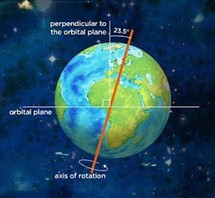
Researchers recently discovered that Earth's axis has tilted by 31.5 inches due to excessive groundwater extraction.
Recent Findings
Polar Motion is the movement of Earth's rotational axis relative to its crust. When Earth rotates on its spin axis an imaginary line that passes through the North and South Poles, it drifts and wobbles.
References
Recently, the Union Cabinet has launched a scheme National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF) under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare.
|
Natural Farming (NF) |
|
References
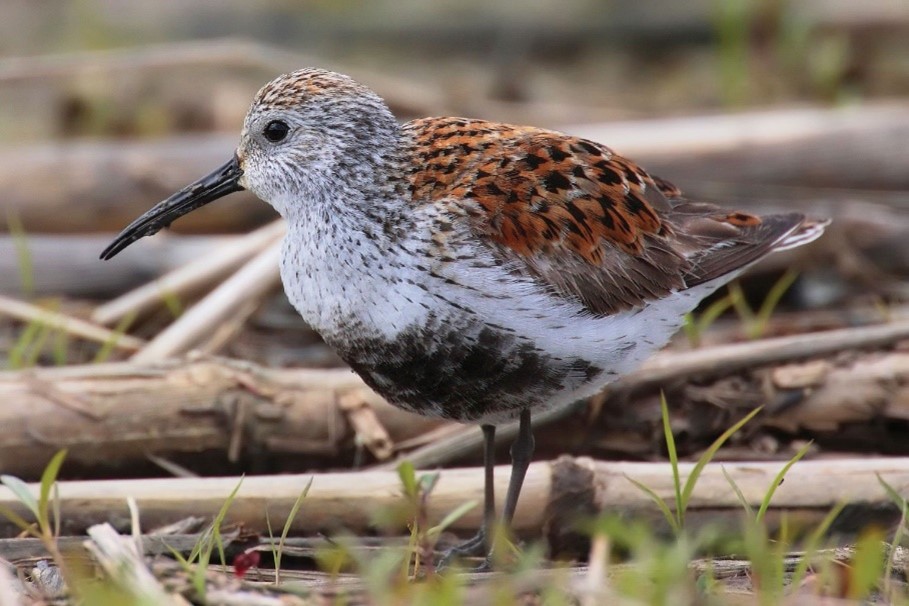
Recently, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) of Red list has updated the status of Dunlin from Least Concern to Near Threatened species spotted during Kerala Bird Race.

References
Recently, Tripura’s Reang community has demanded the government to grant recognition to their language and declare a holiday on Hojagiri Day.
Hojagiri Festival is celebrated on 18-19 October.
References
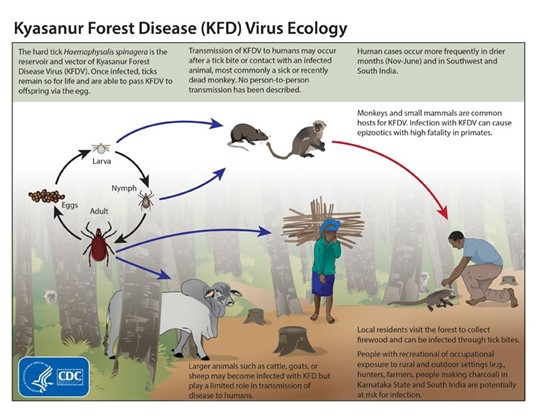
Recently, Karnataka district health officials have created awareness on high alert to prevent Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD).
References