Emblica chakrabartyi
New plant species discovered from Edamalayar forest range in Kerala.
- It is the 16th new plant species discovered from Ernakulam, Kerala.
- Taxonomy – It belongs to the gooseberry (Phyllanthaceae) family.
Emblica chakrabartyi, the plant has been named after Tapas Chakrabarty, former scientist at the Botanical Survey of India, for his contribution to the study on Phyllanthaceae.
- Growing season – The flowering and fruiting occur during December to June.
- Features – It attains a height of approximately 2 metres.
- Leaves – Large with a shiny elongated oval shape of up to 13 cm.
- Flowers – Male flowers are found in inflorescence whereas females ones are in single, on the leaf axils.
- Each flower bears yellowish green coloured 6 petals.
- Fruits – They are brown to black when they ripen and the seeds are black about 8-9 mm diameter.
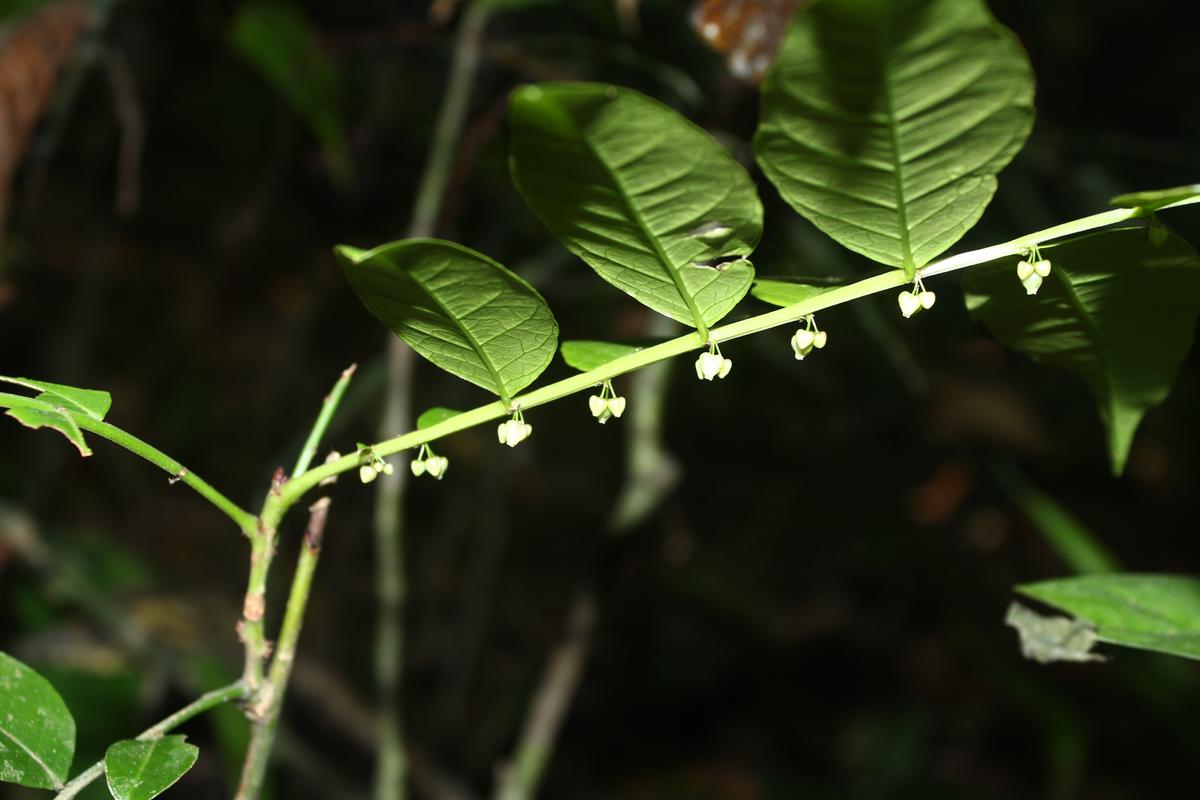

Generally growing as shrubs in tropical rain forests, 55 species of the genus Emblica have been recorded all around the world. The new plant is the 11th from India.
Reference
The Hindu| New plant species ‘Emblica chakrabartyi’ found in Kerala
H5N1 Infection
Scientists believe that the H5N1 virus can be transmitted to humans via an infected cow’s milk that has not been pasteurised.
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) is a disease that is highly contagious and often deadly in poultry, caused by HPAI A (H5) and A (H7) viruses. It is 1st identified in domestic waterfowl in 1996 in China.
- H5N1 – It causes a highly infectious respiratory disease in birds called avian influenza or bird flu.
- Transmitted by – Wild birds to domestic poultry and other bird and animal species through bird droppings.
- New research shows a sub variant of H5N1 can transmit through Air while another study shows that some birds (poultry) as well as cats do show susceptibility to influenza virus infections via oral route.
- Affected population – Both land and sea mammals have been affected and there are few instance of infection in humans as well.
Almost all human influenza virus infections are primarily respiratory infections unlike in some other mammals where gut infections have been reported.
H5N1 in humans
So far, close to 900 human infections have been reported since 2003, of which more than half were fatal.
- Transmission – Almost all of those infected were farm workers who had come in close contact with infected animals.
- Diseases – From mild to severe and in some cases, it can even be fatal.
- Symptoms – Primarily respiratory, but conjunctivitis and other non-respiratory symptoms have also been reported.
- India – It reported its first and only case of human avian influenza A (H5N1) in Haryana in 2021.
- Vaccines – Current seasonal influenza vaccines do not protect against human infection with animal influenza A viruses.
- Misconception - The notion of immunity against H5N1 virus can be developed by drinking raw milk containing viable viruses.
While Food and Agricultural Organisation (FAO) noted that H5N1 virus was detected in high concentrations in milk from infected dairy cattle, still no reports of viable H5N1 virus being found in raw milk samples.
References
- The Hindu| Detection of H5N1 virus in milk of infected dairy cattle
- WHO| Influenza A (H5N1)
Anendophasia
A new study found that some people with anendophasia perform worse in tasks remembering words and rhymes.
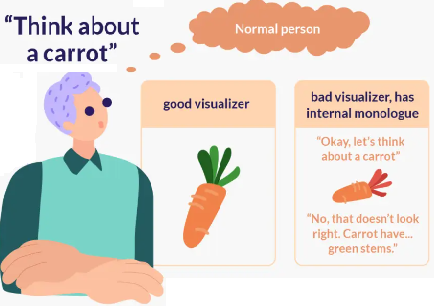
- Anendophasia – It is a condition of having no inner voice.
|
An Inner Voice
|
- Meaning – It is the sound you imagine inside your head when you are consciously thinking.
- Like, for instance, framing a sentence in your mind before typing it out.
- It is also called as internal monologue.
- Grades – Some think in pictures and then translate the pictures into words when they need to say something.
- Some have a verbal, as words without sound.
- Universality – It is not human universal as some lack it.
|
- Impact – Experiments suggested that participants without an inner voice were significantly worse, than those without the condition, at remembering the words and determining whether a set of words, rhyme.
- However, it did not seem to affect cognitive reasoning abilities.
Reference
The Hindu| Anendophasia, the condition of lacking inner voice
Thangjing Hills
Manipur police registered a zero FIR over pictures of a banner placed in the culturally-disputed areas of the Thangjing Hills
In police regulations, information recorded under Section 154 of Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC) is known as First Information Report (FIR).
A Zero FIR can be filed in any Police Station by the victim, irrespective of their residence or the place of occurrence of crime, to provide speedy redressal to the victim.
- Geography – It is somewhere in the middle of buffer zone created between Churachandpur and Bishnupur districts in Manipur
- Status – It falls within the Churachandpur-Protected Forest which was notified in 1966 under Section 29 of the Indian Forest Act, 1927.
- Historical importance – It has been declared as a protected site, under Section 4 of the Manipur Ancient and Historical Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1976.
- Cultural & Religious significance – It is considered sacred to both the Meitei community and the Kuki-Zo community.
- Dispute – Contests over the right to pray and worship on the hill range have only escalated since the ethnic conflict of 2023.

- Dispute over nomenclature
- Kuki-Zo people – ‘Thangting Hills’.
- Meitei people – ‘Thangjing Ching or Thangjing Hills’.
- Current issue – The picture over which the FIR has been registered appeared to be in the area of Thangjing Hills and yet the banner had spelt it as “Thangting” as it was put by Kuki people.
- This indicated unauthorised changing of name and violates the Manipur Names of Places Act of 2024.
Reference
The Hindu| Dispute over Thangjing Hills of Manipur
GloLitter Partnership
In Andhra-Odisha coast, ghost gear poses a serious threat to marine life.
Research indicates that globally, 6.40 lakh metric tonnes of fishing gear are lost in the ocean resulting in a great loss to the fisheries sector and adversely impacting the marine ecosystem.
- It is a project that aims to reduce marine litter.
- Objectives – To support developing countries in identifying opportunities for the prevention and reduction of marine litter.
- Total Budget – Approximately $5 Million.
- Partnership – Government of Norway, International Maritime Organisation (IMO) & Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
In India, the Fishery Survey of India (FSI) is the lead agency of the GloLitter Partnership and has been working towards reducing Sea Based Litter (SBL).
- Focus – It works in 5 key regions, with a total of 30 countries engaged as either Lead Partner Countries (LPCs) or Partner Countries (PCs).
- Services – Equip partner countries with knowledge and tools to address the problems of marine plastic litter.
- Establish public-private partnerships to demonstrate best marine plastic litter management solutions.
- Engage women in tackling marine plastic litter problems and facilitate regional and global partnerships between countries and organizations to have a greater impact.
- Impact – Marine plastic litter originating from the shipping and fisheries sectors is prevented and reduced.
Ghost gear
- It is any fishing equipment that has been lost, discarded or abandoned in water bodies.
- It comprised largely of gill net, nylon and polypropylene rope.
- Causes for accumulation – Due to snagging where the gear gets caught on reefs, rocks and other obstructions on the seafloor
- Adverse weather conditions leading to loss of fishing gear or gear getting cut by marine traffic
- Fishing in deep waters and wear & tear over time.
A recent Mongabay India analysis stated that 144 animals belonging to 35 species across India were trapped in derelict fishing gear. India is the 2nd largest contributor to mismanaged plastic in the ocean.
- Impact – Ghost gear that get submerged or drift in the sea pose serious threats to fish, crustaceans, molluscs, elasmobranchii, marine mammals and sea birds.
- Measures – The World Wide Fund for Nature-India (WWF-India) initiated project studies across the Andhra Pradesh, Goa and Kerala coasts to understand the extent of the problem.
References
- The Hindu| Ghost gear pose threat near Andhra-Odisha coast
- Glolitter| GloLitter Partnership

