European Council
Prime Minister congratulates H.E Antonio Costa on being elected as President of the European Council recently.
- The European Council is the European Union (EU) institution that defines the general political direction and priorities of the European Union.
- It represents the highest level of political cooperation between EU countries.
- Treaty of Maastricht - Under the Treaty of Maastricht, the European Council acquired a formal status and role to provide the impetus and general political guidelines for the EU.
- Founded in – 1974.
- Headquarters - Brussels, Belgium.
- Members - Heads of state or government of the 27 EU member states, the European Council President and the President of the European Commission.
- Functions
- It decides on the EU's overall direction and political priorities but does not pass laws.
- It deals with complex or sensitive issues that cannot be resolved at lower levels of intergovernmental cooperation.
- It sets the EU's common foreign & security policy, taking into account EU strategic interests and defense implications.
- It nominates and appoints candidates to certain high profile EU level roles, such as the European Central Bank (ECB) and the Commission.
- Sessions - The Council meets 4 times per year at least. It usually adopts 'conclusions' at its formal meetings. Conclusions set out the EU's position on key policy matters.
- The European Council mostly takes its decisions by consensus. This means that no member opposes the decision.
- However, in certain specific cases outlined in the EU treaties, it decides by taking a vote.
References
- Press Information Bureau | President of European Council
- Consilium Europa | European Council
Bhuvan Panchayat portal & National Database for Emergency Management
Union Minister launches 2 Geoportals, “Bhuvan Panchayat (4.0)” portal and “National Database for Emergency Management (NDEM 5.0)” recently.
Bhuvan Panchayat Portal (Space based Information Support for Decentralised Planning at Panchyayat level (SIS-DP))
- It is a national initiative of preparing basic spatial layers useful in planning process at grass root levels.
- Formulated by – National Remote Sensing Centre, ISRO.
- Implemented by - In partnership with State Remote Sensing Application Centers in the country.
- Aim - Empowering Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) and the Stakeholders with Space-based Information Support for Decentralized Planning and Governance.
- The project's main deliverables include
- Satellite images - 2.5 m resolution satellite images of the entire country.
- Thematic maps - 1:10K scale thematic maps on natural resources and infrastructure, such as land cover and settlements.
- Resource inventories - Inventories of resources like water sources, road networks, drainage, and rail networks.
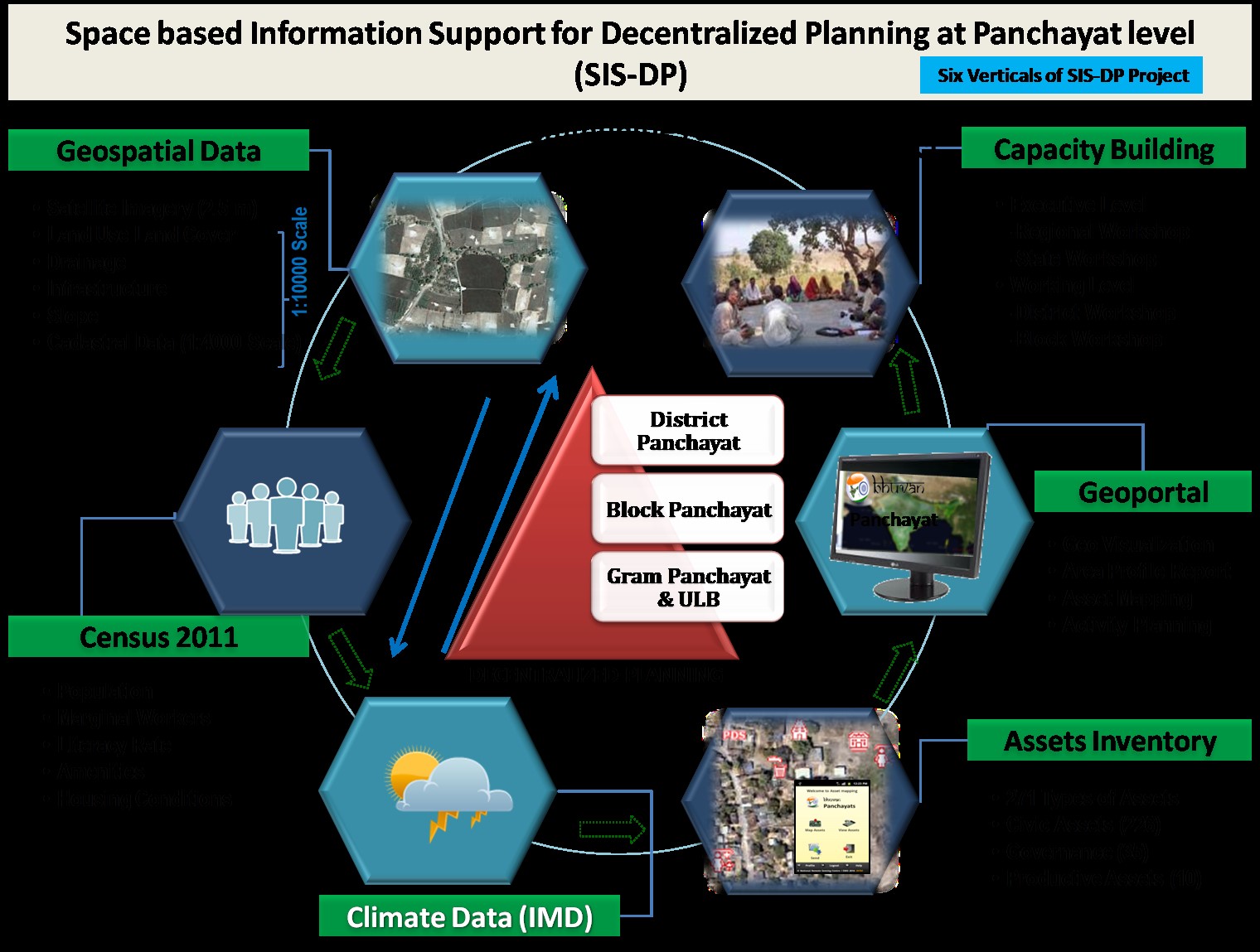
- These deliverables are useful for planning, development, implementation, and monitoring activities at the Panchayat or Village level.
- The project also integrates data from stakeholder departments into the spatial layer in a GIS environment.
National Database for Emergency Management
- It is to provide space-based inputs on natural disasters and aid in disaster risk reduction In India as well as neighboring countries.
- Developed by - National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC), ISRO.
- Ministry - Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- NDEM acts as a geo-portal with the amalgamation of DSS tools and services of disaster forecasting organisations with value addition.
- NDEM will also act as a Disaster Recovery and Data Provider node for the Integrated Control Room for Emergency Response (ICR-ER) being established by MHA, New Delhi.
Reference
Press Information Bureau | Bhuvan Panchayat portal and NDEM
Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence
China is celebrating the 70th anniversary of the Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence, first propounded in the Sino-Indian Agreement of 1954.
- China calls the Five Principles is known in India as Panchsheel agreement.
- The word Panchsheel traces its origin to the Buddhist concept of Pancasila.
- 5 moral vows of Buddhism - Abstinence from murder, theft, sexual misconduct, lying, and intoxicants.
Panchsheel - The Five Principles
- The Panchsheel Agreement, formally known as The Agreement on Trade and Intercourse with Tibet Region is signed between India and China.
- Signed on - April 29, 1954.
- 5 principles
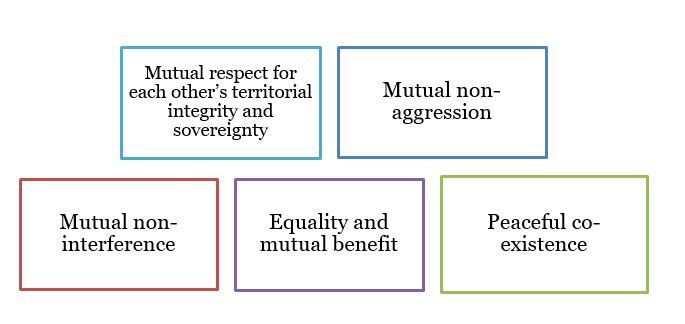
- The agreement aimed to enhance trade and cooperation between the 2 countries, establishing each country’s trade centres in major cities of the other, and laid out a framework for trade.
- The agreement also listed important religious pilgrimages, provisions for pilgrims, and acceptable routes and passes available to them.
- Importantly, India for the 1st time recognized Tibet as the Tibet Region of China.
- Badung Conference - In 1955, the Five Principles would feature prominently at the first African-Asian Conference in Bandung, Indonesia.
- 29 countries of Asia and Africa took part in the Bandung Conference and signed a 10-point declaration that co-opted the Five Principles or Panchsheel.
- The Bandung Conference is the precursor to the Non-Aligned Movement.
The Non-Aligned Movement is a forum of 120 countries that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc.
Reference
The Indian Express | China’s Five Principles of foreign policy
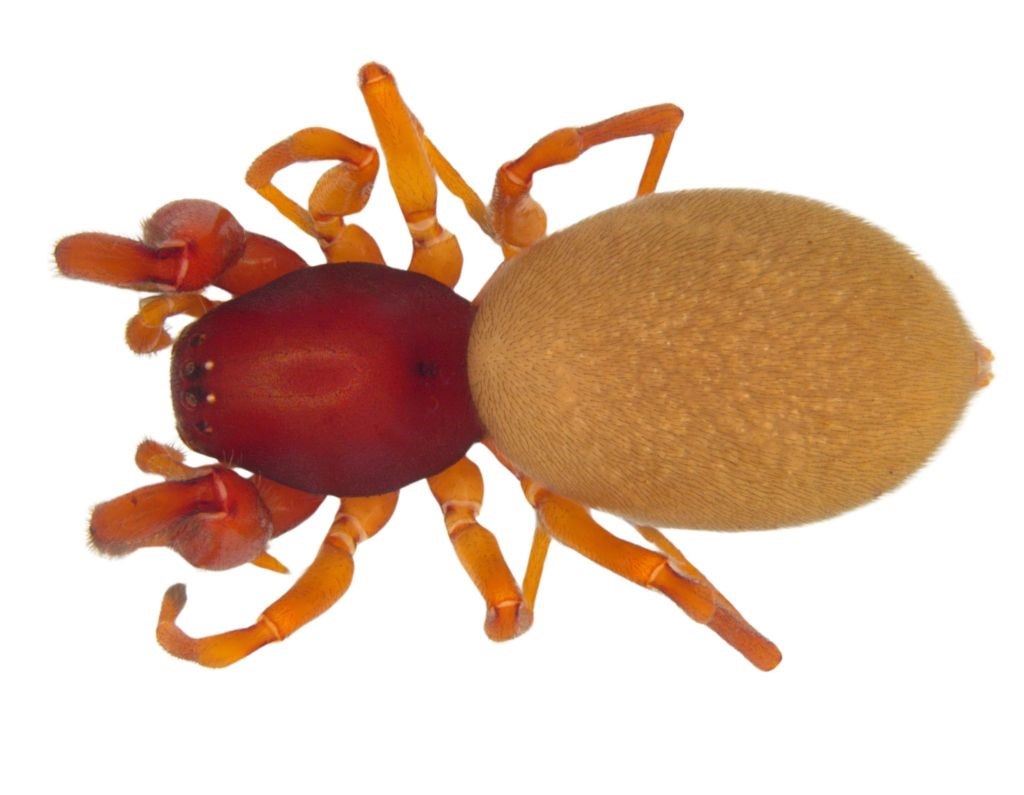
Steriphopus wangala
A newly discovered Spider named after Wangala festival of Meghalaya recently.
- The new spider species discovered recently in West Garo Hills district of Meghalaya.
- Family - Palp-Footed Spider.
- Palp-footed spiders, also known as Palpimanidae, are a family of ground-dwelling spiders with large front legs and distinctive features useful for field identification.
- Genus – Steriphopus
- This discovery added the total number of species in this genus to 5 globally, with 2 found in India.

|
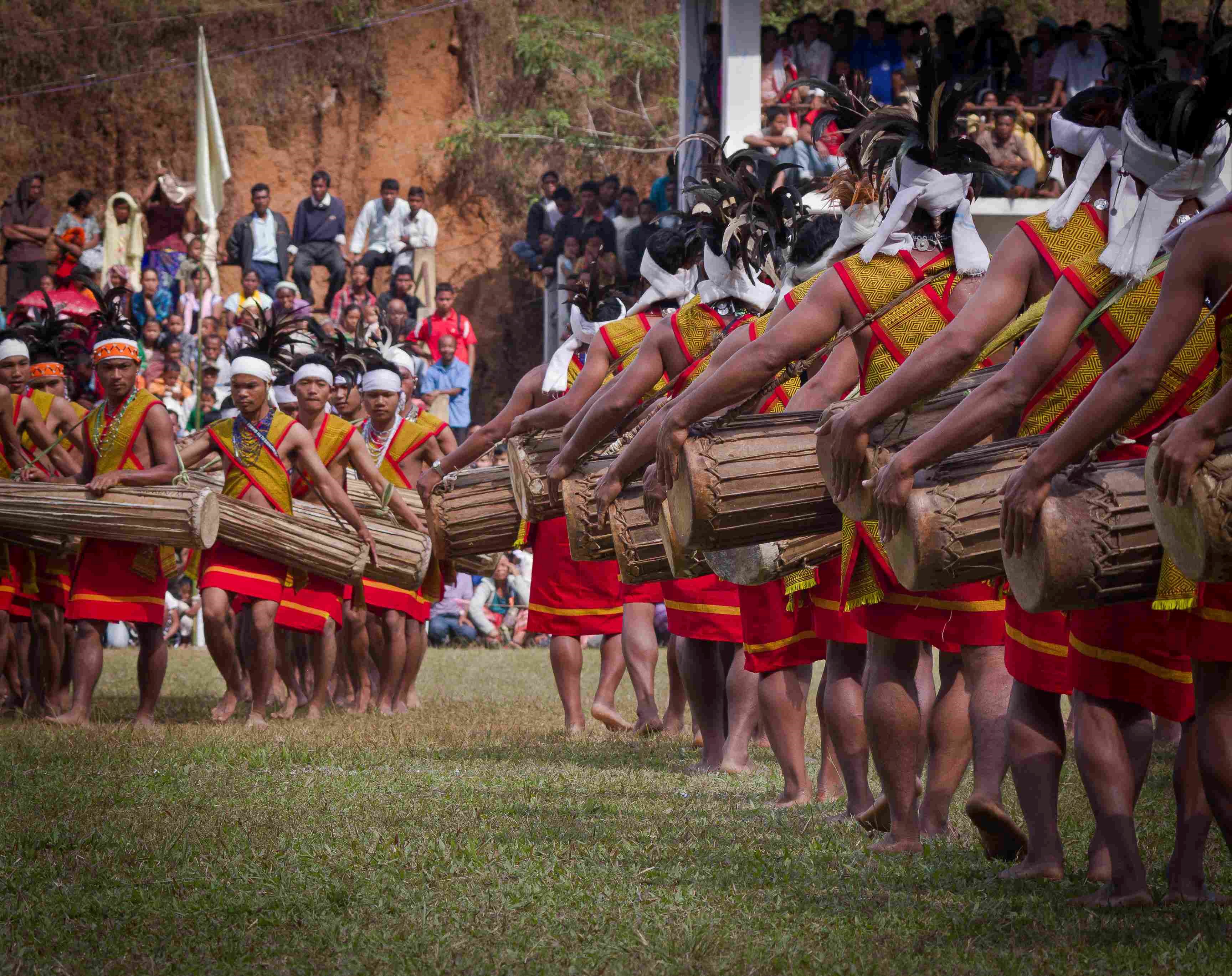
Wangala Festival
|
- Wangala, also known as the "Festival of the Hundred Drums", is a harvest festival celebrated in India and Bangladesh.
- The Wangala Festival marks the end of the agricultural season.
- It is celebrated by the Garo tribe that honors Saljong, the Sun-God of fertility.
- The highlight of Wangala is the rhythmic beat of a hundred drums. The main soundtrack is provided by the Nagra drum.
- These drums are a big part of Garo culture, and they are traditionally made out of tree trunks.
- The Wangala dance is the centrepiece of the festival. The dance is characterised by dancers moving to the rhythmic drumming.

|
References
- East Mojo | Steriphopus wangala
- Meghalaya Government | Wangala Festival
Motor Neuron Diseases (MNDs)
The 3rd annual conference on MND 'Awareness, Care and Management’ at Nimhans held recently in Bengaluru, stated that symptomatic and supportive treatments help manage the condition better.
- MNDs are a group of progressive neurological diseases that destroy motor neurons, cells controlling skeletal muscular activities like walking, breathing, speaking and swallowing.
- In MND, these neurons degenerate and die. This causes the muscles to become weaker and weaker. This eventually leads to paralysis.
- The MND disease group includes:
- Lou Gehrig's disease, also known as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Progressive muscular atrophy (PMA)
- Progressive bulbar palsy (PBP)
- Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS)
- Kennedy's disease, also known as spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA)
- Affecting age - MND is an uncommon disease. The average age that people are diagnosed with MND is 58 years.
- Symptoms - Usually start on one side of the body before spreading that include
- Weakness in their hands and grip,
- Slurred speech
- Weakness in their legs, and a tendency to trip
- Weakness of their shoulder, making lifting difficult
- Cramps and muscles twitching
- Treatment - There's no cure for motor neurone disease, but treatment can help reduce the impact the symptoms have on your life.
Reference
Deccan Herald | Motor Neuron Disease

