Pirola
A recent study has noted the rise of Covid-19 infections in multiple countries, driven by a new Coronavirus variant called BA.2.86, informally being termed as ‘Pirola’.
- Pirola or BA2.86 is one of the lineages of highly-mutated Omicron variant of Covid-19 virus.
- Pirola has around 30 genetic changes (mutations) from its parent Omicron variant. This gives it the capacity to be immune evasive and highly transmissible.
|
Mutation - Once a virus enters the human body, its genetic material, RNA or DNA enters the cells and starts making copies of itself which can infect the other cells.
Whenever an error occurs during this copying process, it triggers a mutation.
|
- It is currently in the WHO list of 'variants under monitoring'.
- Impacted Countries - Isreal, Denmark and U.S., South Africa, UK.
- The strain is quite virulent but the symptoms are mild.
- Symptoms - Stuff nose, fever, fatigue, cough and sneezing, rashes, eye redness, diarrhea.
- Pirola might have a higher affinity for infecting individuals who have either previously contracted COVID-19 or have been vaccinated against it.
- Vaccine - The previously administered vaccines shows an efficacy eventhough the mutations are high.
- So far, no deaths have been reported among cases, according to the WHO.
References
- The Indian express | What is known about ‘Pirola’ so far?
- Yale Medicine | Pirola
- Money Control | the new Covid variant, BA.2.86 or Pirola
- The Hindustan Times | Covid variant BA2.86 aka Pirola
GRIHA Norms
The Indian Army’s new Thal Sena Bhawan (TSB), coming up with GRIHA-IV (Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment) norms.
- Acronym - GRIHA is an acronym for Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment. GRIHA is a Sanskrit word meaning – ‘Abode’.
- About - GRIHA is a national rating system that evaluates the environmental performance of a building holistically over its entire life cycle.
- The rating system will seek to strike a balance between the established practices and emerging concepts, both national and international.
- Aim - It attempts to minimize a building’s resource consumption, waste generation, and overall ecological impact to within certain nationally acceptable limits / benchmarks.
- Developed by - TERI (The Energy and Resources Institute).
- This tool has been adopted by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy.
- Stages for Evaluation
- Pre-construction stage
- Building planning and construction stages
- Building operation and maintenance stage
- Criteria - GRIHA assesses a building out of 34 criteria and awards points on a scale of 100. In order to qualify for GRIHA certification, a project must achieve at least 50 points.
- Certain criteria / sub-criteria are mandatory and have to be complied for the project to be at all eligible for rating.
- Project scoring
- 50-60 points is certified as a 1 star GRIHA rated building,
- 61-70 is a 2 star GRIHA rated building,
- 71-80 is a 3 star GRIHA rating building,
- 81-90 is a 4 star GRIHA rated building and
- 91-100 is a 5 star GRIHA rated building
- The guidelines/criteria and appraisal norms is revised every 3 years or sooner to take into account the latest innovations/best practices happening during this period.
- SVA GRIHA (Simple Versatile Affordable GRIHA) has been developed by ADaRSH in collaboration with TERI and is currently under pilot stage.
- This variant of GRIHA is meant to simplify, and make the greening of small buildings (less than 2500 sqm built-up area) affordable.
- Advantages
- Reduced energy consumption without sacrificing the comfort levels
- Reduced destruction of natural areas, habitats, and biodiversity, and reduced soil loss from erosion etc.
- Reduced air and water pollution (with direct health benefits)
- Reduced water consumption
- Limited waste generation due to recycling and reuse
- Reduced pollution loads
- Increased user productivity
- Enhanced image and marketability

References
- The Hindu | GRIHA green norms
- Griha India | About griha
Tharosaurus Indicus
A recent study published by the scientists from IIT Roorkee have characterized Sauropod dinosaur fossils from the Middle Jurassic period, found in the Thar desert, Rajasthan by the Geological Survey of India.
- Findings - The remains of Tharosaurus indicus were recovered from the Jaisalmer Formation near Jethwai village, the Indian state of Rajasthan.
- It is a plant-eating dinosaur and 167 million years old.
- These fossils are the first dicraeosaurid sauropods to have been found in India and oldest known diplodocoid (superfamily of sauropod dinosaurs) fossils in the world.
- Researchers found that this Sauropod dinosaur has the same clade as the long-necked herbivores in Jurassic Park.
- Naming - Tharo – Thar desert; Saurus (Greek word) - lizard; and indicus from its Indian origin.
- Family - Dicraeosauridae ; Superfamily – Diplodocoidea.
- History - They lived from the Jurassic period (200 million years ago) to the Cretaceous period (65 million years ago) and have been the most dominant clades of dinosaurs.
- Uniqueness - Sauropods can grow more than a 100 feet however members of the Dicraeosauridae family of sauropods were smaller and had shorter necks and tails.
India has also been home to primitive sauropods, like Kotasaurus and Barapasaurus.
Reference
The Hindu | plant-eating dinosaur found in Rajasthan
Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing (DIKSHA)
The National eGovernance Division (NeGD), Ministry of Education, is set to integrate Personalised Adaptive Learning (PAL) into its existing Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing (DIKSHA) platform.
- PAL’s software-based approach will allow each student to have an individualised learning experience over the course of the curriculum based on their unique needs and abilities.
DIKSHA
- It comes under the Ministry of Education, provides e-content for schools via an online portal and a mobile application.
- It also has embedded assistive technologies for learners with visual or hearing impairments.
- However, DIKSHA is a static content repository.
- DIKSHA features digitised National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) textbooks used national and State Boards.
PAL
- The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) has sought the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology’s expertise in facilitating PAL for DIKSHA.
- Example – If a student of Class 9 is learning the Pythagoras theorem and makes a calculation mistake, the AI learning system flags it and loops the student back to a basic video of how to make the calculation.
- In some States, private players are already administering PAL, which works on AI or Artificial Intelligence, but budget constraints have been an obstacle.
Andhra Pradesh has signed contracts with three privately owned edtech companies, Reliance Jio Platform’s start-up Embibe, ConveGenius, and Mindspark, for training teachers to use IT applications in the classroom.
- Building PAL is a massive exercise, content from across subjects will have to be categorised and different chunks will have to be tagged.
Tagging of content is important to create learning loops, where, say, a student faces difficulty at a certain tag, then supportive material offering an explanation of the tagged concept can be provided.
- Apart from PAL, MeitY is also considering the introduction of voice commands in DIKSHA 2.0 as a part of AI-enabled learning.
Reference
The Hindu – Centre’s DIKSHA platform to offer AI help
Preeclampsia
The biomarker used to predict the preeclampsia in the early stage was discovered by scientists.
Preeclampsia
- Preeclampsia is high blood pressure (hypertension) disorder that can occur during pregnancy.
- Preeclampsia typically develops after the 20th week of pregnancy.
- It can also affect other organs in the body and be dangerous for both the mom and developing fetus.
- Gestational hypertension is high blood pressure that begins after 20 weeks without problems in the kidneys or other organs.
- Some women with gestational hypertension may develop preeclampsia.
- People with preeclampsia experience high blood pressure, protein in their urine, swelling, headaches and blurred vision.
- The condition goes away after the baby is delivered.
- Among the few interventions available, low-dose aspirin at early stages of the disease can reduce the risk of developing preeclampsia.
The biomarker
- A liquid-biopsy approach that measures DNA-methylation levels in the blood may improve the detection of pregnancies at risk of developing preeclampsia at early stages.
- Liquid biopsy is a promising emerging tool for non-invasive diagnostics, and it is increasingly being used to detect disease and monitor progression and treatment response.
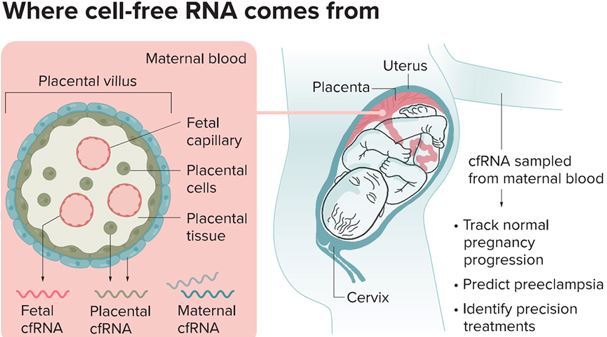
- A pregnant person’s bloodstream contains pieces of cell-free RNA (cfRNA) from the fetus, placenta and mother.
- RNA from the fetus is released through fetal capillaries, which are found in fingerlike structures within the placenta known as villi (cross-section shown) that help bridge fetal and maternal tissue.
- RNA from the placenta, which contains genetic information from both parent and child, is expelled via both the placental villi and the placental tissue.
- Preliminary results suggest that cell-free DNA methylation profiling is a promising tool for presymptomatic PE risk assessment, and has the potential to improve treatment and follow-up in the obstetric clinic.
DNA methylation analysis can help scientists gain valuable insight into gene regulation and identify potential biomarkers.
Liquid Biopsy
- A liquid biopsy detects the small pieces of DNA in the bloodstream from these cancer cells.
- Liquid biopsies are different from other types of biopsies, such as core needle biopsies and fine needle aspiration biopsies, which are the main way doctors diagnose and treat most types of cancer.
References
- The Hindu – Early prediction of preeclampsia using a biomarker
- ASBMB – New noninvasive RNA tests to identify risk of pregnancies
