Why in News?
Recently, India has completed the ‘Genome India’ database’.
A genome is the complete set of genetic information in living organisms, which is stored in long molecules of DNA called Chromosomes.
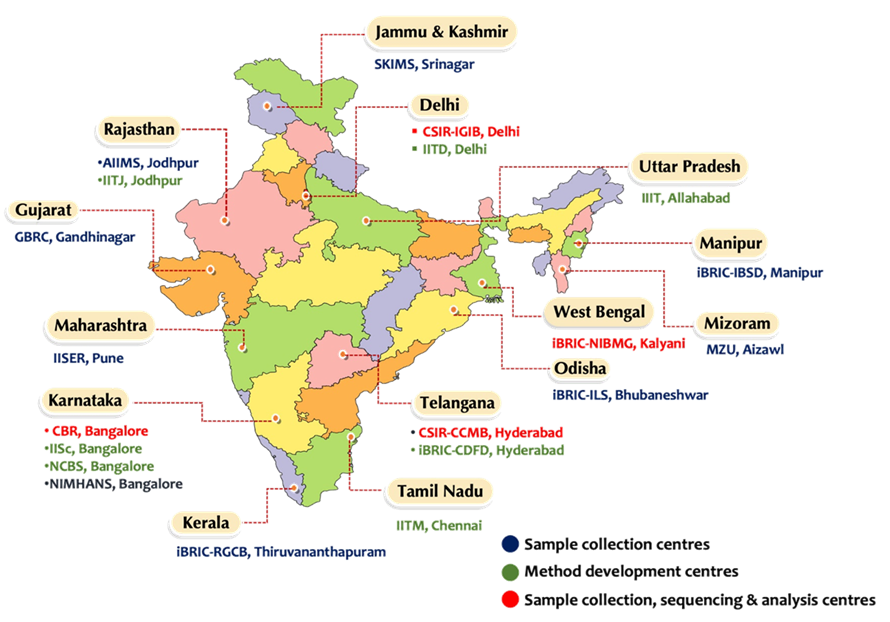
In Biotech, India now ranks 12th globally and 3rd in the Asia-Pacific region.
Why in News?
The Indian Kalaripayattu Federation (IKF) accuses the Indian Olympics Association (IOA) for placing Kalaripayattu in the demonstration section in the 38th National Games to be held in Uttarakhand.
Kalaripayattu is the oldest and most scientific of all martial arts in the world.

|
Indian Kalarippayattu Federation (IKF) |
|
Why in News?
Recently, researchers from the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) have identified 23 species of blood-sucking flies in the Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
Haematophagous means especially an insect or tick feeding on blood.

A study conducted in 2022 and 2023, revealed that 17 of the 23 species identified are known to bite humans, although no human disease transmission has been reported.
|
Bluetongue (BT) |
|
The Hindu| 23 species recorded in Andaman & Nicobar Islands
Why in News?
Recently, January 20 marked the death anniversary of Sewa Singh Thikriwala.
|
Praja Mandal Movement |
|
The Indian Express| Story of Punjab’s Sewa Singh Thikriwala
|
One Liners 21-01-2025 |
|
History, Art and Culture |
|
Excavations of a Buddhist complex in Ratnagiri, Odisha
History of Ratnagiri in Odisha
Maritime Trade of Odisha (Kalinga)
|
|
Social Issues |
|
8th edition of Pariksha Pe Charcha
|
|
Economy |
|
Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT)
|
|
Agriculture |
|
India's Coffee Production Boom India ranks 7th largest globally in coffee production, exports reaching $1.29 billion in FY24.
|
|
Environment |
|
Goby Fish Species
Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary
|