India Meteorological Department (IMD)
Why in News?
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) will be completing 150 years of service as of January 15, 2025.
- IMD – It is the National Meteorological Service of India and the principal government agency in all matters relating to meteorology and allied subjects.
- Historical background – Science and Meteorology in India commenced with the establishment of the 1st Meteorological and Astronomical Observatory in (then) Madras in 1793.
- The Sanitation Committee was formed in 1860 and the Meteorological Committee at the provincial level was set up.
- Established in – 1875 with H.F. Blanford as the Meteorological Reporter.
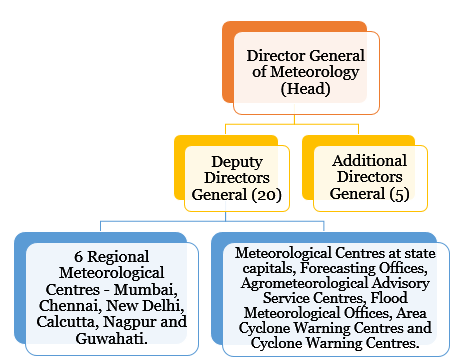
- Headquarters – New Delhi.
- Nodal Ministry – Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- Objectives – To take meteorological observations and to provide current and forecast meteorological information.
- To warn against severe weather phenomena which cause destruction of life and property and to conduct and promote research in meteorology and allied disciplines.
- Networks – It has 6 Regional Meteorological Centres (RMCs) catering to 6 regions of the country, which are further assisted by 26 Meteorological Centres (MCs) at the State level.
- Works
- Preparation of 1st chart in 1877.
- Preparation of 1st Daily Weather Report in 1878.
- Radar age and flood meteorological services between 1947-1959.
- Global monitoring and better forecasting up to 24 hours in 1971-1983
Between 2014 and 2023, there was rapid enhancement of weather and climate services and the forecast accuracy improved by 40-50%.
References
- The Hindu| 150 years of Formation of IMD
- IMD| India Meteorological Department (IMD)
UDISE+ Report
Why in News?
Recently, the Unified District Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+) Report enrolment data has stayed around 26 crores.
- UDISE+ Report – It is a report from Unified District Information System for Education Plus initiative.
- Prepared by – Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L).
- Released by – Ministry of Education (MoE).
- Based on – Voluntary uploading of data by the schools having active UDISE+ codes.
- UDISE+ code – It is allotted to a recognized school by the Central Government based on the recommendation of the respective State/UT Government where the school is located.
|
Unified District Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+)
|
- It is one of the largest Management Information Systems (MIS).
- Aim – To facilitate online uploading of data at school level with inbuilt validation checks and the subsequent data verification at the Block, District and State level.
- It becomes truly “One Nation One Database”.
- Data – It captures data for more than 60 fields for each student.
- Child Aadhaar– They were collected on the voluntarily basis.
- EID – A separate unique Educational ID (EID) for every student created in the UDISE+ portal which covers each and every child across the country.
|
The School Education system in India is one of the largest in the world comprising more than 1.47 million schools, 9.8 million teachers, and over 248 million students from varied socio-economic backgrounds.
UDISE+ Report 2023-2024
- It had the cutoff date as on 31st March 2024.
- It is in alignment with the recommendations of National Education Policy, 2020 (NEP 2020).
- It focuses on individual student for the 1st time at the national level.
- Coverage – It covers all States /UTs except Tamil Nadu and West Bengal as they both directly feed data into UDISE+ portal of DoSE&L.
TamilNadu and West Bengal are the two States that maintains their own Management Information Systems (MIS) and provides bulk data link to UDISE+ portal of DoSE&L.
- Data collection – More than 19.7 crore students provided Aadhaar numbers voluntarily.
- Total enrolment – 24.8 Crore, a drop over by 1 crore from 2018-19.
- It includes a drop in enrolment of both boys and girls students.
- Drop in enrolment - Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra saw among the highest drop in enrolments.
Reference
The Hindu| UDISE+ Report
Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCCs)
Why in News?
According to a recent study by Indian Institute of Management (IIM), the Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC) created safe environment for women across 93 smart cities.
- ICCCs – It is the real-time monitoring systems operationalized in 100 the Smart Cities.
- It works as the brain and nervous system for city operations.
- Launched in – 2015, by Ministry of Housing & Urban Affairs.
- Umbrella Scheme – Smart Cities Mission (SCM).
- Aim – To enable collation of information and collaborative monitoring, thus helping in the analysis of data for quicker decision making.
- Integrated departments – Police, Traffic Police, Health, Water, Solid Waste management, Irrigation department etc. have been integrated with ICCCs.
- 30 out of 100 smart cities have the following in traffic and transportation management
- Adaptive Traffic Control System (ATCS), Integrated Traffic Management System (ITMS), Red Light Violation Detection (RLVD) & Automatic Number Plate Recognition System (AnPR).
- Intelligent operations capability – It shall ensure integrated data visualization, real-time collaboration and deep analytics.
- Significance – It have been successful in improving surveillance, enhancing safety and security of citizens, preventing and resolving crimes etc.
Study Findings
The national level study has focused on smart cities of Chennai (Tamil Nadu), Nagpur (Maharashtra), and Tumakuru (Karnataka) for detailed primary impact assessment.
- 93 smart cities had the installation of over 59,802 CCTV cameras and emergency call boxes in the country.
- Chennai and Tumakuru – Leveraged advanced monitoring systems, integrating safety cameras with ICCCs.
- Nagpur – 14% decline in overall crime rates post-implementation of surveillance measures.
- Women in these 3 cities increased confidence in assessing public spaces.
References
- The Hindu| ICCCs created safe environment in 93 smart cities
- PIB| Integrated Command and Control Centres (ICCCs)
Related News – Smart Cities Mission
ONDC & its Achievements
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister has praised the transformative impact of the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) on India's e-commerce landscape.
|
Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC)
|
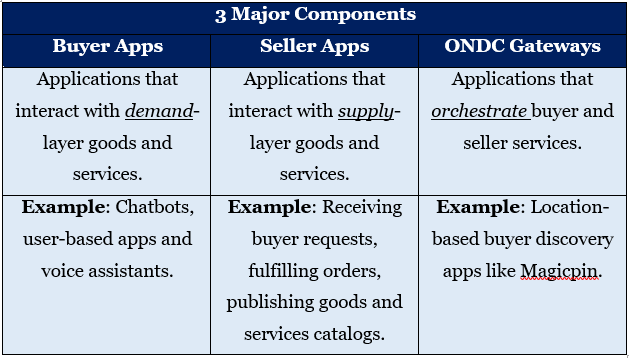
- ONDC – It is an initiative to promote an open e-commerce network that connects shoppers, platforms and retailers.
- Launched in – 2021, by Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Vision – To democratise e-commerce in India
- Aim – To create an inclusive e-commerce environment through an open protocol developed on open-source specifications, making it independent of any one platform.
|
- Drives growth - It has facilitated over 150 million transactions
- Drives inclusivity – Network now boasts more than 200 participants, including sellers, buyers, and service providers.
- Buyers from more than 1,100 cities and towns have engaged with the network.
- Access to wider customer base - 7 lakh sellers and service providers from over 600 cities and towns.
- Empowered farmers - More than 7,000 farmer producer organizations (FPOs), representing 35 lakh farmers, have been onboarded.
- It aligns with ONDC's goal of bridging the gap between rural and urban markets.
- MSME growth – It has placed a strong emphasis on fostering the growth of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) through initiatives like the MSME TEAM scheme.
Reference
The Tribune| ONDC’s Significant Milestones
Related News Article - Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC)
|
One Liners 03-01-2025
|
|
Social Issues
|
|
Mission Suraksha initiative
- It is also called as Mission COVID Suraksha, the IndianCOVID-19 Vaccine Development Mission.
- Part of – 3rd stimulus package, AtmanirbharBharat3. 0.
- Objective – For promoting research and development of Indian COVID-19 vaccines.
|
|
International Relations and Issues
|
|
RCIC scheme
- RCIC - Rural Community Immigration Class.
- Launched by – Canada.
- Aim – To provide a pathway for foreign nationals, including students, to apply for PR if they commit to living and working in designated rural communities.
- Indian students in Canada – They constitute the largest share of international students in Canada, accounting for nearly 40%.
|
|
Economy
|
|
India in Biopharma Sector
- It currently accounts for 60% of global vaccine production.
- It is home to the 2nd largest number of USFDA-approved manufacturing plants outside the United States.
Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
- UPI – A digital payment system that allows users to make payments and transfers using a mobile app.
- Launched in – 2016.
- Developed by - National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- Regulated by - Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Function – It allows users to send and receive money, pay merchants, and make peer-to-peer requests.
- Transaction limit – Rs.1 lakh per transaction and 20 transactions per day, but these limits may vary by bank and app.
- Transaction charges – They are usually free, but some banks may charge for specific services.
UPI Ecosystem in India
- It now accounting for nearly 8 in every 10 digital transactions.
- UPI penetration – It remains at 30% of the population.
- Duopoly - Extreme market concentration of 2 3rd Party App Providers (TPAPs).
- Phone Pe and Google Pay together control over 85% of the total market share.
|
|
Environment
|
|
Smart Compost Monitoring Solution
- It is a prototype for an intelligent IoT system that remotely monitors and manages compost which can be used as fertilizer.
- Developed by – International Institute of Information Technology – Bangalore (IIITB).
- Working – It includes a sensor hub associated with each bin to monitor the compost’s pH, temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels.
- It generates alerts using a mobile phone.
|
|
Science
|
- BIO-E3 Policy
- Bio-E3 – Biotechnology for Economy, Employment, and Environment
- Aim – To shape the country’s economy, employment landscape, and environmental sustainability in the years to come.
- Nafithromycin
- It is India’s 1st Indigenous Antibiotic through public-private collaboration.
- Launched in – 2024.
- Aim – To treat both typical and atypical drug-resistant bacteria.
- Under – Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) Biotech Industry Program.
- Targets - Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia (CABP) caused by drug-resistant bacteria.
- Advantages – 10 times more effective than azithromycin and offers a 3-day treatment regimen.
- Successful Gene Therapy Trial for Haemophilia
- Conducted at – Christian Medical college, Vellore.
- Support of – Department of Biotechnology.
- Haemophilia – A rare inherited blood disorder in which the blood doesn't clot in the typical way because it doesn't have enough blood-clotting proteins (clotting factors).
Nano-formulation of Melatonin for Parkinson's disease
- Melatonin - A neurohormone secreted from the pineal gland, an endocrine gland present in the brain.
- It regulates the sleep-wake cycle and is used to treat insomnia could be a potential inducer of mitophagy to mitigate PD.
- Parkinson's disease (PD) - A neurological disorders caused by the death of dopamine-secreting neurons in the brain due to aggregation of synuclein protein inside it.
|
Related News – Parkinson Disease | Bio-E3 Policy | UPI Lite

