7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Why in News?
A new study, published in Science Advances, shows that bacteria can not only make their way to the brain, they can thrive there.
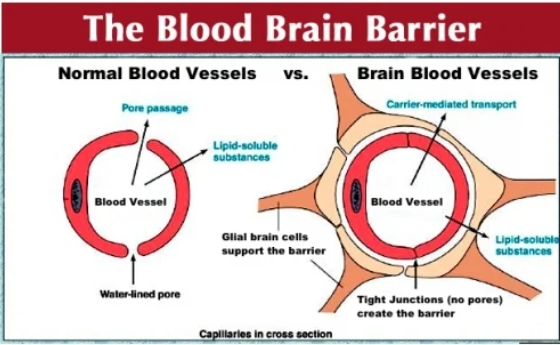
Blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a tightly locked layer of cells that defend the brain from harmful substances, germs and other things that could cause damage.
Reference