Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF)
India participates in the IPEF Ministerial meeting in Singapore in 2024.
- Launched in – 2022 at Tokyo, Japan,
- Aim – To advance resilience, sustainability, inclusiveness, economic growth, fairness, and competitiveness for the member economies.
- It will provide tangible benefits that fuel economic activity and investment, promote sustainable and inclusive economic growth, and benefit workers and consumers across the region.
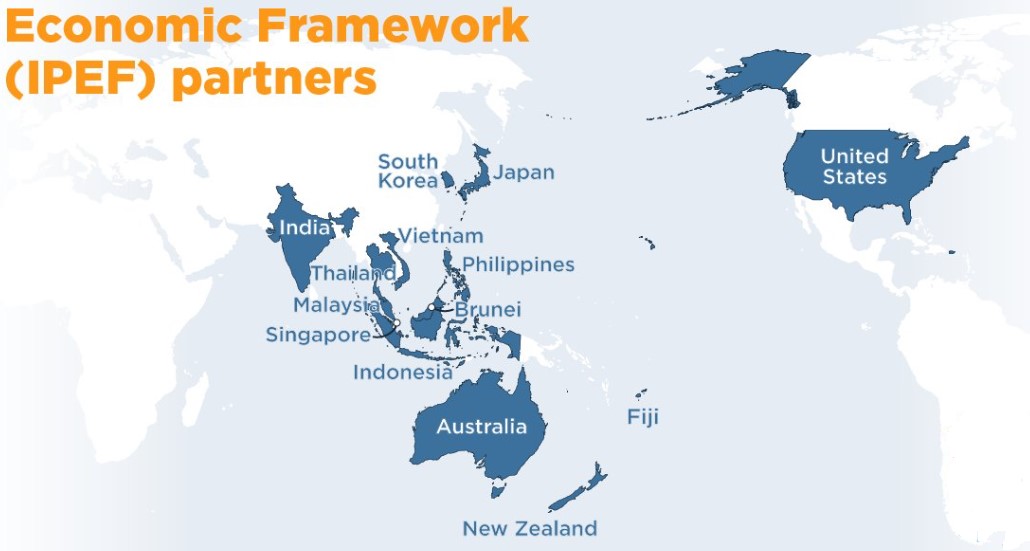
- Member – 14 countries including Australia, Brunei, Fiji, India, Indonesia, Japan, Republic of Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, USA and Vietnam (Taiwan is not part of it).
- 4 Pillars
- Pillar I - Trade
- Pillar II - Supply Chain Resilience
- Pillar III - Clean Economy
- Pillar IV - Fair Economy
- India – It had joined Pillars II to IV, while it has maintained an observer status in Pillar-I.
- IPEF Catalytic Capital Fund – The founding supporters were Australia, Japan, Korea, and the United States.
- 2024 Ministerial Statement – It declared substantial conclusion of negotiations for Clean Economy, Fair Economy, and the overarching Agreement on the IPEF for Prosperity.
- Pursuant to this, the IPEF partners completed legal review of the text for these agreements and domestic approval processes.
- These agreements will enter into force after at least 5 IPEF partners complete their internal legal procedures for ratification, acceptance or approval.
- India did not formally sign these agreements as domestic approval processes are still underway.
- Significance – The bloc represents 40% of global GDP and 28% of global goods and services trade.
- The agreements planned under IPEF are 1st-of-their-kind approaches to address 21st century challenges.
References
- PIB| India participates in IPEF Ministerial meeting in Singapore
- USTR| Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF)
Standard Missile 6 (SM-6)
The US Navy's F/A-18 Super Hornet was recently spotted carrying an air-launched version of the SM-6 (RIM-174) missile.
|
Features
|
|
Developed by
|
Raytheon, a United States company.
|
|
Basing
|
Ship-launched
|
|
Class
|
Surface-to-air and surface-to-surface missile
|
|
Range
|
370 km
|
|
In service
|
2013-Present
|
- The Standard Missile-6 (SM-6) is also known as RIM-174.
- Capability - The SM-6 is the first missile of its kind, with anti-air, anti-surface and sea-based terminal defence capabilities, which enable it to intercept ballistic and cruise missiles.
- Technology - It is an extended range active missile (ERAM) that uses the sophisticated signal processing and guidance technologies of the AMRAAM (Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missile).
- Guidance - The interceptor uses semi-active homing and active homing guidance to achieve accurate engagement of the assigned targets.
Reference
- Naval News | Standard Missile-6
- Standard Missile-6 (SM-6)
Onge tribes
Andaman's Onge tribe king Totoko and Queen Priya welcomed a baby boy.
- About- Onges are one of the oldest tribes in Little Andaman Island.
- Racial ancestry- Negrito.
- Occupation- The Onge tribe is traditionally semi-nomadic and reliant on hunting and gathering.
- Habitat- Until 1940s, the Onge were the sole permanent inhabitants of Goubalambabey (the Onge name for Little Andaman).
- At present, they were confined to the Dugong Creek and South Bay of Little Andaman Island.
- Appearance - Due to their dark appearances, Onge's are regarded as among the darkest people.
- Religion - They do not believe in or follow firm worshipping practices or sacrifices.
- Ornamentation -On special occasions, they place a greater emphasis on body ornamentation.
- Belief – They considered that white teeth is a symbol of death, so they continue to chew the bark to impart a red colour to their teeth.
- Prolific nature - The Onge tribe is also one of the world's least prolific and infertile communities.
- Infertility affects somewhat more than 40% of married couples.
Other tribes in Andaman were Jarawa, Shompen, Great Andamanese, and Sentinelese.
Reference
The Indian Express | Onge Tribe
Antlions
Recently, researchers have discovered two species of antlions namely Pseudoformicaleo nubecula, Creoleon cinnamomeus, for the first time.
|
Antlions
|
- Family- Myrmeleontidae
- Order- Neuroptera
- Antlions are commonly known for their pit-building (funnel-shaped) habit to trap their prey.
- Distribution- Antlions are found throughout the world, primarily in dry, sandy regions.
- Distinction - Antlions can be easily distinguished by their long distinct antennae.
|
- Unique Larvae Behavior - The larvae of Pseudoformicaleo and Creoleon species don't construct pits.
- Instead, they inhabit loose soils underground, sheltered from direct sunlight, wind, and rain.
Pseudoformicaleo nubecula
- It is recently found in Kerala, India and in Chiang Dao, Thailand.
- It has been reported in other countries such as Australia, China, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Sri Lanka and Vietnam.
Creoleon cinnamomeus
- It is recently found in Kerala, India and in Phu Quoc island, Vietnam.
- Creoleon cinnamomeus has been reported only from China, Sri Lanka, and Vietnam.
Reference
The Hindu | Antlions
World Wealth Report, 2024
According to the latest report reveals that in 2023, the number of high-net-worth individuals (HNWIs) and their wealth hit record levels.
- Published by- Capgemini Research Institute.
Report Highlights
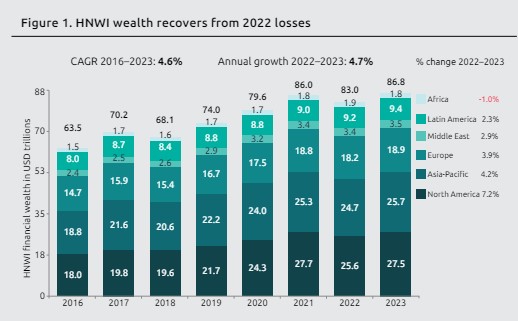
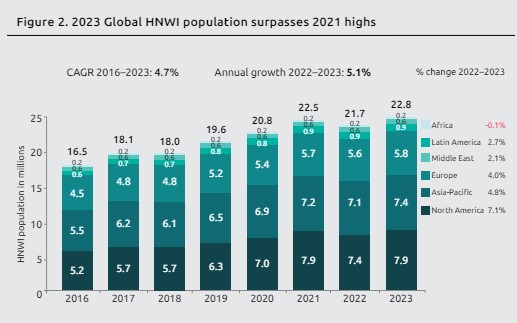
- Wealth expansion - The report noted that global HNWI wealth expanded by 4.7% in 2023 reaching $86.8 trillion.
HNWIs are high-net-worth individuals with investable assets of USD1 million or more, excluding their primary residence, collectables, consumables, and consumer durables.
- HNWI population- Increased by 5.1% to 22.8 million.
- The HNWI continues to grow globally despite market unpredictability.
Global Findings
- Wealth recovery - North America posted the most robust recovery, expanding by 7.2% in HNWI wealth and 7.1% in HNWI population.
- Asia-Pacific – It experienced 4.2% HNWI growth and 4.8% rise in HNWI population.
- Among the Asia–Pacific (APAC) region India and Australia, recorded HNWI wealth growth of 12.4% and 7.9%.
Findings in India
- HNWI in India- The number of high net-worth individuals (HNWI) in India increased by 12.2% in 2023 vs 2022.
The total number of HNWI population in India is 3.589 million.
- Market capitalisation- India’s country’s market capitalisation increased by 29.0% in 2023, after an increase of 6% in 2022.
- National savings- National savings as a percentage of GDP increased to 33.4% in 2023, up from 29.9% in 2022.
- Unemployment rate- India's unemployment rate decreased to 3.1% in 2023, down from 7% in 2022, despite the economy growing 7.3% in 2023, higher than the increase of 7% in 2022.
Reference
The Hindu | World Wealth Report 2024


