7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Digital Map of Moon
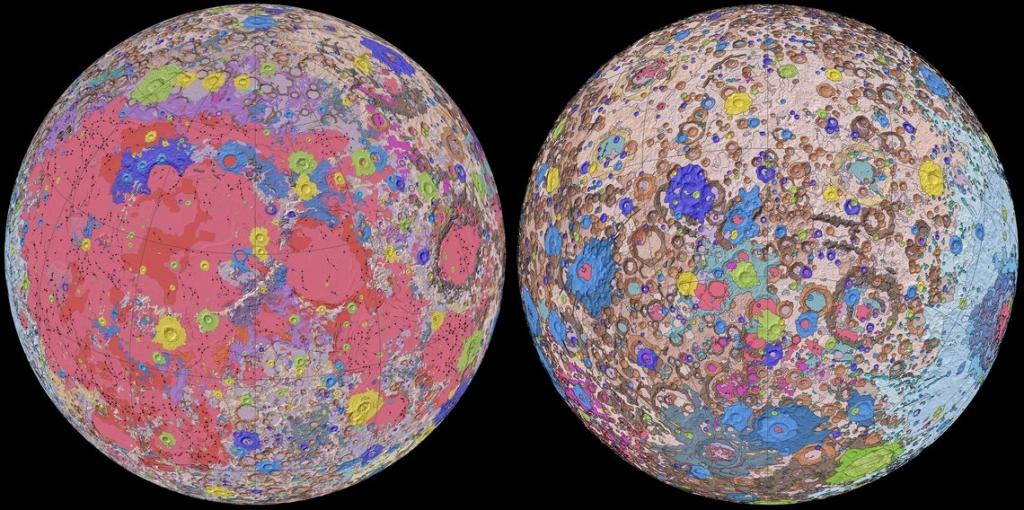
Lunar South Pole
Banking under Public Utility Service
Indian Banks’ Association (IBA)
SIPRI Report
Basava Jayanti
Patachitra Painting
Source: The Hindu, Hindustan Times, Down to Earth