Hamara Samvidhan Hamara Samman
Recently, Vice-President of India had inaugurated 'Hamara Samvidhan, Hamara Samman' to commemorate the 75th Year of India as Republic.
- It is a yearlong pan India campaign.
- Undertaken by – Department of Justice, Ministry of Law and Justice.
- Aims – To reaffirm our commitment to the constitutional principles and celebrate the shared values.
- To instil a sense of pride and responsibility to uphold the constitutional ideals and to give opportunity to every citizen to participate and contribute in our democratic journey.
- Sabko Nyay Har Ghar Nyaya – Connecting the villagers and spreading awareness of legal services.
- The citizens would also get the opportunity to showcase their talents and to test their knowledge on Constitution.
- Vidhi Jagriti Abhiyan – Involving the students to carry the message Panch Pran in the villages adopted by the Law colleges, under the Pro Bono Club scheme.
- Nyaya Setu – Expanding the legal services till the last mile.
- The event also released the achievement booklet of the Scheme on Access to Justice ‘Designing Innovative Solutions for Holistic Access to Justice’ (DISHA).
More than 7 lakh beneficiaries have been made aware on their legal rights, duties and entitlements through support of 14 agencies across the country.
- Partnership with IGNOU – To allow Paralegals to acquire certifications in diverse field of laws to increase their employability.
- Partnership with Bhashini – To break the barriers of language in accessibility to justice.
Bhashini, an AI powered language translation platform which will support digital inclusion in India's diverse languages.
Reference
PIB| Inauguration of 'Hamara Samvidhan, Hamara Samman' campaign
Leprosy & New Leprosy Treatment Regimen
Union Health Ministry of India announces new treatment regimen for leprosy.
- According to the WHO, it is a chronic infectious disease and is also known as Hansen’s disease.
- Caused by – Mycobacterium leprae (bacteria).
- Transmission – Through droplets from the nose and mouth during close and frequent contact with untreated cases.
- Spread – It is reported from all the 6 WHO regions and the majority of new cases are from South East Asia.
- Symptoms – It predominantly affects the skin and peripheral nerves, mucosal surfaces of the upper respiratory tract and the eyes.
- If left untreated, it may cause progressive and permanent disabilities.
- Diagnosis – Pauci-Bacillary (PB) cases shows no signs of advanced disease, while multi-bacillary (MB) cases shows signs of more advanced disease in biopsies.
- Treatment – WHO’s recommends 3 drugs dapsone, rifampicin and clofazimine called as MDT which kills the pathogen and cures the patient.
- The WHO has been providing MDT free of cost and single 3-pack kit to be given to all leprosy patients under ‘Uniform MDT’ scheme.
New Leprosy Treatment Regime
- It introduces a 3-drug regimen for Pauci-Bacillary (PB) cases in place of a 2-drug regimen for 6 months.
- Aim – To stop its transmission at the sub-national level by 2027, 3 years ahead of the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals.
- Approval - WHO had agreed to supply the revised drug regimen from April 1, 2025 and India will implement the same.
Leprosy is now considered a rare disease in India with a prevalence rate of 1 case in a population of 10,000 people since 2005. India aims to eradicate leprosy by 2027.
References
- WHO| Leprosy
- The Hindu| New Leprosy Treatment Regimen
Strength of Supreme Court
Recently, the Centre had cleared the appointment of Karnataka High Court Chief Justice Prasanna B Varale as judge of the Supreme Court (SC) which now attains its full strength.
- Supreme Court (SC) – It came into existence on 26th January, 1950 and was inaugurated on 28th January 1950.
- Determined by
- Article 124 of Indian Constitution
- The Supreme Court (Number of Judges) Act, 1956.
- Original strength – Original Constitution of 1950 envisaged a SC with 8 Judges, a Chief Justice and 7 puisne Judges.
- Power to change – Parliament can increase the strength as provided by the Indian Constitution.
- Evolution – The Supreme Court (Number of Judges) Act, 1956 has been amended in 6 instances to fix the maximum ceiling.
- It increased from 8 in 1950 to 11 in 1956, 14 in 1960, 18 in 1978, 26 in 1986, 31 in 2009 and 34 in 2019.
- Current Strength – As of 2024, it is 34 which includes 33 SC judges and 1 Chief Justice of India.
|
Appointment of SC Judges
|
- Eligibility
- A person must be a citizen of India and
- For atleast 5 years, a Judge of a High Court or of 2 or more such Courts in succession (or)
- An Advocate of a High Court or of 2 or more such Courts in succession for at least 10 years (or)
- He must be, in the opinion of the President, a distinguished jurist.
- Recommendation by – SC collegium headed by Chief Justice of India along with 4 other senior most SC Judges.
- Centre for Research & Planning of the SC – It prepares a compilation of relevant background material to assist the Collegium.
- Appointed by – President of India, after consultation with Chief Justice of India.
|
References
- The Indian Express| Appointment of SC Judge
- SCI| Evolution of SC Strength
Karpoori Thakur & Bharat Ratna Awards
Recently, the President of India has conferred Bharat Ratna posthumously to former Bihar CM Karpoori Thakur.
- A legislator – From 1952 and remained one till his last Assembly election in 1985, also has served as the CM of Bihar twice.
- Contribution – Often remembered as the ‘voice of the oppressed and the downtrodden’ and thus called as ‘Jannayak’.
- He is widely considered as the pioneer of reservations for OBC and EBC (economically backward classes) in the country.
- Socialist Icon – He was firmly against dynastic politics.
- Some current schemes in Bihar bear the mark of Thakur’s socialist politics, like waiving of school fees for girls until their post-graduation and 50% reservation to women in panchayats.
Bharat Ratna Awards
- It is the highest civilian Award in India, instituted in 1954.
- Eligibility – Any person without distinction of race, occupation, position or sex is eligible for these awards.
- It is awarded in recognition of exceptional service/performance of the highest order in any field of human endeavour.
- Recommendation – By Prime Minister himself to the President, no formal recommendations for this are necessary.
- Annual numbers – It is restricted to a maximum of 3 in a particular year, but is not mandatory to award every year.
- Award – A Sanad (certificate) signed by the President and a medallion but no monetary grant is given.
- Title – The award cannot be used as a prefix or suffix to the recipient's name as per Article 18 (1) of the Constitution.
- However, one may use the expression “Awarded Bharat Ratna by the President” or “Recipient of Bharat Ratna Award”.
- Posthumous awards – Though original statutes did not provide for this, 1955 amendment permitted them.
Bharat Ratna was previously awarded in 2019 to Shri Nanaji Deshmukh (posthumously), Dr Bhupendra Kumar Hazarika (posthumously) and Shri Pranab Mukherjee. It has been granted to 49 individuals so far (2024), with 17 posthumously.
References
- The Indian Express| Bharat Ratna Award to Karpoori Thakur
- Hindustan Times| Bharat Ratna Award
Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP) Scheme
Recently, a government official confirmed that there is no relook at duty remission scheme (RoDTEP) needed due to US, EU action of imposing countervailing duties on Indian exports.
- Announced in – 2021, initially notified till 2023 now extended until June, 2024.
- Aim – To provide comprehensive support to exporters by remitting duties and taxes incurred during the production and distribution of exported products.
- Administered by – Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
- RoDTEP Committee’s primary responsibility is to review and recommend ceiling rates for different export sectors.
- RoDTEP rates notified by – Department of Commerce.
- WTO compatible – It replaced the WTO-incompatible Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS) scheme.
- Budget – For FY 23-24, Rs 15,070 crore was allocated to boost exports of items such as pharmaceuticals, organic and inorganic chemicals and articles of iron and steel among other items.
- Coverage – Taxes, duties, and levies at the central, state, and local levels, which are not refunded through other existing mechanisms.
- It refunds embedded duties and taxes, such as VAT on fuel used in transportation, mandi tax and duty on electricity.
- Rebate is based on the allowed % of FOB (Freight On Board) value of exports and issued in the form of a transferable duty credit/electronic scrip (e-scrip).
Freight on Board (FOB) defines the point in the supply chain when a buyer or seller becomes liable for the goods being transported. Purchase orders between buyers and sellers specify the FOB terms and help determine ownership, risk, and transportation costs.
Countervailing duties (CVDs) are tariffs on imported goods that are imposed to offset subsidies given by the exporting country's government, aimed at protecting the domestic industry.
References
- The Indian Express| No relook on RoDTEP needed
- ICMAI| Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products
|
Other Important Topics
|
|
National Voters’ Day (NVD)
- Election Commission of India is celebrating 14th National Voters’ Day (NVD) recently.
- National Voter's Day (NVD), observed annually on January 25th to mark the foundation day of the Election Commission of India (ECI).
- Aim - To create electoral awareness amongst citizens and encourage them to participate in the electoral process.
- The 2024 theme is 'Nothing Like Voting, I Vote For Sure,' emphasizing commitment.
|
|
EXERCISE- DESERT KNIGHT
- Indian Air Force (IAF) recently conducted Exercise Desert Knight along with French Air and Space Force (FASF) and United Arab Emirates (UAE) Air Force.
- Its main focus is to improve collaboration and interoperability between the 3 air forces.
|
|
Melanistic Tiger Safari
- Odisha recently announced to establish a melanistic tiger safari, 1st of its kind in the world in Similipal Tiger Reserve.
- The Similipal Tiger Reserve is the only home for melanistic tigers in wild in the world.
- Melanistic tigers are a rare color variant of Bengal tigers, also known as black tigers because their stripes are darker than those of a normal tiger.
- Melanistic tigers are caused by a single mutation in the Transmembrane Aminopeptidase Q (Taqpep) gene, which is called as Pseudo Melanism.
|
|
National Tourism Day
- The National Tourism Day is celebrated on January 25, while the World Tourism Day is celebrated on September 23.
- The main focus of celebrating this day in India is to educate people about the benefits of traveling, to appreciate the country’s beauty and spread awareness of the importance of tourism.
- The theme of 2024 is “Sustainable Journeys, Timeless Memories.”
|
|
Operation Sarvashakti
- Indian Army launches 'Operation Sarvashakti' to counter militancy on both sides of Pir Panjal range in Jammu & Kashmir.
- The operations are likely to follow in the footsteps of Operation Sarpvinash, initiated in 2003 to eradicate terrorists from the same locations in the Pir Panjal range's southern reaches.
|
|
Arambai Tenggol
- Arambai Tenggol (dart wielding cavalry) is a Meitei activist organization in the Manipur.
- The organization is often described as radical or a radical armed militia.
- It is also a revivalist organization that aims to reestablish the pre-Hindu, native Sanamahi religion among the Meiteis.
- Arambai is a dart weapon used by the Meitei cavalry soldiers of Kangleipak.
|
|
Kyanjin glacial lake
- Kyanjin glacial lake is located above Kyanjin Gompa, halfway up the Langtang valley in Nepal.
- The lake is drained to provide clean hydropower for Langtang and Kyanjin, two villages in the high Kyanjin Valley.
|
|
Wandering Albatross
- The wandering albatross (Diomedea exulans) is the world’s largest flying bird, with a wingspan reaching an incredible 3.5 metres.
- It is also known as the snowy albatross and the white-winged albatross and can be found in all oceans except the North Atlantic.
- Conservation Status
|
|
Gigantopithecus blacki
- Gigantopithecus blacki, also known as "Giganto", was a giant ape that lived in southern China during the Pleistocene Epoch (2.6 million to 11,700 years ago).
- It was a distant human ancestor and the largest primate that ever lived and the mightiest of all the primates.
- It was a relative of today's orangutans and G. Blacki went extinct between 295,000 and 215,000 years ago.
|
|
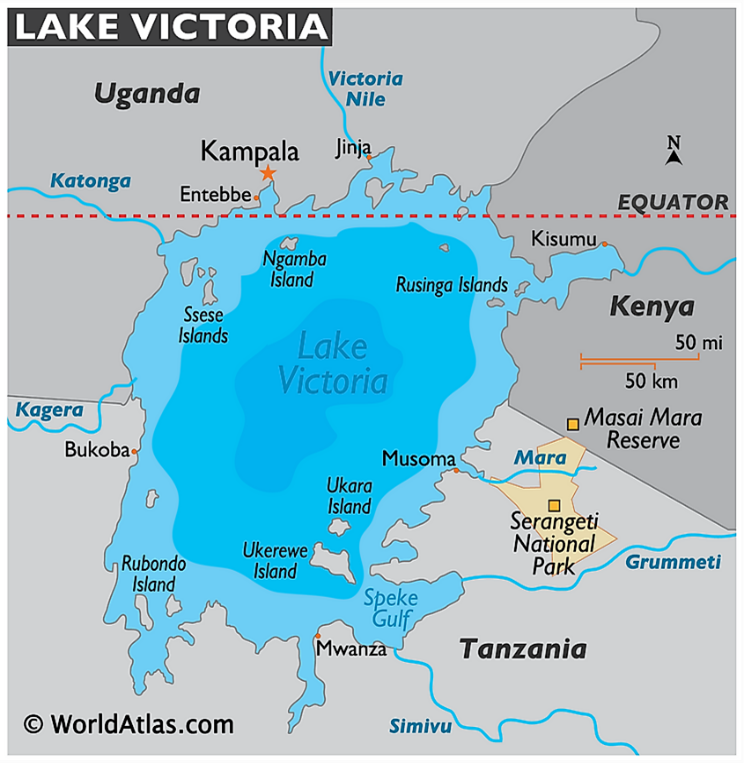
Lake Victoria
- Lake Victoria in Africa is the world's largest tropical lake and the 2nd -largest freshwater lake after Lake Superior by surface area.
- It's shared by Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda, and touches the equator on its northern side.
- It's the chief reservoir of the Nile.
- It is home to the world's largest freshwater fishery.
|