Elon Musk's brain chip firm, Neuralink wins US approval for human study.
A paralysed man from the Netherlands was able to walk simply by thinking about it, because of a system of implants which wirelessly transmit his thoughts to his legs and feet.
Features
Health Benefits
Bacillus cereus is a food-borne pathogen that causes gastro-intestinal illnesses, and Staphylococcus aureus can infect soft tissue in the body.
Status of India
The GSLV-F12/NVS-01 mission was launched from the second launch pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre SHAR, Sriharikota.
An atomic clock is an extremely accurate type of clock which is regulated by the vibrations of an atomic or molecular system such as caesium or ammonia.
L1, L5 and S bands
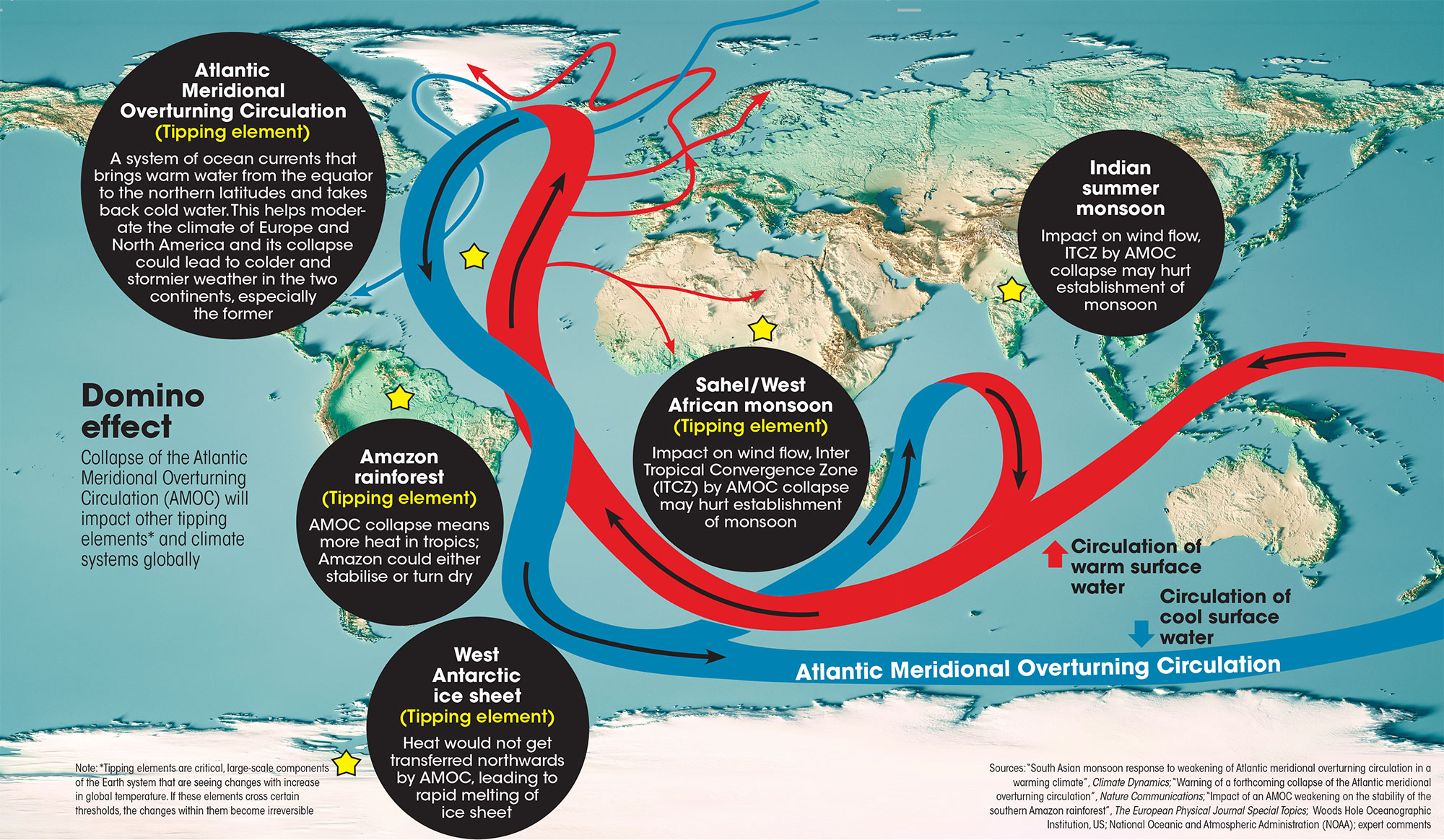
Deep ocean currents in Antarctica are slowing earlier than predicted.
Recent findings
Implications
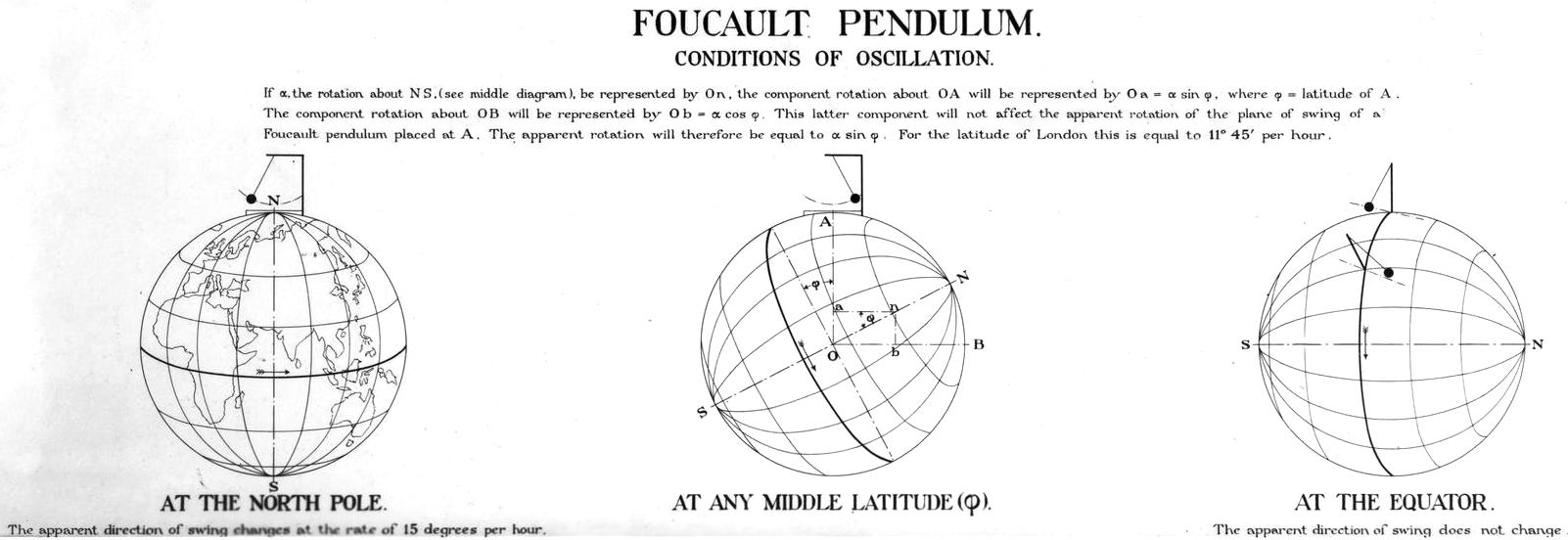
The pendulum hangs from a skylight at the top of the Constitution Hall at the new Parliament building.
Working
India