Harvest festivals of India
Why in News?
Harvest festivals are being celebrated across India.
|
Harvest Festivals Name |
States in which it is Celebrated |
Day |
Significance |
|
Lohri |
Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Himachal Pradesh and Jammu and Kashmir. |
13th January |
|
|
Makar Sankranti |
Maharashtra, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Himachal, West Bengal, Punjab. |
Usually on 14th of January |
|
|
Pongal |
Tamil Nadu |
January 14 ( First day of Tamil month “Thai” |
|
|
Magh Bihu |
Assam |
January |
|
|
Onam |
Kerala |
Malayalam month of Chingam (August-September) |
|
|
Baisakhi |
Punjab, parts of Haryana & Delhi |
13th or 14th of April every year. |
|
|
Nuakhai |
Odisha |
Panchami Tithi of the lunar month of Bhadraba (August-September). |
|
|
Vaisakha |
Bihar |
Sixth day of the Hindu month of Kartik (October-November) |
|
|
Hemis |
Ladakh |
June-July every year |
|
|
Dree |
Arunachal Pradesh |
July 5th in the Ziro area of Arunachal Pradesh |
|
|
Hornbill |
Nagaland |
First week of December. |
|
|
Nabanna |
West Bengal |
On the day of Vishwakarma Puja in the Hindu month of Bhadra (August-September) |
|
Reference
PIB | LOHRI, MAKAR SANKRANTI, PONGAL AND MAGH BIHU
The sada
Why in News?
The land-use patterns sada region are changing and they are increasingly being converted to orchards or residential areas.

Reference
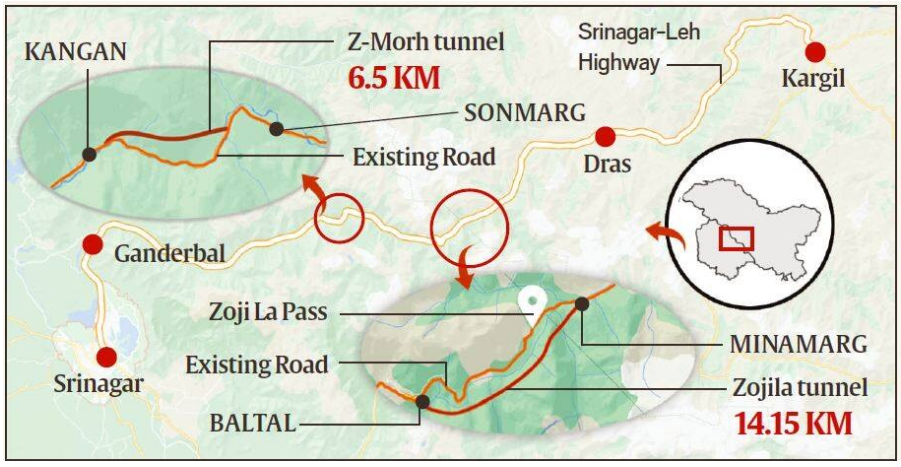
Sonamarg tunnel
Why in news?
Recently Sonamarg tunnel has been inaugurated by the Prime Minister.
Reference
Nag Mk 2
Field Evaluation Trials of Nag Mk 2 Anti-Tank Missile, were successfully conducted recently.
Nag Mk 2 – It is an indigenously-developed third-generation Anti-Tank Fire-and-Forget Guided Missile.
Characteristics – It is an all-weather, fire-and-forget, lock-on after launch, anti-tank guided missile (ATGM).
Range - While the exact range remains classified, the Nag Mk-2 is estimated to have a range of seven to 10 kilometres.
Its predecessor the Nag Mark 1, which had a 4-kilometre range.
HEAT warhead - The missile also boasts a tandem high-explosive anti tank (HEAT) warhead for increased destructive power .
It also has top-attack capability to strike the most vulnerable part of armoured targets.
Launch vehicle - Nag Mk-2 missile is launched from the NAMICA, an armoured vehicle based on the Indian-made BMP-2 Sarath.
Sarath – It is based off a Russian-origin BMP-II based system with amphibious capability.
NAMICA – It provides a robust and mobile platform for the Nag missile system, allowing it to be deployed quickly and effectively across various terrains.
Effectiveness – It is effective against modern armoured vehicles, including those equipped with Explosive Reactor Armour.
Reference