Mice study on COVID’s True Cause
A recent study suggests that fibrin, a key player in blood clotting, may be the primary driver of long COVID symptoms, rather than just a consequence of the disease.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
- It is an infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
- Most people infected with the virus will experience mild to moderate respiratory illness and recover without requiring special treatment.
- However, some will become seriously ill and require medical attention.
- Older people and those with underlying medical conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic respiratory disease, or cancer are more likely to develop serious illness.
- Anyone can get sick with COVID-19 and become seriously ill or die at any age.
- The SARS-CoV-2 virus is well-known as a vasculopathic agent, a damager of blood vessels.
- The dominant respiratory symptoms associated with COVID-19 are largely due to clotting and inflammation in the blood vessels of the lungs (rather than the direct involvement of the airways).
- Its more severe complications, including neurological ones like stroke, are rooted in vasculopathy as well.
Recent findings
- Role of fibrin- The study noted that fibrinogen binds with the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, forming fibrin, which causes inflammation and complications in the lungs and brain.
- This contradicts the earlier view that inflammation due to the virus was responsible for clotting.
Fibrinogen is a glycoprotein complex and a soluble protein is produced in the liver, that circulates in the blood of all vertebrates
- Spike protein interaction- The study demonstrates that the spike protein binds with fibrinogen in the lungs, altering the clot structure and triggering an immune response.
- This interaction may drive long COVID symptoms even after active infection is gone.
A spike protein is a protein that forms a large structure known as a spike or peplomer projecting from the surface of an enveloped virus.
- Implications for treatment- A monoclonal antibody was found to block the interaction between the spike protein and fibrinogen without affecting normal clotting functions.
- This antibody is undergoing clinical trials, offering potential for new treatments.
Monoclonal antibodies are proteins made in a lab that bind to one antigen only.
- Limitations- The findings come from a preliminary mouse model, not long-term human studies, and require further research for confirmation.
- The study offers hope for a breakthrough in managing long COVID, but more research is necessary to validate its conclusions
Reference
The Hindu | Study on COVID’s True Cause
Green Haryana manifesto, 2024
In a first-of-its-kind initiative, People for Aravallis group initiated the process of creating ‘Haryana Green Manifesto 2024’ to address urgent environmental concerns.
- Aim- To include their environmental demands in the manifestoes of various political parties ahead of the upcoming Haryana Assembly election.
Environmental concerns in Haryana
- Degradation of land - Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas of India, 2021, shows that 8.24% of the total geographical area of Haryana has degraded.
- Air pollution- Haryana is home to 8 of the 50 most polluted places in the world.
- Waste management- Unsegregated waste is dumped across the state, leading to toxic landfills, affecting natural ecosystems and water bodies.
- Groundwater depletion- Groundwater levels have dropped significantly, especially in South Haryana, reaching depths of 1,500-2,000 feet.
- Industrial pollution- Chemical waste from industries is polluting water sources, affecting both humans and animals with ailments like skin diseases and breathing problems.
Green Manifesto, 2024
- Critical Ecological Zones - The main demand is to legally designate the Aravallis including the Bhood areas and the Shivaliks as ‘Critical Ecological Zones’.
- Deemed forests - It asks for legal protection be given to all the state’s forests by including un-notified forests as ‘deemed forests’ under the Punjab Land Preservation Act (PLPA).
- Tree Act- A demand for a strict ‘Tree Act’ for Haryana, similar to the Delhi Preservation of Trees Act 1994.
- It asks to declare all open natural ecosystems (ONEs), such as the blackbuck natural habitat in Fatehabad district, as conservation or community reserves.
Haryana has the lowest forest cover in India, at just 3.6%, compared to national average of 21%.
- Increasing tree Cover- A call for an action plan to reach a target of 10% native forest and tree cover within 4 years.
- Crop-Diversification - It asks for promoting crop diversification as a key climate-change adaptation strategy by ensuring
- Guaranteed purchase of every crop grown by the farmers on the MSP announced by the Centre,
- Creating an action plan to restore soil and its microbial diversity,
- Incentivising natural farming practices that improve soil health.
Reference
The Hindu | Green Haryana manifesto
Digital Solutions for Universal Access to Healthcare
Recently, a National Conference on Universal Access to Healthcare was organized by National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) in collaboration with other stakeholders.
- Objective- To bring together practitioners, experts, policymakers, and innovators in the field of healthcare and digital healthcare technology.
- To discuss universal access to affordable and quality healthcare, particularly in rural, remote, and hilly areas.
- Participants- National Human Rights Commission (NHRC), Sankala Foundation, supported by NITI Aayog and the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoHFW).
- Report- During the conference a report title "Leveraging Digital Solutions for Universal Health Coverage" was released by Sankala Foundation research.
The Sankala Foundation is a non-profit organisation registered in 2022 under Section (8) of the Companies Act, 2013 of India.
|
Digital Health Initiatives of India
|
- Universal access to healthcare has emerged as a basic human right.
- India has committed to achieve Universal Health Coverage by 2030, by utilizing digital health solutions to strengthen primary-level public health infrastructure.
- Bridgital Model - Ministry of Health and Family Welfare addressed overcrowding in AIIMS, New Delhi, by the Bridgital Model for registration and appointments.
- Digital Nerve Centre (DiNC) – It is a unique healthcare delivery model to enable quick access to primary health care and provide a well coordinated continuum of care for citizens visiting government health facilities.
- Global Initiative on Digital Health(GIDH) - India launched along with the WHO during the 2023 G20 Health Ministerial Meeting.
- National Digital Health Mission (NDHM)– It is implemented by National Health Authority aims to make India Self-reliant in providing universal health coverage to all the citizens in the country.
- Digital Health Incentive Scheme – It aims at digitising patients’ health records and linking them with the Ayushman Bharat Digital Health Account.
|
References
- PIB | Universal Access to Healthcare
Vishvasya Blockchain Technology Stack
Recently Government has launched Vishvasya-Blockchain Technology Stack and other block chain related Initiatives.
- Vishvasya – It is a Blockchain Technology Stack consists of blockchain related platforms and frameworks.
- It facilitates in enabling trust by developing new types of distributed software architectures and providing a single source of truth.
- Nodal Ministry - Ministry of Electronics & IT.
Blockchain is a Technology suitable for developing applications with transactional data stored across network of nodes. It provides tamper resistant storage with audit trail for future verification.
- Vishvasya contains BaaS, NBF, NBFLite, Praamaanik, National Blockchain Portal.
- Vishvasya BaaS – It is Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) model that provides security assurance of various Blockchain components across the stack.
- It enables technological support to organizations in developing and deploying Blockchain applications.
- It provides geographically distributed infrastructure designed to support various permissioned Blockchain based applications.
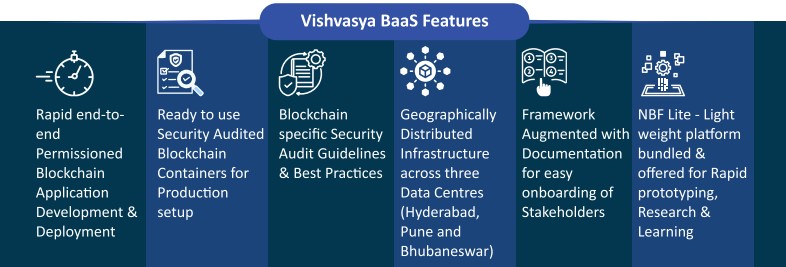
- National Blockchain Framework – It aims to create trusted digital platforms for promoting research and application development.
- It facilitates state of the art, transparent, secure and trusted digital service delivery to citizens.
- Features
- Distributed Infrastructure
- Core Framework functionality
- Smart Contracts & API Gateway
- Security, Privacy & Interoperability
- Applications development offering Blockchain as a Service (BaaS).
- NBF currently supports two permissioned Blockchain platforms and is extensible.
- NBFLite – It is a Blockchain sandbox platform developed especially for startups/academia for rapid prototyping of applications, carrying out research and capacity building.
- Developed by - Collaborating efforts of C-DAC, NIC, IDRBT Hyderabad, IIT Hyderabad, IIIT Hyderabad and SETS Chennai.
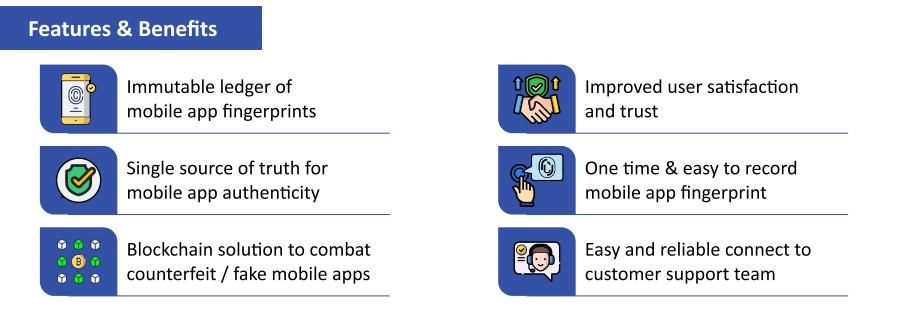
- Praamaanik- Praamaanik is a solution that harnesses Blockchain technology to verify mobile app origins.
- It is powered by the National Blockchain Framework.
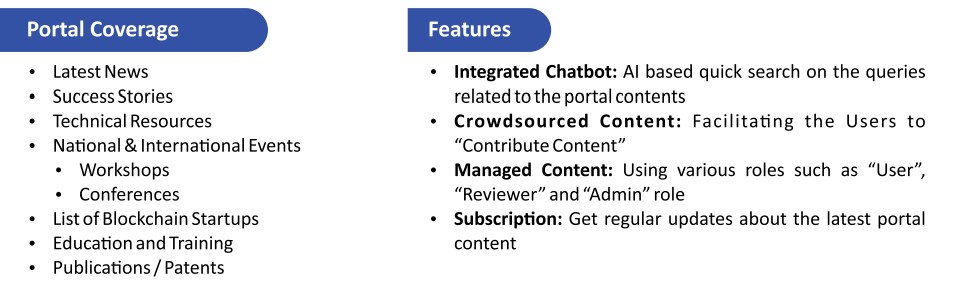
- National Blockchain Portal - It is developed to manage the contents related to the National Blockchain Framework initiatives.
References
PIB | Vishvasya Blockchain Technology Stack
Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM)
Recent research report found that districts with more toilets constructed under SBM corresponded fewer infant deaths.
- Swachh Bharat Mission - is a massive mass movement that seeks to create a Clean India by 2019.
- Components - The mission will cover all rural and urban areas.
- SBM Rural - Implemented by Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation.
- SBM Urban - Implemented by Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs
- Swachh Bharat Mission Phase I (2014-12019)
- Launched in - October 2, 2014.
- Objective – Eliminate Open Defecation by 2 October 2019.
- Swachh Bharat Mission Phase II (2019-2025)
- SBM Urban 2.0 launched on October 1, 2021 to achieve Garbage Free Status for all cities.
- SBM Gramin 2.0 was launched to transform all the villages from ODF to ODF Plus Model.
- Performance - From 2014 to 2020, the government constructed 109 million household toilets and declared that more than 600,000 villages were free from open defecation.
- Relation between SBM & IMR - Districts with over 30 per cent toilets constructed under SBM corresponded with 5.3 fewer infant deaths and 6.8 fewer child deaths per 1,000 births.
- Every 10-percentage-point increase in district-level toilet access, corresponded with a reduction in district-level IMR by 0.9 points and U5MR by 1.1 points.
Reference
DownToEarth | Swachh Bharat Mission


