Dozer Push Mining Trial
Why in News?
Recently, India has successfully conducted the 1st trial blast of the Dozer Push Mining Method.
- Dozer Push Mining – It is a cutting-edge technological solution that integrates advanced digital technologies to revolutionise coal extraction processes.
- It is a viable alternative to the conventional truck-shovel mining technique or shovel-dumper and dragline methods.
Truck-Shovel (TS) systems are the most common mining system used to remove the upper and thinner overburdens found within a deposit. Dragline methods remove the much deeper overburdens.
- Trial in – Parsa East and Kete Basen (PEKB) Coal Mine in Chhattisgarh by Adani Natural Resources.
- Developed by – Dhanbad based CSIR-Central Institute of Mining and Fuel Research (CSIR-CIMFR).
- Objective – To ensure the vibration and flyrock which are controlled within safe limits.
- Key technical innovation - Automated drilling process with unmanned operations.
- Precise cast/throw blasting techniques for optimal material displacement.
- Automated dozer for efficient material movement.
- Integration of advanced digital technology for operational oversight.
- Trial – It involved drilling of 108 holes using automated drill machine, followed bycast/throw blasting using 60 tons of bulk emulsion explosives.
- The blasted material will be pushed in decoaled area using specially designed, large-sized automated dozer machine.
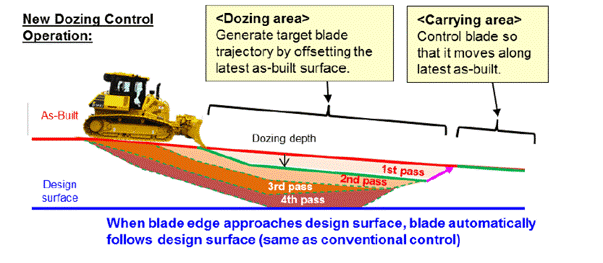
- Benefits – Faster coal recovery rates, accelerating project timelines.
- Reduced weather-related production delays, ensuring consistent output.
- Enhanced dragline machine utilisation, maximising equipment efficiency.
- 7-10% reduction in operational costs and lower unit production costs, improving competitiveness in the market.
Reference
PIB| 1st Trial Blast of Dozer Push Mining Method in India
World Braille Day
Why in News?
Recently, the World Braille Day was observed on January 4th, to commemorate the birthday of Louis Braille.
- Braille – It is a tactile representation of alphabetic and numerical symbols using 6 dots to represent each letter, number and even musical, mathematical and scientific symbols.
- Significance – It is used by blind and partially sighted people to read the books and periodicals as those printed in a visual font.
Braille, named after its inventor, Louis Braille in 19th century in France.

According to the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPWD) Act, 2016, there are 21 types of Disabilities which includes Locomotor Disability, Visual Impairment, Hearing Impairment, Speech & Language Disability, Intellectual Disability, Multiple Disabilities, Cerebral Palsy, Dwarfism etc.
|
Initiatives for Visually Impaired Person
|
- National Association for the Blind – It aims to make approximately 10,000 pages of documents of government schemes and legal reliefs, accessible to persons with visual disabilities.
- National Institute for the Empowerment of Persons with Visual Disabilities (NIEPVD) (Divyangjan) – It works in the field of visual disability for the education, training, rehabilitation & empowerment of persons since 1943.
- Model School for the Visually Handicapped (MSVH) – It imparts education to children from the Bal Vatika to senior secondary level.
- Braille Development Unit – Contribution to the development of Braille Codes in different Indian languages.
- National Accessible Library – To provide learning materials in various accessible formats Braille, large print, audio and E-pub.
- Braille Production – NIEPVD infrastructure for printing Braille textbooks and magazines.
- It infrastructure comprises the Central Braille Press established in 1951, the Regional Braille Press established in 2008 at Chennai and 25 other Braille Presses established by the Government.
- The Braille literature in the following 14 languages, that include Assamese, Bangla, English, Garo, Hindi, Khasi, Kannada, Lusai, Nagamese, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Telugu, Tamil and Urdu.
|
Reference
PIB| Braille & Initiatives for Visually Impaired Persons
Faral Sakhi
Why in News?
Recently, the Faral Sakhi initiative was launched by Mira Bhayandar Municipal Corporation (MBMC) to empower women entrepreneurs.
- Faral Sakhi – It is a flagship initiative, aimed at empowering women entrepreneurs in the city of Mira Bhayandar, Maharashtra.
- Aim – To create permanent employment opportunities for women by engaging them in the production and sale of traditional festive snacks (‘Faral’).
- Launched by – Mira Bhayandar Municipal Corporation (MBMC), in collaboration with Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP).
- Technical training – 25 women from Mira Bhayandar have been selected to receive technical training in business operations.
- The training is facilitated by the Centre for Education, Governance, and Public Policy (CEGP Foundation).
- Supports local economy – This initiative equips participants with essential skills and knowledge to establish sustainable businesses, contributing significantly to the local economy.
- MBMC – Has established a central kitchen that allows women from self-help groups (SHGs) to produce festive snacks (‘Faral’) professionally.
- Award to Reward (ATR) initiative of WEP – Faral Sakhi initiative was unveiled the ATR.
Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP)
- Focuses – On empowering women entrepreneurs by addressing information gaps and providing support across critical areas such as:
- Access to finance, market linkages, training and skilling, mentoring and networking, compliance and legal assistance and business development services.
- An initiative of NITI Aayog.
Over 30,000 women entrepreneurs already engaged with Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP).
- Award to Reward initiative is a component under it.
|
3 Guiding Principles of WEP
|
|
Iccha Shakti
|
Power of motivation to start & scale business.
|
|
|
Gyaan Shakti
|
Power of knowledge to overcome information asymmetry.
|
|
|
Karma Shakti
|
Power of action through handholding & support.
|
|
References
- PIB| Faral Sakhi Initiative
- The Statesman | Faral Sakhi Initiative
Rat-Hole Mining
Why in News?
Recently, several workers have been trapped for more than 12 hours in a rat-hole mine after it was flooded with water in Dima Hasao district, Assam.
- Rat-hole mining – It is a method of extracting coal from narrow and horizontal seams.
- The term “rat hole” refers to the narrow pits dug into the ground, typically just large enough for 1 person to descend and extract coal.
- It is prevalent in Meghalaya.
- Process – Once the pits are dug, miners use ropes or bamboo ladders to reach the coal seams.
- The coal is then manually extracted using primitive tools such as pickaxes, shovels and baskets.
|
Types of Rat-Hole mining
|
|
Side cutting
|
Box cutting
|
|
Narrow tunnels are dug on the hill slopes and workers go inside until they find the coal seam.
|
A rectangular opening is made.
|
|
Size – Very thin, less than 2 m in most cases.
|
Size – Varying from 10-100 sqm and through that a vertical pit is dug, 100-400 feet deep.
|
- Issues – The mines are typically unregulated and lacking safety measures such as proper ventilation, structural support or safety gear for the workers.
- The mining process cause land degradation, deforestation and water pollution.
- Unregulated mining lead to water with high concentrations of sulphates, iron, and toxic heavy metals, low dissolved oxygen, and high biochemical oxygen demand.
The two rivers, Lukha and Myntdu, became too acidic to sustain aquatic life because of unregulated mining in Meghalaya.
- Its hazardous working conditions, environmental damage and numerous accidents leading to injuries and fatalities.
- Ban – The National Green Tribunal (NGT) banned the practice in 2014 and retained the ban in 2015.
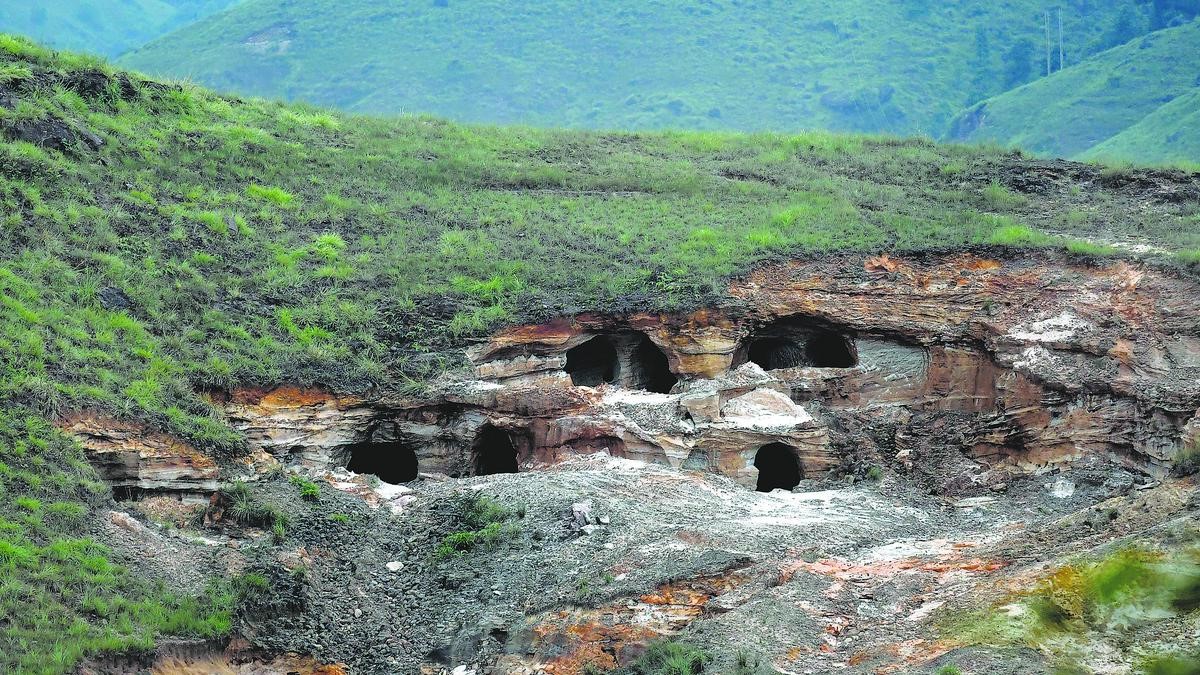

Reference
The Indian Express| Rat Hole Mining trapped workers in Assam
Related News Article
Rat Hole Mining to rescue trapped workers in Uttarakhand
|
Environment
(Initiatives for Water Conservation)
|
|
Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA)
- Launched – In 2019.
- A nationwide campaign focusing on saving and conserving rainwater.
- Tagline - Catch the Rain.
- 2024 Theme - Nari Shakti se Jal Shakti.
AMRUT 2.0
- AMRUT – Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation.
- Launched in – 2021 for 5 years (2021-22 to 2025-26).
- Aim – To provide universal coverage of water supply through functional taps to all households in all the statutory towns.
- Supports – Rainwater harvesting via storm-water drains and promotes groundwater recharge through 'Aquifer Management Plans.
Atal Bhujal Yojana
- Launched in - 2019.
- Targets- Water-stressed Gram Panchayats in 80 districts across 7 states, focusing on groundwater management.
Master Plan for Artificial Recharge to Groundwater
- Developed in – 2020.
- Developed by – Central Ground Water Board.
- Plan – 1.42 crore rainwater harvesting and recharge structures to harness 185 BCM of rainfall.
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY)
- Launched in – 2015.
- Aim – To expand irrigation coverage and improve water use efficiency.
- Motto – Har Khet Ko Pani, which means Repair, Renovation and Restoration (RRR) of Water Bodies.
- Components – Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme, Watershed Development and Per Drop - More Crop (Micro Irrigation).
Ground Water Management and Regulation (GWMR)
- A Central Sector Scheme.
- Period – 2021-26.

Bureau of Water Use Efficiency (BWUE)
- Setup under – National Water Mission, 2022.
- Act as a facilitator – For promotion of improving water use efficiency across various sectors namely irrigation, drinking water supply, power generation, industries, etc. in the country.
Mission Amrit Sarovar (2022)
- Launched in – 2022.
- Objectives – To conserve water for the future.
- To create or rejuvenate 75 Amrit Sarovars in every district for water harvesting and conservation.
National Water Awards
- Launched in – 2018, by the Department of Water Resources.
- Objectives – To raise public awareness about the importance of water and motivate the adoption of best practices in water usage.
- To recognize and encourage exceptional contributions towards water conservation and management across India.
National Compilation on Dynamic Ground Water Resources of India
- Launched in – 2024.
- Launched by – Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) in collaboration with State Groundwater Departments.
- It provides a comprehensive state-wise overview of Ground Water, serving as a foundation for effective policies and management strategies.
|


