7667766266
enquiry@shankarias.in
Prelims – Indian Polity and Governance, Public Policy.
Mains (GS II) – Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
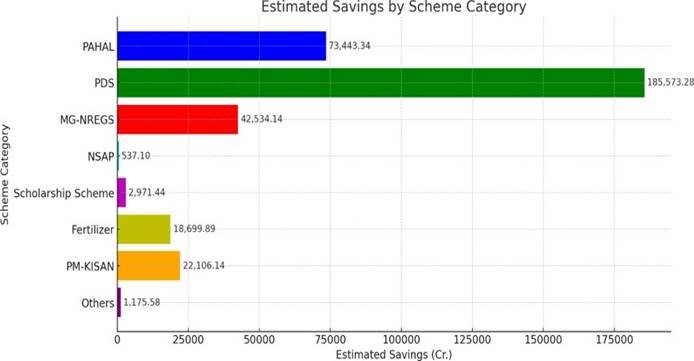
Recent report by Blue Kraft Digital Foundation (NGO) reveals India’s Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) system has helped to reduce Expenditure on subsidy.

Key findings of the report