Snakebites as a notifiable disease
The Union Health Ministry has urged states to make snakebites a notifiable disease, a disease that is legally required to be reported to the government by both private and public hospitals.
- Notifiable diseases - Infections that are likely to cause an outbreak, lead to deaths, and those that need to be investigated quickly to take appropriate public health measures.
- List of notifiable diseases differs from state to state, state governments are responsible for bringing out the notification.
- Most of them consider infections such as tuberculosis, HIV, cholera, malaria, dengue, and hepatitis among others to be notifiable.
- Snakebites - Snakebites can lead to acute medical emergencies that require immediate care.
- They can cause severe paralysis that can prevent breathing, can lead to a fatal haemorrhage, and damage different tissues.
- Snakebites need to be treated with antivenoms to prevent death and severe symptoms.
- Snakebites in India - India accounts for more than half of all snakebite deaths in the world with an average of 58,000 deaths from snakebites annually.
- According to NAPSE, the most burden of snakebite deaths states are
- Bihar, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Uttar Pradesh, undivided Andhra Pradesh (which includes Telangana), Rajasthan and Gujarat.
- It accounts for more than 70% of deaths during the period between 2001 and 2014.
- The chance of an Indian dying from snakebite is about 1 in 250.
- World Health Organisation states that around 90% of snakebites in India are caused by the 'big four' among the crawlers - common krait, Indian cobra, Russell's viper and saw scaled viper.
- The commercially available polyvalent antivenom contains venom from all 4species, and is effective against 80% of snakebites.
- National Action Plan for Prevention and Control of Snakebite Envenoming (NAPSE) with the aim of halving snakebite deaths by 2030.
Reference
The Indian Express | Snakebites
Indian star tortoise
A recent study has identified two genetically distinct groups of Indian star tortoises, northwestern and southern, the findings could help strategies on where and how to release and conserve rescued tortoises.
- Scientific Name - Geochelone elegans.
- Nomenclature - Its name comes from the star-like patterns that feature on its high-domed shell.
- The shell's upper part is called the carapace, and the bony plates that make up the shell are called scutes.
- Appearance - It has a star-shaped pattern on its shell, a rounded shell, and a tan head, limbs, and tail.
- Size - Adult female Indian star tortoises are usually larger than males, growing to be about 10–12 inches long, while males are usually 6–8 inches long.
- Distribution – It resides in northwest India (bordering Pakistan), South India, and Sri Lanka.
- Habitat- It inhabits dry areas and scrub forest.
- Diet - These tortoises are hardy herbivores, feed mostly on mixed grasses as well as weeds, flowers, leaves of succulent plants
- Hatching -Baby Indian star tortoises hatch without the star pattern on their shell and are almost completely brown in color. They develop the pattern as they grow.
- Conservation status
- IUCN – Vulnerable
- CITES - Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972 - Schedule I.
- The increasing demand for Indian star tortoise as pets has entangled them in one of the largest global wildlife trafficking networks.
- It is illegal to own one in India but also unethical since they are vulnerable in the wild.

References
- The Hindu | Indian Star Tortoise
- iNaturalist | Indian Star Tortoise
Pradhan Mantri Poshan Shakti Nirman (PM POSHAN) Scheme
The Ministry of Education has increased the funding for the Pradhan Mantri Poshan Shakti Nirman (PM POSHAN) scheme by 13.70%.
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme under which one hot cooked meal is served to students studying in Balvatika (preschool) and Classes 1 to 8.
- It is served in Government and Government-aided schools on all school-days.
- The Scheme aims at providing nutritional support and enhancing school participation of students.
- It was earlier known as Mid-Day Meal Scheme in schools.
- Ministry – Ministry of Education.
- It aims to address 2 of the pressing problems for the majority of children in India, viz. hunger and education by improving the nutritional status.
- Nutrition norm per child per day:
- For Primary - Calorie – 450; Protein - 12 gms
- For Upper Primary - Calorie – 700; Protein - 20 gms
- Objectives - Improving the nutritional status of eligible children in Government and Government aided schools.
- Encouraging poor children, belonging to disadvantaged sections, to attend school more regularly and help them concentrate on classroom activities.
- Providing nutritional support to children of elementary stage in drought-affected and disaster affected areas during summer vacation.
Reference
PIB | Pradhan Mantri Poshan Shakti Nirman (PM POSHAN) Scheme
Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL)
Recently, the University Grants Commission (UGC) finalised the guidelines for Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL) in Higher Education.
- RPL is a platform to provide recognition to the informal learning or learning through work to get equal acceptance as the formal levels of education.
- It is a skill certification component to enable Indian youth to take on industry relevant skill certification.
- Through RPL, such individuals can access higher education, earn formal qualifications, and improve their employability.
- Established Under – Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY).
- Implementing Agency - PIA can be any legal entity such as SSC, Industry Association, Training Partner, Government Body, NGO and Corporate, except Assessment Agency.
- Objectives - Align the competencies of the un-recognized workforce of the country to the standardized National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF).
- Enhance the employability and/or entrepreneurial opportunities of an individual and
- Provide opportunities for reducing inequalities based on privileging certain forms of knowledge over others.
- PMKVY assess candidates and provides a certificate and monetary reward on successful completion of assessments.
- Average monetary reward would be around Rs.2, 200 per candidate.
- Important Eligibility Criterias
- Age between 18-45 years.
- Has prior experience in the job role for which they want RPL certification and as specified by the SSCs for those job roles.
- Fulfils other criteria related to work experience as defined by the SSCs.
- RPL Process
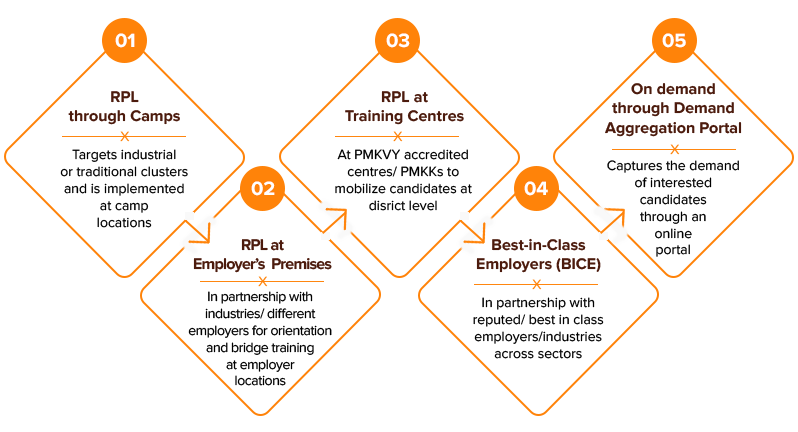
|
University Grants Commission
|
- It is a statutory organization under the Ministry of Education.
- Established in –1956.
- Aim - To coordinate, determine, and maintain standards of teaching, examination, and research in university education.
- It became an important pillar of higher education.
- It also advises the Central and State Governments regarding the measures for the development of Higher Education.
|
References
- The Hindu| Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL)
- PMKVY| Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL)
- PMKVY| Guidelines on Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL)
National Panchayat Awards
Recently, the Ministry of Panchayati Raj announced that 7 gram panchayats from Tripura have been selected for the National Panchayat Awards 2024.
- It is given annually on 24th April, to the best performing panchayats under Incentivization of Panchayats scheme.
National Panchayati Raj Day is celebrated on 24th April every year.
- It recognizes the panchayats good work for improving delivery of services and public goods.
- To assess the performance of Panchayats in attainment of SDGs, promote competitive spirit among them and catalyse the process of LSDGs.
- It aligning with 9 Localization of Sustainable Development Goals (LSDGs) themes aggregating 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Ministry – Ministry of Panchayati Raj.
- Launched in - 2022.
- Awarded by – President of India.
- The award is given to Various Gram, Block and District Panchayats of the states respectively.
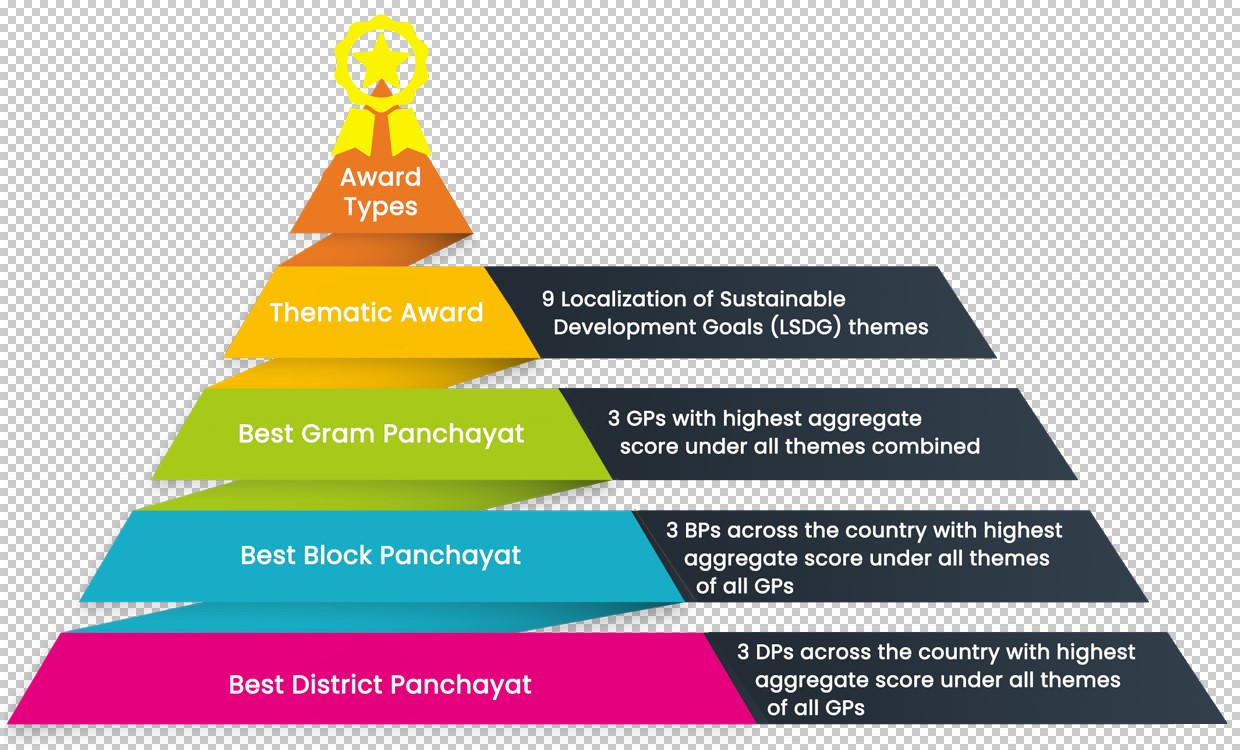
- Criteria – It is conferred with trophies, certificates and financial incentives.
- All the Panchayats ranked based on their performance under 9 LSGD themes:
- Poverty free and enhanced livelihoods Panchayat.
- Healthy Panchayat.
- Child Friendly Panchayat.
- Water Sufficient Panchayat.
- Clean and Green Panchayat.
- Self-sufficient infrastructure in Panchayat.
- Socially just and socially secured Panchayat.
- Panchayat with Good Governance.
- Women-Friendly Panchayat.
- All the Gram Panchayats mandatorily to fill the 9 award themes.
- 7 Categories
- Deen Dayal Upadhyay Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar (DDUPSVP).
- Nanaji Deshmukh Sarvottam Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar (NDSPSVP).
- Gram Urja Swaraj Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar.
- Carbon Neutral Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar.
- Panchayat Kshamta Nirmaan Sarvottam Sansthan Puraskar.
- Nanaji Deshmukh Sarvottam Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar.
- Best Participant (State/District).
- National Panchayat Awards 2024 – It is the prestigious award for the appraisal year 2022–2023.
- 1.94 lakh Gram Panchayats participated in the competition.
- It executes the digital transfer of award money to the winning Panchayats.
45 awardees selected under various categories in that 42% Panchayats are led by Women.
References
- The Indian Express| National Panchayat Awards
- MPR| Panchayat Award
- PIB| National Panchayat Awards 2024


