BIMSTEC
Recently, India hosted the 2nd Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) foreign ministers' meeting in Delhi.
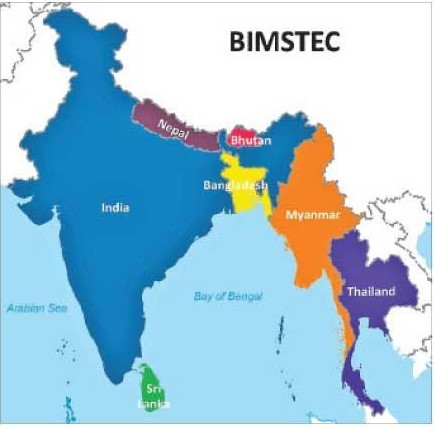
- BIMSTEC - It is a regional organization, established in 1997 with the signing of the Bangkok Declaration.
- It is initially known as BIST-EC (Bangladesh-India-Sri Lanka-Thailand Economic Cooperation), now known as BIMSTEC.
- Headquarters - Dhaka, Bangladesh.
- Members -It comprises 7 Member States from South and Southeast Asia lying in the littoral and adjacent areas of the Bay of Bengal.
- 7 members
- South Asia - India, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal and Bhutan.
- Southeast Asia – Myanmar and Thailand.
- Objectives
- Promote mutual assistance in economic, social, technical, and scientific fields.
- Provide training and research facilities in education and technical spheres.
- Collaborate to combat terrorism, organized crimes, and address disasters and diseases.
- Maintain cooperation with similar international and regional organizations.
- Strive to eradicate poverty in the region.
- Promote trade and investment to foster regional development.
- BIMSTEC Centres
- BIMSTEC Energy Centre
- BIMSTEC Centre on Weather and Climate
BIMSTEC houses 1.73 billion people and having a combined gross domestic product of US$5.2 trillion (2023).
References
1. The Hindu | BIMSTEC Foreign Ministers
2. BIMSTEC | About BIMSTEC
Vaccine for Shigella
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has recently found an Indian partner to manufacture the breakthrough vaccine for the Shigella infection.
- Shigella - It is an intestinal infection caused by bacterium that belongs to the enterobacter family.
- Four species of Shigella
- Shigella sonnei
- Shigella flexneri
- Shigella boydii
- Shigella dysenteriae
- The main sign of shigella infection is diarrhea, which often is bloody.
- Symptoms - Diarrhea (often containing blood or mucus), Stomach pain or cramps, Fever, Nausea or vomiting.
- Some people have no symptoms after they've been infected with shigella but their feces may still be contagious up to a few weeks.
- Transmission - Shigella is very contagious.
- People get infected with shigella when they come in contact with and swallow small amounts of bacteria from the stool of a person who is infected with shigella.
- Eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
- It can also be spread during sexual activity with a sick person.
- Vulnerable Age - Children under age 5 are most likely to get shigella infection, but it can occur at any age.
Shigellosis affects about 188 million cases per year that result in about 1 million deaths per year around the world.
- Prevention - Washing your hands frequently with soap and water is key to preventing the spread of this infection.
- Vaccine - There is no vaccine or cure yet.
References
1. The Print | Shigella
2. Mayo Clinic | Shigella infection
Mineral nano particles
Recently, IIT-Madras team makes mineral nanoparticles with water.
- Background - Water droplets are ubiquitous in our environment which exist in various sizes from large raindrops to minute aerosol particles.
- Among these, microdroplets, which are a thousandth the size of typical raindrops, display unique properties and behaviors.
- Surface Molecules vs. Bulk Molecules - In bulk water, surface molecules participate in chemical reactions more readily than those inside.
- Microdroplets, due to their confined space and close-packed molecules, engage in chemical reactions more eagerly and up to a million times faster than bulk water.
- Electrically Charged Microdroplets - Microdroplets at the beach can carry ions from seawater, settling on skin.
- As larger droplets evaporate and shrink, remaining water molecules bond closer, potentially leading to the formation of negatively charged hydroxyl ions (OH-) and free protons (H+).
- Research Findings on Microdroplets - The team conducted an experiment using quartz, ruby, and fused alumina crystals.
- Applying a high voltage to mineral microparticles in water, they observed the particles breaking into nanoparticles within milliseconds.
- Free protons might infiltrate crystal layers and break them apart.
- Surface tension and electric fields could contribute to creating shockwaves that fragment the microdroplets.
- Implications of the Study
- Origins of Life - The study's findings could aid research on proto-cells, potential precursors to modern cells, providing insights into the origins of life.
- Agricultural Applications - Silica nanoparticles, essential for plant growth, can be supplied to soil, improving agricultural productivity.
- This method could transform unproductive soils and desertified areas into fertile lands.
|
Nanoparticles
|
- Nanoparticles - They are tiny particles that measure between 1 and 100 nanometers in size.
- A nanometer is one-billionth of a meter, making nanoparticles incredibly small, often comparable in size to atoms and molecules.
- Property - Due to their small size, nanoparticles have a large surface area relative to their volume.
- This enhances their chemical reactivity and physical properties.
- Applications - Medicine, Electronics, Energy, Environmental, Materials Science.
|
Reference
- The Hindu | Mineral nano particles
Uropeltis caudomaculata
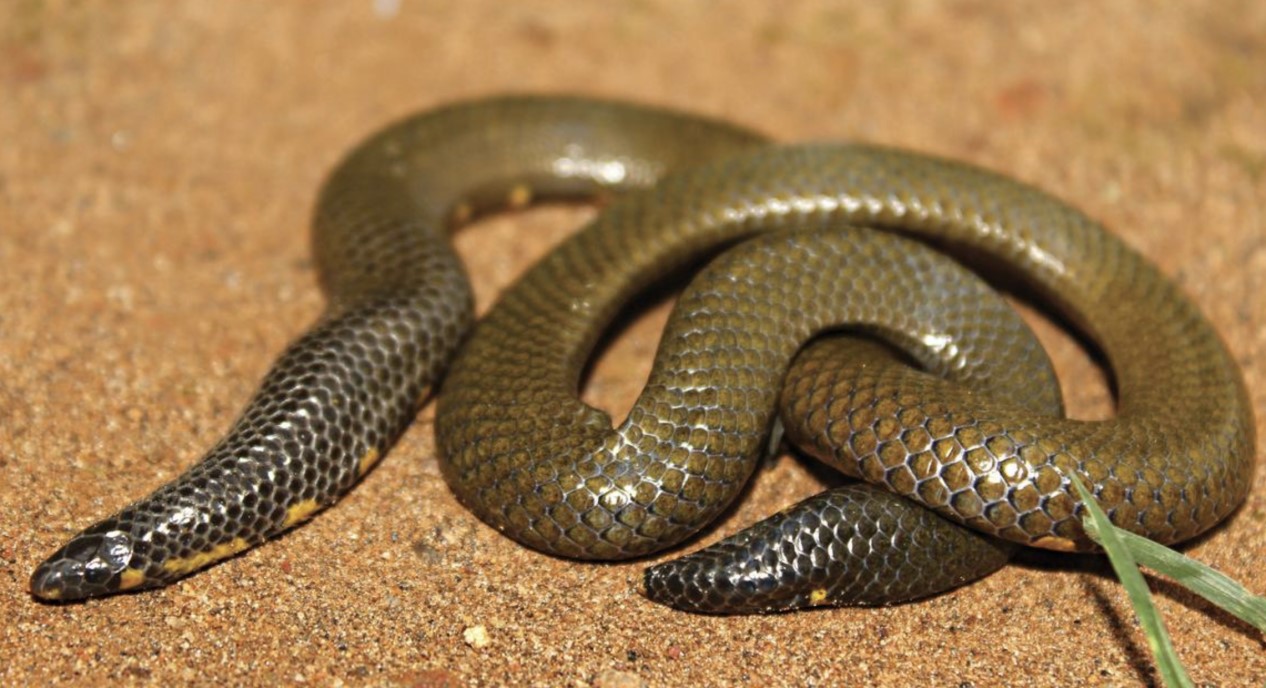
A team of researchers have recently discovered a new species of shieldtail snake in the Meghamalai-Munnar hill region of the Western Ghats.
- Shieldtail snakes - These are a non-venomous, small, and fascinating group of burrowing snakes with over 50 species identified from the Western Ghats.
- Shield-tail snakes belong to the Uropeltidae family, endemic to peninsular India and Sri Lanka.
- They have a large keratinous shield at the tip of the tail and hence called shield tailed snakes.
- Habitat – Inhabit Hilly forests, occupy tunnels in the leaves, humus, rocks & logs.
Uropeltis caudomaculata
- It is a shieldtail snake recently found in Western Ghats have similarities with its closest known relative, Uropeltis pulneyensis.
- The name, Uropeltis caudomaculata, refers to the lateral yellow spot on each side of the base of the tail.

- Endemic - Uropeltis caudomaculata is known to be found in only 3 localities
- Meghamalai Tiger Reserve in Tamil Nadu
- Periyar Tiger Reserve
- Yellapetty, Munnar in Kerala.
- Breeding - These snakes spend most of their life underground and emerge during the monsoons for breeding.
- Diet - They feed on earthworms and other small snakes.
|
Quick facts
|
- Sky island habitats - These are separated from each other physically and environmentally but have similar communities of species distinct from those elsewhere in the Western Ghats.
- In the Western Ghats, the shola grassland forests of the Agasthyamalai region, Meghamalai, Anamalais, Nilgiris, and Wayanad are some of the important sky islands with rich and unique biodiversity.
- The fragile sky islands are highly threatened by the rapid encroachment of highly invasive species such as acacia, lantana, wattle, and pine trees.
- Reptiles - The Western Ghats is one of the most diverse regions for reptiles in India, with more than 50% endemic species.
- 15 new species of snakes have been described from the Western Ghats in the past 5 years.
|
Reference
The Hindu | shield-tail snake
Makhana Cultivation
Makhana have become a popular 'super snack', with prices rising sharply in both domestic and international markets since 2019.
- About - Foxnuts or Makhana is an aquatic crop traditionally grown in India.
- Botanical Name- Euryale ferox.
- Common Names- Fox nut, Gorgon nut, Phool Makhana.
- Production- Makhana, is mainly cultivated in the states of Bihar, West Bengal and Assam.
Bihar is the leading producer of makhana accounting for more than 90% of the total production of India. India contributes to 80% of the world’s demand.
- Climate- Makhana is an aquatic crop and requires a warm, humid climate. It is typically cultivated in areas with temperatures ranging from 20°C to 35°C.
- Soil- It thrives in loamy and clayey soils with good water retention capacity. The pH of the soil should be between 5.5 to 7.5.
- Nursery Preparation- Seeds are collected from mature Makhana fruits.
- Seeds are soaked in water for 24-48 hours before sowing.
- Seeds are sown in nursery beds or trays filled with a mixture of soil and cow dung.
- Main Field Preparation- Select low-lying areas or water bodies like ponds, lakes, or wetlands.
- Transplanting- Seedlings are transplanted into the main field after 30-40 days when they are about 15-20 cm tall.
- Fertilization- Organic fertilizers like cow dung can be applied. Chemical fertilizers are generally avoided.
- Harvesting- Makhana plants take about 4-5 months to mature.
- The seeds are harvested when the fruits start to crack and the seeds float on the water surface.
- Nutritional value- The crop is a good source of vegetarian protein, at 10%, and contains five of the nine amino acids.
- There are also quercetin and kaempferol flavonoids, both of which protect against diabetes and obesity.
- It is considered a 'super snack' because they are low in calories, rich in protein, and contain essential nutrients.
- Makhana Development Scheme- The Bihar government runs the Makhana Development Scheme that gives a 75% subsidy on the Suvarna Vaidehi variety of seeds, calculated at ₹97,000 per hectare.
- Makhana is approved under the Union government's One District One Product scheme, which provides subsidies to food processors for branding, marketing, and infrastructure development.
Reference
- The Hindu | Makhana
- Niftem | Foxnut

