Idate Commission Report
The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) stressed on the need for the implementation of the Idate Commission report.
The Commission
- Headed by - Bhiku Ramji Idate.
- Setup by - The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- Constituted in - 2015, for a three-year temporary term.
- Purpose - For the empowerment of the Denotified Tribes (DNT), Semi Nomadic (SNT), and Nomadic Tribes (NT).
Nomadic and semi-nomadic communities are defined as those who move from one place to another rather than living at one place all the time.
- The committee had to submit its report identifying the above communities state wise, assessing their development status, and recommending ways to uplift them.
- In May 2018, the National Commission for Denotified Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Tribes, chaired by Bhiku Ramji Idate has submitted its report.
The commission has studied the earlier report of Renke Commission.
Recommendations
- The Idate Commission has made a total of 20 recommendations which concern the various ministries and departments.
- The government must act to repeal the Habitual Offenders Act, 1952, if not, the appointment of a representative of De-notified Tribe community with the nodal officers as stipulated in the Act.
- Non-inclusion - It also suggested the non-inclusion of DNTs/NTs/SNTs under the SC/ST/OBC and formulation of specific policies for the former, among many others.
- Protection - The commission has recommended giving protection to Denotified Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Tribes, the communities under the Atrocities Act.
- Poorest of the Poor - The report has called Denotified Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Tribes poorest of the poor, most marginalised and most downtrodden communities.
- These communities are subject to social stigma, atrocity and exclusion.
- Constitutional amendment - It recommended a Constitutional amendment so that Scheduled NT/ DNT/ SNT can be added as a third category after Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes in the Act.
- It stated that the government should provide strong legal protections and constitutional safeguards, including the extension of the Protection of Atrocities Act to the NT/ DNT/ SNT communities.
- Third schedule - This can be done by creating a separate Third schedule as Scheduled De-notified Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Tribes.
- Criminal Tribes Act - In its report, the commission has noted that entire communities were branded as criminals under the colonial rule through enforcement of the Criminal Tribes Act, 1871.
- Despite repeal of the Act after Independence, subsequent legislations have forcibly alienated them from their traditional occupations and habitations.
- 2011 caste census - Advocated for release of 2011 caste census, which is yet to be made public, at least on the DT/ NT/ SNT community, so that policies can be made specifically for these communities.
- The report of the commission is under the consideration of the government.
A National Commission for De-notified, Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Tribes (NCDNT) was first set up in 2003 and later reconstituted in 2005.
References
- The Hindu – Protection of nomadic tribes
- The Wire – A National Commission that failed the Denotified Tribes
- BNN – NHRC Urges Implementation of Idate Commission Report
National Multidimensional Poverty Index
Over 24.8 crore people moved out of poverty in India in nine years: NITI report.
The Index
- Released by - Niti Aayog, which is the nodal agency to release Multidimensional Poverty (MDP) report for States and Union Territories.
- Purpose - Plays a role in assessing advancements towards Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) 1.2.
SDG 1.2. - By 2030, reduce at least by half the proportion of men, women and children of all ages living in poverty in all its dimensions according to regional definitions.
- Multidimensional Poverty - Poverty – According to the World Bank, those who are unable to earn 2.15 dollar per day are living in extreme poverty.
- As per UNDP, it is the measure of poverty that considers various deprivations experienced by people in their daily lives including poor health, insufficient education and low standard of living.
- It is a means to capture the complexity of poverty that considers dimensions of well-being beyond just monetary poverty.
- Indicators of National MPI - India’s national MPI has 3 equally weighted dimensions, which are then represented by 12 other indicators.
- Health
- Education
- Standard of living
- These 12 include nutrition, child and adolescent mortality, maternal health, years of schooling, school attendance, cooking fuel, sanitation, drinking water, electricity, housing, assets, and bank accounts.
- Sub-indices of National MPI:
- Headcount ratio (H): How many are poor?
- Intensity of poor (I): How poor are the poor?
- Formula - MPI= H*I
- If the deprivation score (sum of the weighted status of all the indicators) for an individual is more than 0.33, then an individual is considered multidimensionaly poor.
- Global MPI Report - It is jointly published by the Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI) and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- It is based on the Alkire-Foster (AF) methodology that captures overlapping deprivations in health, education, and living standards.
Findings
- Report based on - The report said the recent National MPI was based on National Family Health Surveys 4 (2015-16) and 5 (2019-21).
- As many as 24.82 crore people moved out of multidimensional poverty in nine years to 2022-23, with Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and Madhya Pradesh registering the largest decline.
- At the State level, Uttar Pradesh topped the list with 5.94 crore people escaping poverty followed by Bihar at 3.77 crore and Madhya Pradesh at 2.30 crore.
- The rate of decline of multidimensional poverty has accelerated during the period 2013-14 to 2022-23.
- All 12 indicators of MPS have shown remarkable improvement during this period.
References
- The Hindu – Over 24.8 crore people moved out of poverty
- Times of India – Over 24.8cr people moved out of poverty
- The Indian Express – India’s multidimensional poverty rate down
- MPPN – Multidimensional Poverty
Ingenuity
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) regained contact with its Mars helicopter Ingenuity, after it was unable to communicate with it towards the end of its 72nd flight.
- Launched on - July 30, 2020.
- Ingenuity - It is a small solar-powered helicopter that landed on the Martian surface on February 18, 2021, along with the Perseverance Rover.
- Purpose - The rover’s mission was to study signs of ancient life, and collect samples that might be sent back to Earth during future missions.
- Ingenuity was sent to Mars as an experiment to test powered, controlled flight on another world for the first time.
- The chopper made its first flight on Mars on April 19, 2021.
- Records - It rose to a height of 10 feet, hovered for 30 seconds, and then descended back to the ground.
- The flight lasted 39.1 seconds, which was a big deal for two reasons.
- One, Ingenuity was the first aircraft to fly on another planet.
- Two, it managed to fly in Mars’ thin atmosphere, which is not conducive for flying.
- Ingenuity is an autonomous aircraft.
- Guidance by - It is piloted by onboard guidance, navigation, and control systems running algorithms developed by the team at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
- Perseverance acts as a relay between the chopper and Earth.
Before it went missing, Ingenuity had made 72 flights, staying aloft for more than 128 minutes and covering a total of 17.7 kilometres.

References
- The Indian Express – NASA regains contact with Mars helicopter
- Times of India – NASA loses contact with Mars helicopter Ingenuity
- NASA – Ingenuity
Somnath Temple
Prime Minister will inaugurate the Ram temple in Ayodhya, 73 years ago; the President of India inaugurated another temple in a grand ceremony.
- Located in - Prabhas Patan, Veraval, in Gujarat.
- Significance - It is the holy place of the first Aadi Jyotirling Shree Somnath Mahadev, among the twelve Jyotirlinga shrines of Shiva.
- It is also the place where Lord Shri Krishna took his last journey.
- Built by - In 1782, Maratha queen Ahalyabai Holkar built a small temple at the site.
- Other names - The Somnath temple, also called Somanātha temple or Deo Patan.
The temple faced several attacks from raiders, with the most damaging by Mahmud of Ghazni in 1026 CE.
- Under Mughals - In the sixteenth century, Akbar permitted the worship of the linga in the Somanatha temple and appointed desais /officers to administer it.
- Three generations after Akbar, Aurangzeb gave orders for its destruction.
- He subsequently issued an order for its destruction and its conversion into a mosque in 1706 just before he died.
- After Independence - Those ruins were demolished and the present Somnath temple was reconstructed in the Maru-Gurjara style of Hindu temple architecture.
The contemporary Somnath temple's reconstruction was started under the orders of the first Home Minister of India Vallabhbhai Patel and completed in May 1951 after his death.
Maru-Gurjara Style
- It is also known as Solaṅki style is the style of West Indian temple architecture.
- The style originated in Gujarat and Rajasthan from the 11th to 13th centuries, under the Chaulukya dynasty.
- The Chaulukya dynasty is also called the Solaṅki dynasty.
- Although originating as a regional style in Hindu temple architecture, it became especially popular in Jain temples, and mainly under Jain patronage later spread across India.

References
- The Indian Express – Somnath: A brief history of the temple
- The Print – Rajendra Prasad’s Somnath temple inauguration speech
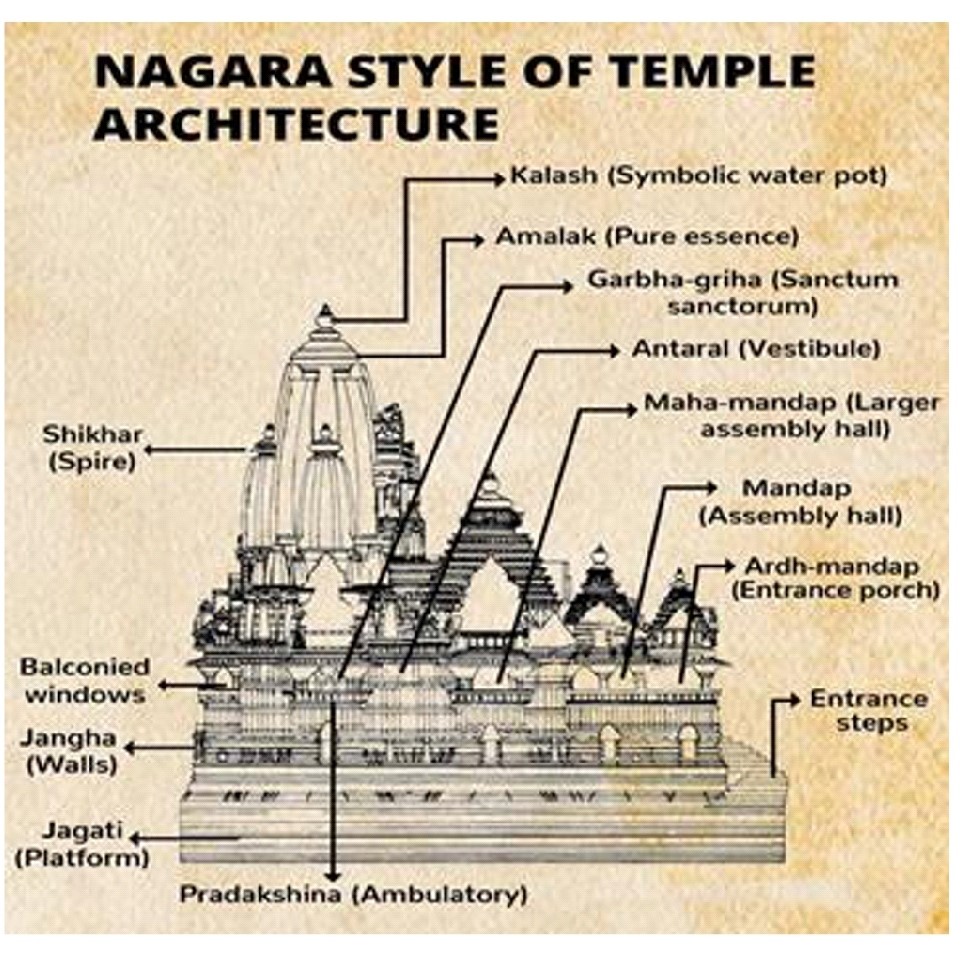
Nagara Style of Architecture
Ayodhya’s Ram Temple is built on the Nagara Style of Architecture.
- The Nagara style of temple architecture emerged some time in the fifth century CE, during the late Gupta period, in northern India.
- It is seen in juxtaposition with the Dravida style of southern India, which too emerged in the same period.
- Nagara temples are built on a raised plinth, with the garbha griha (sanctum sanctorum), where the idol of the deity rests, the most sacred part of the temple.
- Towering over the garbha griha is the shikhara (literally ‘mountain peak’), the most distinguishable aspect of Nagara style temples.
- As the name suggests, shikharas are human-made representations of the natural and cosmological order, as imagined in Hindu tradition.
- A typical Nagara style temple also comprises a circumambulatory passage around the garbha griha, and one or more mandapas (halls) on the same axis as it.
Five modes of Nagara architecture
- Depending on the period and geography, there is a large variation when it comes to what a shikhara looks like, or how it is used in a temple’s design.
- On this basis, five modes of Nagara temple architecture, namely, Valabhi, Phamsana, Latina, Shekhari, and Bhumija.
- The first two are associated with what scholars have classified as Early Nagara Style.
- The Valabhi begins as a masonry rendering of the barrel-roofed [wooden] structure, simple or with aisles, familiar through chaitya halls [prayer halls, most associated with Buddhist shrines].
- A formalisation of multi-eave towers, wedded to a piling up of slabs, leads to the Phamsana.
- From these modes emerged the Latina, a shikhara that is a single, slightly curved tower with four sides of equal length.
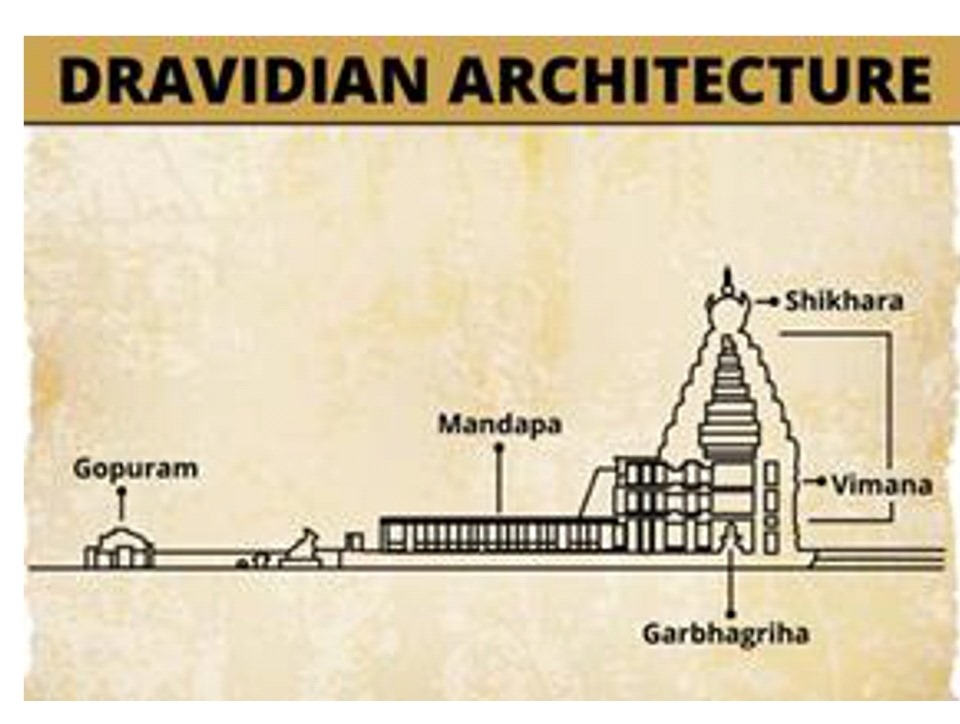
Comparison to Dravida style
- The Dravida counterpart to the shikhara is the vimana there exists, however, a fundamental difference.
- In the Dravida style temples, vimanas are typically smaller than the great gatehouses or gopurams, which are the most immediately striking architectural elements in a temple complex.
- Moreover, while shikharas are mentioned in southern Indian architectural sources, they refer to only the dome-shaped crowning cap atop the vimana.
- The existence of gopurams also points to another unique feature of the Dravida style, the presence of a boundary wall.
- Few Nagara style temple complexes are lined with distinctive boundary walls that are a part of the temple’s design.
This is one of Ayodhya’s Ram temple’s hybrid features, although no elaborate gopuram has been built, a 732m long wall runs around the temple compound.
References
- The Indian Express – What is the Nagara Style?
- News 18 – Ayodhya Ram Temple built in Nagara Style
- Hindustan Times – Ayodhya Ram Temple is an architectural marvel
|
Other Important Topics
|
|
Project BHISHM
- BHISHM -Bharat Health Initiative for Sahyog, Hita and Maitri).
- It is a project that aims to provide immediate medical assistance during humanitarian crises or natural disasters.
- It is a joint project of the Indian Navy and the DRDO (Defence Research and Development Organisation).
- The project also includes the world's first indigenous portable hospital.
|
|
IInvenTiv
- The 2nd edition of the Ministry of Education’s flagship R&D Innovation Fair, IInvenTiv-2024 was inaugurated by Union Education Minister recently.
- It aims to showcase the holistic impact of the research and innovation carried out by the country's top higher education institutes.
|
|
Harni lake
- Harni Motnath Lake is a green lake in Vadodara, Gujarat, India.
|
|
Zanskar River
- The Zanskar River is a tributary of the Indus River.
- It originates from the Doda and Lungnak rivers, and flows entirely within Ladakh.
- The Zanskar River's headwaters are known as the Tsarap Chu, and originate from the snows of the Himalayas.
- The river's entire catchment area is formed by glaciers.
|
|
Veerbhadra Temple
- The temple is dedicated to the deity Veerabhadra, the fiery form of Lord Shiva. The temple is closely associated with the Ramayana. Top of Form
-
- It was built during the 16th century, the architectural features of the temple are in the Vijayanagara style with profusion of carvings and paintings.
- The Veerabhadra Swamy temple and the Nandi statue in Lepakshi, India were added to UNESCO's tentative list of world heritage sites in 2022.
|
|
Boeing India Engineering and Technology Centre (BIETC)
- Prime Minister inaugurated aircraft manufacturing giant Boeing’s largest investment facility outside the USA in Bengaluru recently.
- It aims to be a cornerstone for partnership with the vibrant startup, private and government ecosystem in the country.
- PM will also launch the Boeing Sukanya Program that aims to support the entry of more girl children from across India into the country’s growing aviation sector.
|
|
Biswanath Ghat
- Biswanath Ghat is a village in Assam, located on the banks of the Brahmaputra River and is known as "Gupta Kashi".
- The name "Gupta Kashi" is a comparison to Kashi during the Gupta Empire era.
- The village is named after the ancient Biswanath temple, a prominent religious site for centuries.
- Biswanath Ghat is also known for its ghat, island, and temple built by the Ahom king.
|
|
ReTro
- Chinese scientists recently announced that they have cloned a Rhesus monkey named ReTro that lived to adulthood.
- The scientists created ReTro using a slightly modified version to create Dolly the Sheep and other mammals like the long-tailed macaque, which was the first primate to be cloned.
|
|
Wings India 2024
- Wings India 2024 is a civil aviation event that took place at Begumpet Airport in Hyderabad, India.
- This event is organized by the Ministry of Civil Aviation, AAI, and FICCI.
- The event celebrated India's status as the world's third-largest domestic aviation market.
|
|
Operation AMRITH
|


