
|
Islami Resistance of Iraq (IRI)
|
Iraq, Syria and Jordan
|
- Umbrella militias – Hashd al-Shaabi.
- Operation – Iraq, Syria and Jordan.
- Strength – A powerful military and political forces, boast 1000s of fighters and are also integrated into the state.
- Recent attacks – It carried out a drone attack in Iraqi Kurdistan, strikes into Syria during 2023 Israel-Hamas conflict.
|
Tower 22
|
|
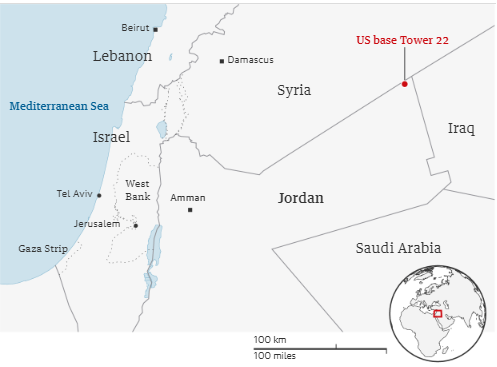
- It is a strategically important location in Jordan, at the most north-eastern point where the Jordan meet Syria and Iraq.
- It is near al-Tanf garrison, which houses a small number of US troops across the border in Syria.
- It serves as a logistics hub for US military units in Syria.
|
Jordan is bordered by Israel to its west, Saudi Arabia to its southeast, Iraq to its northeast and Syria to its north.
References
- The Indian Express| US troops killed in Jordon
- The Guardian| Islamic Resistance of Iraq (IRI)
|
Other Important Topics
|
|
Exercise Sada Tanseeq
|
|
The inaugural edition of the exercise Sada Tanseeq commenced recently at Mahajan, Rajasthan.
- It is a joint military exercise between India and Saudi Arabia.
- Aim - To train troops of both sides for Joint Operations in Semi Desert terrain.
|
|
Old Smoker
|
|
Astronomers have recently discovered a new type of red giant star nicknamed as “Old Smoker”.
- It was found in a densely packed and metal-rich region at the centre of the Milky Way called the Nuclear Stellar Disc.
- These stars looked dim for several years before they puffed out huge clouds of smoke into space.
- The matter ejected plays a key role in the life cycle of the elements, helping to form the next generation of stars and planets.
|
|
Sloth Bear
|
- A Sloth Bear (Melursus ursinus) is an omnivorous mammal that can live up to 40 years.
- Sloth bears occupy a significant 67% of potential habitat in India.
|
Conservation Status
|
|
IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
|
Vulnerable
|
|
CITES
|
Appendix I
|
|
Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972
|
Schedule I (Highest Protection)
|
- India has four sloth bear sanctuaries namely
- Daroji Sloth Bear Sanctuary (Karnataka)
- Gudekote Sloth Bear Sanctuary (Karnataka)
- Jessore Sloth Bear Sanctuary (Gujarat)
- Ratanmahal Sloth Bear Sanctuary (Gujarat)
- Daroji Sloth Bear Sanctuary in Karnataka is Asia’s first sloth bear sanctuary.
- To know more click here
|
|
Rajmargyatra
|
|
The details of tourist sites in the vicinity of national highways will soon be available on the Rajmargyatra mobile application.
- Rajmargyatra is a unified mobile application that aims to create a seamless, user-friendly experience for highway users.
- It works under the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI).
|
|
ECOWAS
|
|
Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger has recently announced their immediate withdrawal from the West African bloc ECOWAS.
- Struggling with jihadist violence and poverty, these regimes have had tense ties with ECOWAS since coups took place.
- All three were suspended from ECOWAS with Niger and Mali facing heavy sanctions.
- The junta leaders of Mali, Burkina Faso and Niger signed a charter in 2023 to establish a NATO like defence alliance known as the Alliance of Sahel States.
|
