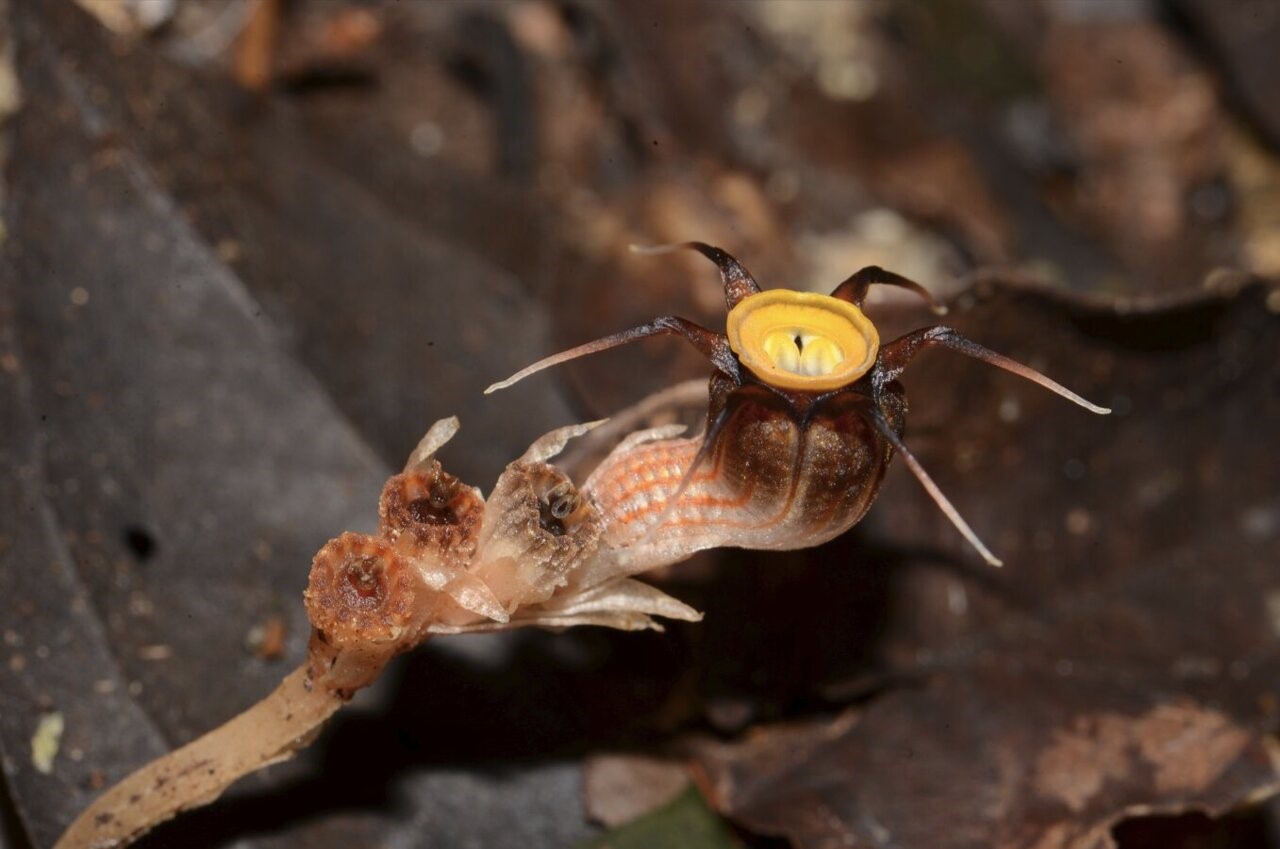
Thismia malayana
Researchers recently discovered that a new plant species, Thismia malayana steals nutrients from underground fungi.
- About – It is a new plant species steals nutrients from underground fungi, typically found hidden in leaf litter and growing near tree roots or old rotten logs.
- Group – Mycoheterotrophs.
Mycoheterotrophs do not perform photosynthesis, instead they act as a parasite, stealing carbon resources from the fungi on their roots.
- Habitat - Discovered in the tropical rainforests of Peninsular Malaysia.
- Nutrition- Carbon resources from the fungi on their roots.
- Interconnectedness- Malayana underscores the complex interconnectedness within ecosystems.
- Adaptation- Symbiotic relationship between colonizing fungi and a plant's roots, typically benefiting both parties.
Symbiotic relationship is an ongoing interaction between organisms of different species. The interaction usually benefits at least one of the organisms and can benefit both.
- Proliferation- It thrives in the low-light conditions of dense forest understories, with its specialized flowers pollinated by fungus gnats and other small insects.
- Conservation status
- IUCN Red List- Vulnerable

Reference
Physics Org | Thismia Malayana
Musankwa sanyatiensis
Recently, Scientists have discovered a new dinosaur species, named Musankwa sanyatiensis from fossils.
- About - It is a newly discovered dinosaur species found from fossils on the shoreline of Lake Kariba in Zimbabwe.
- Genus- Musankwa.
- Group – Sauropodomorpha, a group of bipedal, long-necked dinosaurs that were widespread during the Late Triassic.
Sauropodomorpha is a group of bipedal, long-necked dinosaurs that were widespread during the Late Triassic.
- Dietary habits- Herbivores.
Recent Findings
- Triassic period- The rocks yielding this new specimen date back to the Late Triassic period, approximately 210 million years ago.
- Finding significance - It is the 1st dinosaur to be named from the Mid-Zambezi Basin of northern Zimbabwe in over 50 years and the 4th dinosaur species named from Zimbabwe.
- Evolution representation- Remains of a single hind leg, including its thigh, shin, and ankle bones.
Quick facts
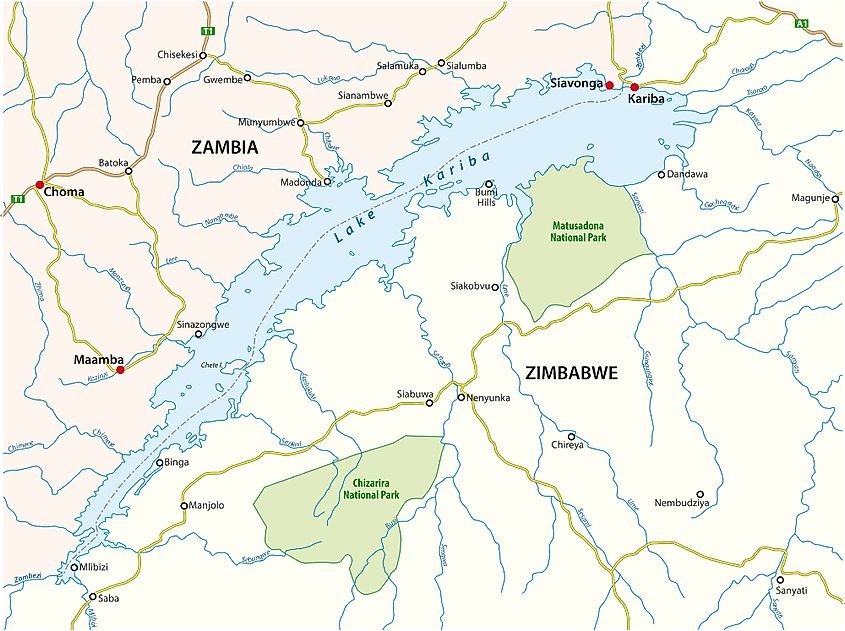
Lake Kariba
- Lake Kariba is located on the Zambezi River in southern Africa, on the border of Zambia and Zimbabwe.
- It is the world's largest artificial lake and reservoir by volume.
- It witnessed the establishment of hydroelectric facilities through the Kariba Dam after 1960.
Reference
The phys | Musankwa sanyatiensis
Boeing starliner
A Boeing Starliner capsule carrying its first-ever astronauts docked with the International Space Station.
Starliner is the 6th US-built spaceship to carry NASA astronauts, following Mercury, Gemini, Apollo, the Space Shuttle, and SpaceX's Crew Dragon.
- Aim – It is a spacecraft that carried astronauts to International Space Station (ISS).
- It is a partially reusable crew capsule, officially known as CST-100 (crew space transportation).
- Launched by- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).
- Rocket- A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
- Modules – It consists of crew module and the service module.
SpaceX launched astronauts into orbit in 2020, becoming the first private business to achieve only in 3 countries — Russia, the U.S. and China.
- Scope for taxi flights- If the mission goes well, NASA will alternate between SpaceX and Boeing for taxi flights, beginning next year.
References
- The Hindu | Boeing Starliner
PraVaHa Software
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has developed Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) software named PraVaHa.
- PraVaHa Software - Parallel RANS Solver for Aerospace Vehicle Aero-thermo-dynamic Analysis.
- About PraVaHa- It is a software tool designed to analyze the aerodynamics and thermodynamics of aerospace vehicles.
- Developed by- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- The software simulates external and internal flows on launch vehicles, winged & nonwinged re-entry vehicles.
- Usage- It has been used extensively in the Gaganyaan program for aerodynamic analysis of human-rated launch vehicles, viz, HLVM3, Crew Escape System (CES), and CM.
- The software is designed to make use of CPU as well as GPU architecture of available and upcoming supercomputing facilities.
- Currently, the PraVaHa code is operational to simulate airflow for Perfect Gas & Real Gas conditions.
- PraVaHa soon will replace most of the CFD simulations for aero characterization, which is currently being carried out using commercial software.
|
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
|
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is the process of mathematically predicting physical fluid flow by solving the governing equations using computational power.
- In a CFD software analysis, fluid flow and its associated physical properties, such as velocity, pressure, viscosity, density, and temperature, are calculated based on defined operating conditions.
- In order to arrive at an accurate, physical solution, these quantities are calculated simultaneously.
- The most common CFD tools are based on the Navier-Stokes (N-S) equations.
|
Reference
The Hindu | PraVaHa software
UNESCO State of Ocean Report 2024
UNESCO’s State of Ocean report released recently on World Oceans Day highlights key knowledge gaps in research & data on spiking oceanic warming.
- Initiated by - The report is initiated by the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC-UNESCO).
- It supports for UN Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development Outcomes.
Recent findings of the report
- Critical issues in ocean climate regulation, emphasizing the need for better understanding and data to address ocean crises and validate new carbon dioxide removal technologies.
- Greenhouse gas emissions- The increased greenhouse gas emissions from human activities have increased the uptake of the Earth's energy imbalance (EEI) by oceans.
EEI is the balance between incoming energy from the Sun and outgoing energy from the Earth.
- Energy and Heat Imbalance- Oceans absorb about 90% of the Earth’s energy imbalance, leading to increased heat content in the upper 2,000 meters.
- This inhibits ocean mixing, causing deoxygenation, which harms marine ecosystems and coastal communities relying on oceans.
- Coastal Blue Carbon Habitats- There's growing interest in restoring coastal blue carbon habitats like mangroves, seagrasses, and tidal marshes to enhance carbon sequestration.
- Marine Carbon Dioxide Removal (mCDR)- A rising interest in marine Carbon Dioxide Removal (mCDR) technologies since 2020, supported by scientific research, start-up initiatives, and substantial funding from the U.S. and EU.
- Ocean Warming trend- From 1960 to 2023, the upper 2,000 meters of oceans warmed at a rate of 32 ± 0.03 W/m², accelerating to 0.66 ± 0.10 W/m² in the past two decades.
- This trend is expected to persist, leading to irreversible changes over centennial to millennial timescales.
- Ocean Acidification- Coastal waters can turn acidic due to natural processes, such as freshwater influx, biological activity, temperature change and climate patterns like El Nino/Southern Oscillation (ENSO).
- Human activities like nutrient input from agricultural and industrial activities also influence the chemistry of coastal areas.
- Sea Level Rise - From 1993 to 2023, the global mean sea level rose at a rate of 4 ± 0.3 mm/year.
- Data and Research- The report highlights a pressing need for comprehensive and regular data to monitor ocean warming and its impacts, essential for maintaining healthy and resilient oceans.
References
Down to Earth| UNESCO’s State of Ocean report

