Artificial Sun
Korean Fusion Reactor 'Artificial Sun' sets record for sustaining plasma at 100 million Degree Celsius.
- KSTAR – South Korean scientists have set a new world record using the Korea Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research (KSTAR) device, an artificial Sun nuclear fusion reactor.
- 48 Seconds – The team generated plasma temperatures of 100 million degrees Celsius for 48 seconds (30 seconds in 2021) during tests between December 2023 and February 2024.
- This temperature is seven times that of the Sun's core, which is 15 million degrees Celsius.
- Aim – KSTAR aims to sustain plasma temperatures of 100 million degrees Celsius for 300 seconds by 2026.
- Tokamak – Common way of achieving fusion energy involves a doughnut-shaped reactor called a tokamak in which hydrogen variants are heated to extraordinarily high temperatures to create plasma.
- The activities of KSTAR will feed into the development of the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) in Southern France.
- ITER – ITER is the world’s biggest tokamak which aims to prove the feasibility of fusion.
- It will not produce any electricity; instead, ITER will resolve the critical scientific and technical issues to take fusion to the point where industrial applications can be envisioned.
- Funds – ITER is funded and run by seven member parties, China, the European Union, India, Japan, Russia, South Korea and the United States.
- India – India became a full partner of the ITER Project in 2005.
- ITER is intended to advance India's own nuclear fusion programmes and research.
- The Institute for Plasma Research (IPR), a dedicated research institute under the Department of Atomic Energy, supervises the ITER-India as well as India’s two tokamaks, ADITYA-U and SST-1.
China’s artificial Sun, the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) reactor is an advanced nuclear fusion experimental research device.
|
Quick Facts
|
|
Nuclear Fusion
|
- Nuclear fusion is defined as the combining of many small nuclei into a large nucleus with the subsequent release of huge amounts of energy.
- It powers our sun and harnessing this fusion energy could provide an unlimited amount of renewable energy.
- Nuclear fusion energy is a good choice as the base load energy in the future as it has many advantages.
- Advantages – Inexhaustibility of resources, inherent safety, no long-lived radioactive wastes, and almost no CO2 emissions.
- In the experiment, lasers were used to heat a small fuel pellets, having deuterium and tritium, in the inertial confinement fusion process.
- This pressurised the fuel pellets at conditions similar to that at the centre of the Sun.
- This triggered the fusion reactions.
- These reactions released alpha particles (positively charged), which in turn heated the surrounding plasma.
- [At high temperatures, electrons are ripped from atom’s nuclei and become plasma or the 4th state of matter or an ionised state of matter.]
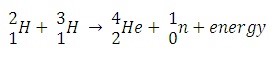
- Heated plasma released alpha particles and a self-sustaining reaction called ignition took place.
- Ignition amplifies the energy output.
- Significance – This could help provide clean energy for the future.
- Reproducing the conditions at the centre of the Sun will help studying the states of matter we were unable to create in the lab before.
- Often referred to as the holy grail of climate solutions, fusion has the potential to provide limitless energy without planet-warming carbon pollution.
- Nuclear fusion is also called as thermonuclear reaction which is possible only at an extremely high temperature and high pressure to push the hydrogen nuclei closer to fuse with each other.
- Base load energy refers to the minimum amount of electric power needed to be supplied to the electrical grid at any given time.
|
References
- NDTV – Artificial Sun
- CNN – Artificial sun sets record for time at 100 million degrees
- WION – New record of ‘artificial sun’ at 100 million degrees Celsius
One Vehicle, One FASTag
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) has rolled out the ‘One Vehicle, One FASTag’ scheme.
|
FASTag
|
- FASTag is an electronic toll collection system in India, operated by the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI).
- The fast tag (FASTag) are a Radio Frequency Identification Card (RFID) pasted to the windscreen of the vehicle.
- These tags store data such as vehicle registration, class of vehicle, engine and chassis number, etc., these details will help to arrive at the exact toll to be charged.
- The system operates on the lines of a prepaid phone card, which enables electronic payment at tolls on national highways.
- An RFID reader which is installed few meters from the toll plaza will act a sensor and verify tags validity and the account balance.
- If the amount is available with the prepaid card, the vehicle may pass through.
- Where there is a discrepancy in the card the vehicle will be alerted to eject from the lane, and pass through the eject lane.
- The vehicle can pass any number of toll plazas, all over the country, as long as there is amount in the account, and it can be recharged once the amount gets depleted.
|
- Aim – The 'One Vehicle, One FASTag' concept aims to deter the practice of using a single FASTag for multiple vehicles or associating multiple FASTags with one vehicle.
- Issues – NHAI has taken this initiative after the recent reports of multiple FASTags being issued for a particular vehicle and FASTags being issued without KYC in violation of RBI’s mandate.
- FASTags are deliberately not fixed on the windscreen of the vehicle, resulting in unnecessary delays at the toll plazas and causing inconvenience to fellow National Highway users.
Users will be free to recharge their FASTag from any bank and different payment methods such as Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS) UPI internet banking etc.
|
Quick Facts
|
|
National Highways Authority of India (NHAI)
|
- The National Highways Authority of India or NHAI is the nodal agency of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways in India.
- National Highways Authority of India was formed under the NHAI Act in 1988.
- It is an autonomous organization that looks after the management of the complete network of National Highways in the country.
- Headquarters – New Delhi
- NHAI is mandated to implement the National Highways Development Project (NHDP) which is India’s largest-ever Highways Project in a phased manner and accordingly government of India has launched many initiatives to strengthen the National Highways.
|
References
- The Economic Times – One Vehicle, One FASTag implemented
- Hindustan Times – One Vehicle, One FASTag rule comes into force
- Deccan Herald – One Vehicle, One FASTag rule is here
Allocation of Election Symbols
The Naam Tamilar Katchi has been allotted a new common symbol and the Viduthalai Chiruthaigal Katchi has been denied a common symbol, raising questions on allotment of symbols to registered unrecognised political parties (RUPPs).
- A party is recognised as a ‘national’ or ‘state’ party under the provisions of the Election Symbols (Reservation and Allotment) Order, 1968 (Symbols Order) by the Election Commission of India (ECI).
- Criteria – The criteria for recognition at the State level consists of:
- Winning one Lok Sabha seat for every 25 seats or 3% of Legislative Assembly seats (or)
- Winning one Lok Sabha or two Assembly seats along with 6% of votes polled (or)
- Securing 8% of votes polled in a general election.
- Symbols Order – Symbols are allotted to political parties and contesting candidates as per the provisions of the Symbols Order by ECI.
- Recognised Party – A recognised political party has a reserved symbol that is not allotted to any other candidate in any constituency.
- RUPPs – RUPPs are either newly-registered parties or those which:
- Have not secured enough percentage of votes in the Assembly or general election to become a State party
- Those that have never contested elections after being registered.
- Free Symbols – For RUPPs, one of the free symbols is allotted as a common symbol during an election if that party contests in two Lok Sabha constituencies or in 5% of seats to the Assembly of a State as the case may be.
- Rule 10B – Rule 10B of the Symbols Order provides that the concession of a common free symbol shall be available to a ‘registered unrecognised party’ for two general elections.
- Common Symbol – A party shall be eligible for a common symbol in any subsequent general election if it had secured at least 1% of votes polled in the State on the previous occasion when the party availed of this facility.
- Common symbols are provided to RUPPs based upon an undertaking that they would put up at least 5% of total candidates with regard to said Legislative Assembly election of a State.
- Such an unrecognised party should however apply for a symbol every time in the prescribed format.
- This application can be made any time during the period commencing six months prior to the expiry of the term of the Lok Sabha or State Assembly as the case may be.
- First-Come-First-Served – The symbols are thereafter allotted on a ‘first-come-first-served’ basis.
The candidates set up by recognised parties enjoy the advantage of being listed at the top of the ballot in the Electronic Voting Machine.
|
New Rules for RUPPs
|
- The Election Commission of India, brought in new rules for allocation of symbols to RUPPs, in January 2024.
- The ECI made it mandatory for the RUPPs to furnish audited accounts of last three financial years, expenditure statements of last two elections, and the signature of the authorized office-bearer of the party along with the application form for symbols.
|
The EC had in 2014 given directions that RUPPs wanting to avail the benefits of having a common symbol have to submit the proof of having filed up-to-date contribution reports, audited annual accounts, update of election expenditure statements, and their latest organisation details.
References
- The Hindu – How are symbols allotted to political parties?
- ECI – Political Parties and Election Symbols
- The Hindu – EC tweaks rules for allocation of symbols to RUPPs
Quds Force
Israeli war jets attacked an Iranian consulate building in Damascus, Syria, killing at least 13 people, including General Mohammad Reza Zahedi, who was a senior leader of the Iranian Quds Force.
- IRCG – The Quds Force is the paramilitary and intelligence wing of the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRCG).
- Islamic Revolution – The IRCG was set up by the leader of the Islamic Revolution and Iran’s first Supreme Leader, Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, in 1979.
- After the 1979 Islamic Revolution dislodged the ruling Shah from power, a theocratic state was established in Iran.
- For its protection, the IRCG was created to deal with both domestic and external threats.
- Parallel Force – IRCG remains a force parallel to that of Iran’s regular armed forces.
- It has army, naval, and air force wings, and its total membership numbers around 125,000.
In 2019, the United States designated the IRGC (and the Quds Force as part of it) a terrorist organisation.
- Role – The Quds forces are a specialized unit within the IRGC responsible for carrying out unconventional warfare and extraterritorial operations.
- The IRGC is also involved particularly in supporting proxy groups and conducting intelligence activities abroad.
|
Quick Facts
|
|
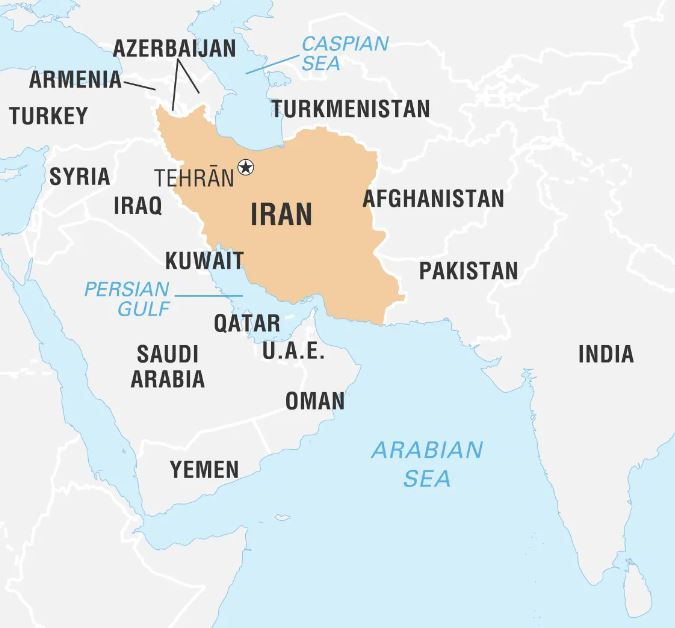
Iran
|
- Capital – Tehran
- Iran is a mountainous, arid, and ethnically diverse country of southwestern Asia.
- Geographically, much of Iran consists of a central desert plateau, which is ringed on all sides by lofty mountain ranges that afford access to the interior through high passes.
- Chabahar is Iran's only oceanic port.
- It is situated in Sistan and Baluchistan Province, on the Makran coast in the Gulf of Oman.
- There are two main ports in Chabahar, the Shahid Kalantari port and the Shahid Beheshti port.
- Its geographic proximity to Afghanistan, Pakistan, India and International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) gives it the potential to develop into one of the most important commercial hubs.
- Chabahar is one of the few places in Iran that is exempt from U.S. sanctions.
|
References
- The Indian Express – Who are the Quds Force?
- News 18 – Iranian Commander killed in Israel strike
- Britannica – Quds Force
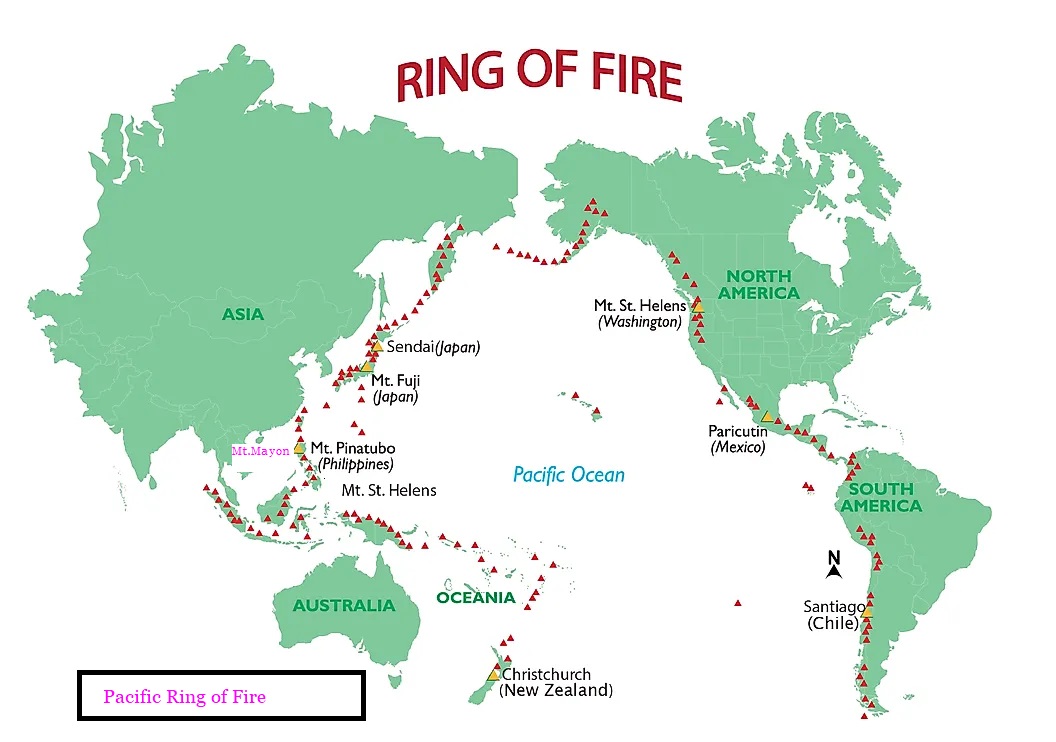
Ring of Fire
Taiwan is prone to earthquakes as it lies along the Pacific Ring of Fire, where 90% of the world’s earthquakes take place
- Circum-Pacific Belt – The Ring of Fire is also referred to as the Circum-Pacific Belt.
- It is a path along the Pacific Ocean characterized by a string of hundreds of active volcanoes and frequent earthquakes.
- It is a semicircle or horse shoe in shape and stretches nearly 40,250 kilometres.
- The majority of Earth’s volcanoes and earthquakes take place along the Ring of Fire.
- It traces boundaries between several tectonic plates, including the Pacific, Juan de Fuca, Cocos, Indian-Australian, Nazca, North American, and Philippine Plates.
- Reasons for predominant volcanoes – Along much of the Ring of Fire, plates overlap at convergent boundaries called subduction zones.
- That is, the plate that is underneath is pushed down, or subducted, by the plate above.
- As rock is subducted, it melts and becomes magma.
- The abundance of magma so near to Earth’s surface gives rise to conditions ripe for volcanic activity.
Taiwan's geographical location on the western edge of the Pacific Ring of Fire makes it highly susceptible to seismic activities.
- A significant exception is the border between the Pacific and North American Plates.
- This stretch of the Ring of Fire is a transform boundary, where plates move sideways past one another.
- This type of boundary generates a large number of earthquakes as tension in Earth’s crust builds up and is released.
The Pacific Ring of Fire runs through countries including the USA, Indonesia, Mexico, Japan, Canada, Guatemala, Russia, Bolivia, Ecuador, Chile, Peru, Costa Rica, Philippines, New Zealand, Australia, and Papua New Guinea.
|
Quick Facts
|
|
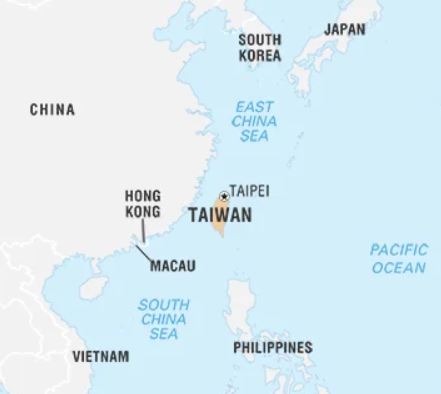
Taiwan
|
- Taiwan, island in the western Pacific Ocean that lies roughly 100 miles off the coast of southeastern China.
- Taipei, in the north, is the seat of government of the Republic of China (ROC; Nationalist China).
- In addition to the main island, the ROC government has jurisdiction over 22 islands in the Taiwan group and 64 islands to the west in the Penghu (Pescadores) archipelago.
- Prior to the 1600s, Taiwan was self-governing, although there was no central ruling authority.
- It was a colony of the Netherlands for about 40 years in the early to mid-17th century and was subsequently independent again for about two decades.
- China gained control there in the late 17th century and ruled Taiwan for some two centuries.
- Japan acquired Taiwan in 1895 following the first Sino-Japanese War, and it became a colony.
- Taiwan was returned to Nationalist Chinese control in 1945 following Japan’s defeat in World War II.
|
References
- The Indian Express – Massive earthquake hits Taiwan
- Times of India – What's Ring of Fire?
- National Geographic – Ring of Fire
|
Other Important Topics
|
|
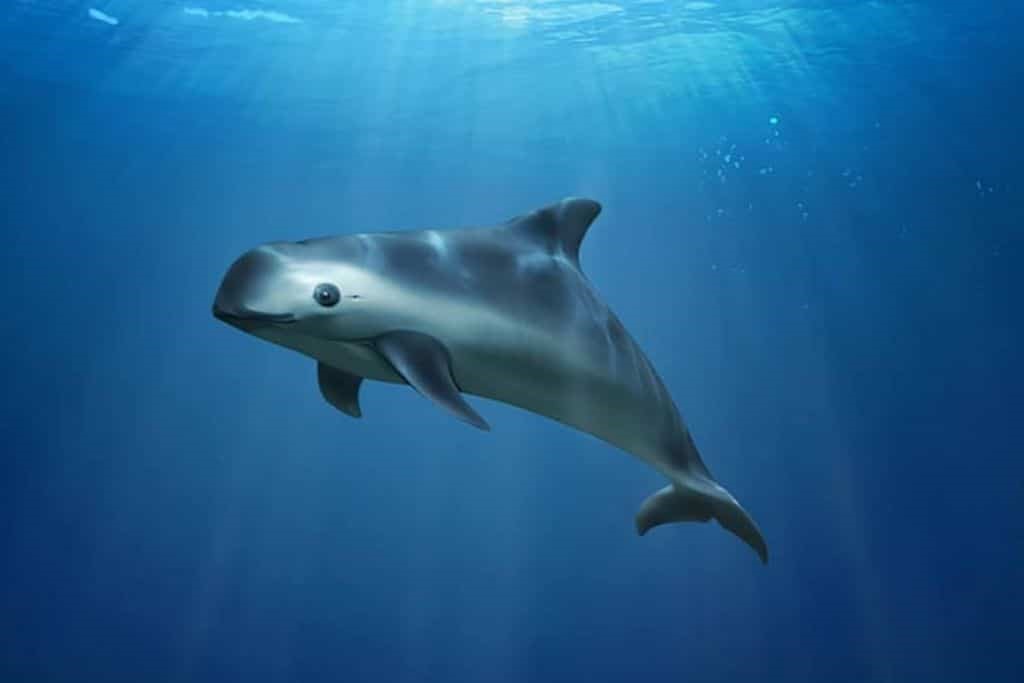
Vaquita (Phocoena sinus)
|
|
A new partnership between Re wild and Colossal Biosciences hopes to prevent the extinction of some of the world’s rarest animals, like vaquita.
- Vaquita means "little cow" in Spanish is a type of porpoise discovered in 1958, now on the edge of extinction.
- Porpoise are a group of fully-aquatic marine mammals.
- Habitat – Vaquitas are found only in northern-most part of the Gulf of California, Mexico.
- It is the only species of porpoise family found in warm waters.
- Conservation Status
- IUCN Red list - Critically Endangered.
- CITES - Appendix I.
- In August 2023, the International Whaling Commission issued it’s first-ever Extinction Alert.

|
|
Kathiya Gehu
|
|
The indigenous farm produced wheat, popularly known as Kathiya Gehu has been conferred the Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
- It is the 1st farm produce that got its GI Tag in Bundelkhand region, Uttar Pradesh.
- Nutritional Values – It is gluten-free, contains essential vitamins A, B, and E, as well as beta-carotene, iron, calcium, phosphorus, zinc, and copper.
- Kathiya Gehu is also high in fiber, which can help with digestive health, cholesterol levels, and weight management.
- Resilience - It can grow with very less irrigation and in harsh climatic conditions with minimum requirement of water.
Uttar Pradesh has achieved the distinction of being the 1st state to acquire 69 GI tags.
|
|
Exercise Gagan Shakti-24
|
- It is a Pan-India exercise to test capabilities and preparedness for high-intensity operations of the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- The drills are being carried out in a realistic environment.
- ‘Gagan Shakti’ was last held in 2018.
- Other demonstration Exercises - Vayu Shakti, Bharat Shakti, Tarang Shakti.
|
|
Agni-Prime Missile
|
|
Missile Agni-Prime successfully flight-tested by Strategic Forces Command & DRDO off the Odisha coast.
- The ‘Agni Prime’ or ‘Agni-P’ is a nuclear-capable new-generation advanced variant of the Agni class of missiles.
- It is lighter than all the earlier Agni series of missiles.
- Developed by - Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
-
|
Target
|
Surface-to-surface
|
|
Stage
|
It is a two-stage canisterised missile
|
|
Fuel
|
Solid fuel
|
|
Range
|
Medium Range (1200-2000 kilometres)
|
|
|
Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA)
|
- It is an integral component of the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY).
- About - Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA) is an account/ number used to link all the health records of a person.
- Aim - To create a digital health ecosystem & aims to promote digitization of healthcare.
- Ministry –Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Any individual can enroll in Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) to generate a Health ID or ABHA, free of cost.
|
|
Project Akashteer
|
- It is a cutting-edge initiative designed to automate air defence control and reporting processes by digitising the entire process.
- The project aimed at enhancing the operational efficiency and integration of the Army's air defence mechanisms.
- Developed by - Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) as part of the 'Atmanirbhar Bharat' initiative.
Indian Army has declared the year 2024 as the "Year of Tech Absorption'
|
|
Papikonda National Park
|
|
The State government of Andhra Pradesh has been receiving technical inputs to identify and prevent forest fires in the Papikonda National Park (PNP).
- The Papikonda national park is located in the Eastern Ghats of Andhra Pradesh.
- The area plays a key role in high precipitation and the perennial River Godavari runs through this national park.
- It was declared as a wildlife sanctuary in 1978, and as a national park in 2008.
- It has been recognized as an Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) by BirdLife International.
- A unique dwarf breed of goat known locally as the “kanchu mekha” belongs to this region.
|
|
Rock paintings at Kumittipathi (Pathimalai Cave)
|
- The cave is situated in Coimbatore district of Tamil Nadu.
- The paintings in the Pathimalai cave are drawn with white pigments, believed to be around prehistoric (3,000 years old).
- They depict an elephant chariot.
- Similar rock paintings can be found at Vellarukkam Palayam near Thondamuthur, Viraliyur, and Kovanur in the district, all on hill tops that depicts hunting and other activities.
|
|
PRATUSH
|
|
India’s PRATUSH among telescopes astronomers want to put on, around the moon.
- PRATUSH - Probing ReionizATion of the Universe using Signal from Hydrogen.
- It is a future radiometer to be sited on the moon’s far side that will reveal the Cosmic Dawn of our Universe.
- It is being built by the Raman Research Institute (RRI) in Bengaluru collaboration with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- PRATUSH will detect the first stars formed in our universe, the nature of the first stars, and the colour of the light of Cosmic Dawn.
- PRATUSH will be the pioneering space telescope that will reveal, for the first time, the history of our infant Universe as it transformed after the Big Bang.
|
|
Criollo
|
- Criollo cattle breed are a small, hardy breed of cattle that originated in Andalusia, Spain.
- They are known for their ability to survive in hot and humid climates.
- It has a short, slick-hair coat that provides improved thermotolerance.
|
