Why in News?
India announced new Ramsar Sites on the World Wetlands Day recently.
World Wetlands Day, 2025
Ramsar Convention
|
Newly Added Ramsar Sites, 2025 |
|
|
Udhwa Lake |
Jharkhand |
|
Theerthangal |
Tamil Nadu |
|
Sakkarakottai |
Tamil Nadu |
|
Khecheopalri |
Sikkim |
The Indian Express | World Wetlands Day
Why in News?
WHO verifies Niger as the 1st country in the African Region to eliminate Onchocerciasis.
Why in News?
Caribbean and North Brazil shelves (Large Marine Ecosystem) are recently brought under the initiative, Ocean Coordination Mechanism (OCM).
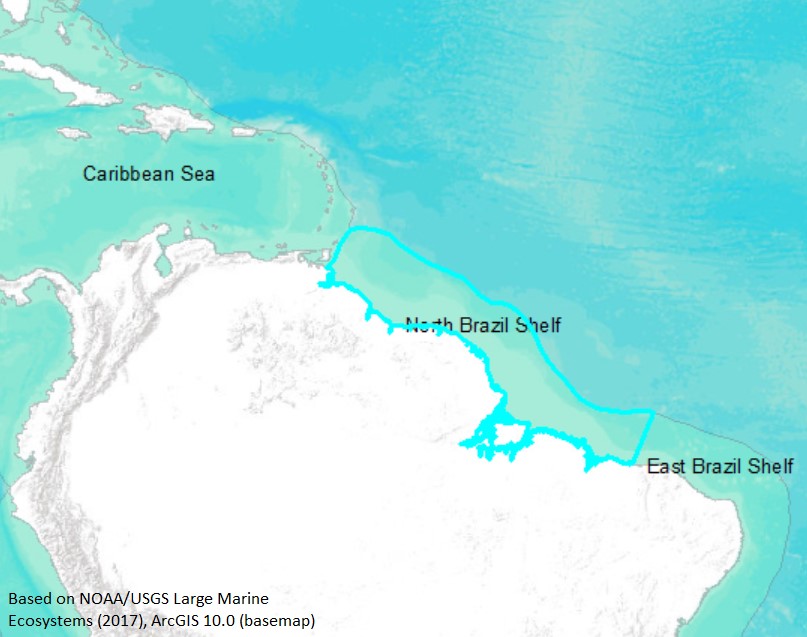
|
Carribean Sea |
North Brazil Shelf |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Down to Earth | Ocean Coordination Mechanism (OCM)
Why in News?
Recently, an article suggested that black kites have nesting habitats at a tower structure in Chennai.

|
One Liners 03-02-2025 |
|
Polity & Governance |
|
Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) PM Jan Arogya Yojana to now provide health cover for gig workers.
Pradhan Mantri Dhan Dhanya Krishi Yojana
Tailings Policy
Bharatiya Bhasha Pustak Scheme
|
|
Environment |
|
Important Ramsar sites in India |
|
Harike wetlands
Kanjli wetlands
Ropar Wetlands
Nangal Wetlands
|
|
Index |
|
State Mining Index (SMI)
|
|
Miscellaneous |
|
World Forum of Accountants (WOFA) 2025
|