7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
PM Gati Shakti program celebrated third anniversary of the launch of the initiative.
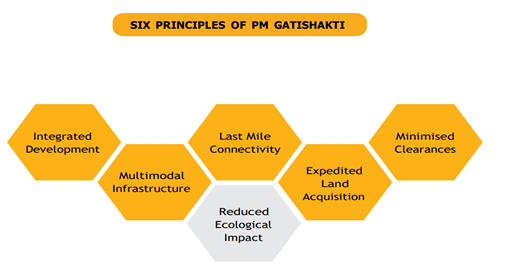

Gati Shakti Sanchar portal is a Centralised Right of Way (RoW) Portal that enables applicants such as Telecom Service Providers/Infrastructure Providers / Internet Service Providers (TSP/IP/ISPs) to apply for RoW approvals.