Schemes for improving farmers’ lives and livelihoods
The Union Cabinet approved 7 schemes to improve farmers’ lives and increase their incomes.
Digital Agriculture Mission
- The mission aims to integrate modern technologies such as AI and big data into the farming process to improve decision-making and efficiency.
- The project has 3 main pillars
- Agri Stack
- Krishi Decision Support System
- Soil Profile Maps
Crop Science for Food and Nutritional Security
- The investment is aimed at bolstering agricultural research and education, with a focus on various key areas critical to ensuring food security in the future.
- Research and education- Enhancing academic and research capabilities in agriculture.
- Plant genetic resource management- Conserving and utilising genetic resources for crop improvement.
- Genetic improvement for food and fodder crops- Focusing on pulses, oilseeds, and commercial crops.
- Research on insects, microbes, pollinators, etc.- Addressing issues that impact crop health and productivity.
Strengthening Agricultural Education, Management and Social Sciences
- It target to strengthening agricultural education, management, and social sciences under the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- This initiative aims to modernise agricultural education in line with the New Education Policy 2020.
- It will incorporate the latest technologies, including digital public infrastructure, artificial intelligence (AI), big data, and remote sensing.
Sustainable Livestock Health and Production
- This project focuses on
- Animal health management and veterinary education- Improving animal healthcare and veterinary education.
- Dairy production and technology development- Enhancing dairy production capabilities.
- Animal genetic resource management- Managing and improving animal genetics.
- Animal nutrition and small ruminant production- Developing sustainable practices for animal nutrition and the production of small ruminants.
Sustainable Development of Horticulture
- The initiative will cover a wide range of horticultural activities, including the cultivation of tropical, sub-tropical, and temperate crops, as well as root, tuber, bulbous, and arid crops.
- The project will also focus on vegetables, floriculture, mushrooms, and the development of plantation, spices, medicinal, and aromatic plants.
Krishi Vigyan Kendra and Natural Resource Management
- These projects aim to provide farmers with the necessary knowledge and tools to manage their resources effectively and sustainably.
Reference
PIB | Cabinet approves seven agricultural projects
Drug Repurposing
Researchers at the Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST) have found the repurpose potential of an antidepressant drug for cancer management.
- Drug Repurposing – It is the technique of using an existing drug or drug candidate for a new treatment or medical condition for which it was not indicated before.
- It is also known as drug repositioning or drug reprofiling.
- Drug repurposing bypasses the pre-clinical work and facilitate targeted treatment.
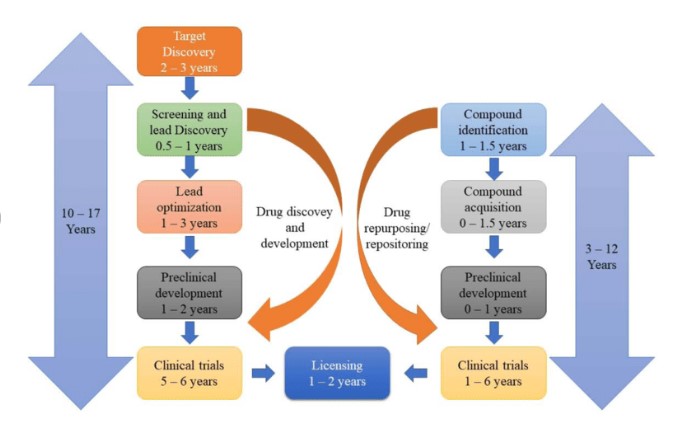
- Application – Pharmaceutical companies are undertaking drug repurposing projects for rare diseases, oncology, infectious and autoimmune diseases and more.
- Benefits - Fasten the drug discovery process and find quicker solutions.
- Helps in quickly identify compounds with an established safety profile and known therapeutic advantages.
- It is particularly useful where traditional drug development is not cost-effective.
|
Selegiline Repurpose
|
- Selegiline (L-deprenyl) – It is an antidepressant drug from a class of drugs called monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors.
- Researchers at IASST have found the repurposing potential of it for Cancer treatment.
- IASST -Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST) in Guwahati.
- It is an autonomous institute under the Department of Science & Technology (DST), Govt. of India.
- Function - Selegiline interacts with genes intricately linked to various types of cancer.
- Particularly, it can induce cell death in breast cancer cells.
|
References
PIB| Repurposing antidepressant drug for treating cancer
AgriSURE Fund
Recently, the Union government launched the AgriSURE Fund and Krishi Nivesh Portal.
- AgriSURE Fund- Agri Fund for Startups and Rural Enterprises (AgriSURE) is a fund supporting agri start-ups and rural enterprises.
- Aim - AgriSURE aims to foster innovation and sustainability in India's agricultural sector.
- The fund is structured to support approximately 85 agri startups with investment sizes of up to Rs 25 crore each.
- Managed by - NABVENTURES, a wholly owned subsidiary of NABARD.
- Ministry – Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare.
- Features - It will support through investments in sector-specific, sector-agnostic, and debt Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs).
- The initiative includes direct equity support for start-ups in agriculture and allied sectors.
- The fund will offer both equity and debt support, focusing on high-risk, high-impact activities in the agriculture value chain.
|
Quick Facts
|
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF) scheme – It was launched in 2020 for creation of Post-harvest Management infrastructure and Community farming assets.
- Krishi Nivesh Portal - This portal will be a one stop place for availing the benefits promulgated by different Government departments and ministries in agriculture sector.
|
Reference
PIB | AgriSURE Fund
Digital Agriculture Mission (DAM)
Recently, Union Cabinet has approved the Rs 2,817-crore Digital Agriculture Mission.
- Aim - Creation of Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in the farm sector.
- It is conceived as an umbrella scheme to support digital agriculture initiatives, such as
- Creating Digital Public Infrastructure
- Implementing the Digital General Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES)
- Taking up other IT initiatives.
- Ministry - Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare.
- Digital General Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES) – It is a tech-based ecosystem to provide accurate estimates of agricultural production.
- Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for Agriculture – It aims to provide comprehensive and useful data on farmers comprising of
- Authenticated demographic details
- Land holdings
- Crops sown
- It will include cultivators & tenant farmers, as per the policy of the State Government.
- Stakeholders - Central Government, State Governments, and Academic and Research Institutions.
- Funding – Shared between Union and State/UTs.
- Components of DAM.
- AgriStack
- Krishi Decision Support System (DSS)
- Soil Profile Maps
- Each of these DPI components will provide solutions that will allow farmers to access and avail of various services.
- AgriStack - It is a farmer-centric DPI being built in a federated structure.
- It is collaborative project between the various agencies of the Central and State Governments.
- Agristack consists of three foundational registries or databases in the agriculture sector.
- Farmers’ Registry - Under Farmer’s Registry, farmers will be given a digital identity (Farmer ID) similar to Aadhaar.
- This will be linked dynamically to the State’s land records, livestock ownership, crops sown, demographic details, family details, schemes and benefits availed etc.
- Geo-referenced village maps - The maps will link geographic information on land records with their physical locations.
- Crop sown Registry - Crops sown by farmers will be recorded through mobile-based ground surveys to be conducted in each season.
- Implementation – All these registries are created and maintained by the State Governments/ Union Territories.
- Krishi Decision Support System (Krishi DSS) – It will create a comprehensive geospatial system to unify remote sensing-based information on Crops, Soil, Weather, water resources, etc.
- Soil Profile Map - Detailed Soil Profile Map on a 1:10,000 scale of about 142 million ha of the country's agricultural land will be prepared.
- Benefits – It will have a catalytic effect in creating both direct and indirect employment in the agriculture sector.
- Make service delivery mechanisms more efficient and transparent for the farmers and the stakeholders in the agriculture sector.
- Obviating cumbersome paperwork and reduces physical visit to various offices or service providers.
- Help government agencies make schemes and services more efficient and transparent.
- Helps in accurate crop production estimation and evaluate irrigation needs according to the crop and season.
- Enables the stakeholders in the agriculture ecosystem to establish efficient value chains for agricultural inputs and post-harvest processes.
References
- Indian Express | Digital Agriculture Mission
- PIB | Digital Agriculture Mission
Su-30MKI Fighter Aircraft
The Cabinet Committee on Security approved the procurement of aero engines for the Sukhoi Su-30 MKI fighter jets under the ‘Buy (Indian)‘ category from Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) recently.
The "Buy (Indian)" category is a category in the Defence Procurement Procedure that refers to the purchase of products from Indian vendors.
- The Sukhoi Su-30MKI is a two-seater, twinjet multirole combat fighter aircraft.
- Developed by - The Sukhoi Design Bureau, Russia and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- It is one of the most advanced and versatile fighter jets in the IAF's inventory.
- It is equipped with thrust vectoring control and canards.
- Maiden Flight- November 2000.
- Service Entry- September 2002.
- Maximum Speed- Mach 2.
- Range- 3,000 km.
- It supports all-weather, air-to-air and air-to-surface deep interdiction missions.
Su-30 MKI vs Rafale
|
Features
|
Su-30MKI
|
Rafale
|
|
Design and Role
|
- The Su-30MKI is primarily an air superiority fighter but has also been adapted for various roles, including air-to-ground and maritime strike missions.
- It has a larger airframe and is designed for long-range missions and heavy payloads.
|
- The Rafale is a versatile fighter capable of performing a wide range of missions, including air superiority, ground attack, reconnaissance, and nuclear deterrence.
- It is known for its advanced avionics and sensor suite, making it a highly capable multirole aircraft.
|
|
Weaponry
|
- The Su-30MKI can carry a wide array of air-to-air and air-to-ground missiles, rockets, bombs, and even anti-ship missiles, giving it considerable firepower.
|
- The Rafale is equipped with advanced weaponry, including Meteor beyond-visual-range air-to-air missiles, Scalp cruise missiles for long-range strike capability, and various precision-guided munitions.
|
|
Maximum speed
|
|
|
|
Armament carrying
|
|
|
|
Generation
|
- 4th -generation fighter aircraft
|
- 4.5-generation fighter aircraft
|
|
Range
|
- 3,000 km at a high altitude
- 1,270 km at low altitude
|
- 1,850 km on penetration mission (combat range)
|
|
Hardpoints
|
|
|
|
Ferry range
|
|
|
|
Service ceiling
|
|
|
|
Rate of climb
|
|
- 304.8 m/s (60,000 ft/min)
|
References
- The Hindu | Su-30MKI fighter jets
- Airforce Technology | Su-30MKI Fighter Aircraft
