Fish Mint
Fish mint, an herb which has a fish-like taste and smell has recognised health benefits.
- Scientific name – Houttuynia cordata
- Morphology – It has white flowers and broad, heart-shaped leaves.
- It has a fish-like taste and smell and hence the name.
- Native – Believed to be from Southeast Asia.
- Literary sources – Documented in ancient texts of traditional Chinese and Japanese medicine, as well as Ayurveda and Siddha.
- Growing conditions – It grows on moist soils and resistant to flooding.
|
Different names
|
States
|
|
Ja mardoh
|
Meghalaya
|
|
Tokning-khok
|
Manipur
|
|
Masunduri
|
Assam
|
- Medicinal purpose – The Chinese herb is used to treat asthma due to its anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory properties.
- It is used to alleviate symptoms of jaundice, pneumonia or simple stomach infections.
- In Japan, as an herbal tea it prevents periodontal disease and other infectious oral diseases.
- It is a potential nutraceutical agent for the therapy of viruses such as SARS-CoV-2, HIV, herpes simplex and influenza.
Nutraceuticals are products derived from food sources that are purported to provide extra health benefits, in addition to the basic nutritional value found in foods.
- Health benefits – It has the ability to reduce body weight, epididymal fat, insulin resistance, plasma and liver lipids.
- Cosmetics - The leaves are used in cosmetics such as serums for acne-prone irritated skin.
Reference
Down to Earth | Fish Mint
Nobel Prize in Medicine 2023
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2023 was awarded jointly to Katalin Karikó and Drew Weissman "for their discoveries concerning nucleoside base modifications that enabled the development of effective mRNA vaccines against COVID-19”.
- Contribution of Kariko and Weissman – In human cells, genetic information encoded in DNA is transferred to messenger RNA (mRNA), which is used as a template for protein production.
- In the 1980s, researchers were able to produce mRNA “in vitro”, which was highly unstable and triggered the immune system, leading to inflammatory responses in the body.
- Kariko and Weissman found out that mRNA with chemically modified bases did not lead to inflammatory reactions.
- They also found that using mRNA with altered bases significantly increased protein production.
- Kariko and Weissman’s discoveries helped to develop two base-modified mRNA vaccines (Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna's vaccine) at record speed.
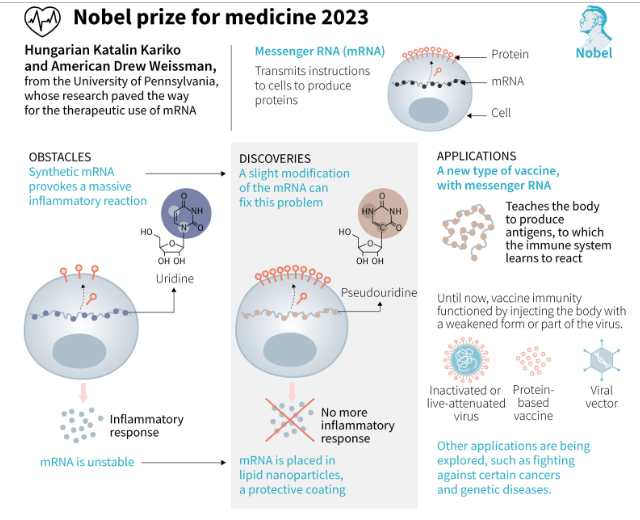
- mRNA vaccine – mRNA vaccines only introduce a piece of the genetic material that corresponds to a viral protein (usually a protein found on the membrane of the virus called spike protein).
- Therefore, it does not expose individuals to the virus itself.
- It then activate the immune system to produce antibodies that help counter an infection from a live virus.
- Significance
- Helps in vaccine development
- Has the potential to revolutionize the treatment of deadly illnesses including cancer, HIV, and influenza
- Advantages over traditional vaccine approaches - It can be developed more quickly and inexpensively than traditional vaccines because it does not require the production of viral proteins or inactivation of the virus.
- The mRNA vaccines can be easily modified to target new variants of the virus by simply changing the mRNA sequence that encodes the spike protein.
- Challenges - Since the mRNA molecules are fragile, it was difficult to deliver them to the system without altering them.
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine has been awarded 114 times since 1901. There have been 227 recipients including this year’s winners, but Kariko is only the 13th woman to receive the accolade.
Related links - GEMCOVAC-OM
References
- The Hindu| mRNA Vaccines
- IE| mRNA research
Project Udbhav
The Indian Army has started an initiative, named Project Udbhav in collaboration with the United Service Institution (USI) of India.
- Aim - To rediscover the Indic heritage of statecraft and strategic thoughts derived from ancient Indian texts of statecraft, warcraft, diplomacy and grand strategy.
- It focuses on indigenous military systems, historical texts, regional texts and kingdoms, thematic studies, and intricate kautilya Studies from 4th century BCE to the 8th century CE.
- Project Udbhav seeks to bridge the historical and the contemporary.
- The project also aims develop an indigenous strategic vocabulary, which is deeply rooted in India’s multifaceted philosophical and cultural tapestry.
- The first scholarly outcome of the initiative is the Paramparik Bhartiya Darshan Ranniti aur Netriyta ke Shashwat Niyam.
- English translation - Traditional Indian Philosophy Eternal Rules of Warfare and Leadership.
- It lists 75 aphorisms selected from ancient texts.
An aphorism is a memorable expression of a general truth or principle. Aphorisms are often handed down by tradition from generation to generation.
References
- The Hindu | Project Udbhav
- The Print | Project Udbhav
Operation Kachchhap
Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) saves 955 live Gangetic turtles in a crackdown on illegal wildlife trade in multicity Operation Kachchhap.
- Operation Kachchhap - This operation is part of a series of determined efforts by the DRI to combat illegal wildlife trafficking and preserve the environment.
- Rescued turtles - Indian Tent Turtle, Indian Flapshell Turtle, Crown River Turtle, Black spotted/Pond Turtle and Brown Roofed Turtle.
Gangetic Turtles
- The Ganges river system is home to 13 species of turtles.
- Red crowned roofed turtle, Narrow-headed soft-shell turtle,
- Three-striped turtle, Black spotted turtle,
- Crowned river turtle, Indian softshell turtle,
- Indian peacock softshell turtle, Brown roofed turtle,
- Indian black turtle, Indian tent turtle,
- Indian flap shell turtle, Indian roofed turtle,
- Northern river terrapin.
|
Rescued Species
|
|
Indian Tent Turtle
|
Scientific name
IUCN Status
CITES
|
Pangshura tentoria,
Least Concern,
Appendix II, Schedule I.
|
|
Indian Flapshell Turtle
|
Scientific name
IUCN Status
CITES
|
Lissemys punctate,
Vulnerable,
Appendix II, Schedule I.
|
|
Crown River Turtle
|
Scientific name
IUCN Status
CITES
|
Hardella thurjii,
Endangered,
Appendix II, Schedule IV.
|
|
Black spotted Turtle
|
Scientific name
IUCN Status
CITES
|
Geoclemys hamiltonii,
Endangered,
Appendix I, Schedule I.
|
|
Brown Roofed Turtle
|
Scientific name
IUCN Status
CITES
|
Pangshura smithii,
Near Threatened,
Appendix II, Schedule IV.
|
Reference
PIB | Operation Kachchhap
Moscow Format
Recently, 9 countries attended the 5th edition of Moscow format at Kazan in Russia with UAE, Saudi Arabia, Turkiye, and Qatar as observers.
|
Moscow Format
|
- It was established in 2017 as a six-party mechanism involving Russia, Afghanistan, India, Iran, China and Pakistan which later expanded with the inclusion of more countries.
- Since the Taliban takeover of Kabul in 2021, the Moscow format consultations were held in 2021 and in 2022.
- While Taliban attended the meeting in 2021, it did not participate in the 2022 meeting.
|
Moscow Format 2023
- Participants - Russia, India, China, Iran, Pakistan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan.
- Kazan Declaration – It was adopted at the end of the Moscow format 2023
- Key features
- To create conditions that will improve the well-being of the Afghan people.
- To provide equal rights to work, education and justice, without distinction as to gender, ethnicity or religion.
- To prevent further migration, and enable the return of refugees.
- Concerns – No timeline was provided for government formation or on restarting girl’s education.
References
- The Hindu| Kazan Declaration
- The Hindu| Moscow Format
