Why in News?
A cross-sectional study conducted among 600 older adults across 6 Indian cities has found that the prevalence of polypharmacy and unsafe self-medication is high in this population.
Ocelot
Why in News?
Recently, fewer than 100 ocelots in the United States are feline species which are in the face of extinction.
A feline is a member of the cat family Felidae, which includes lions, tigers, cheetahs, leopards, pumas, and lynxes.
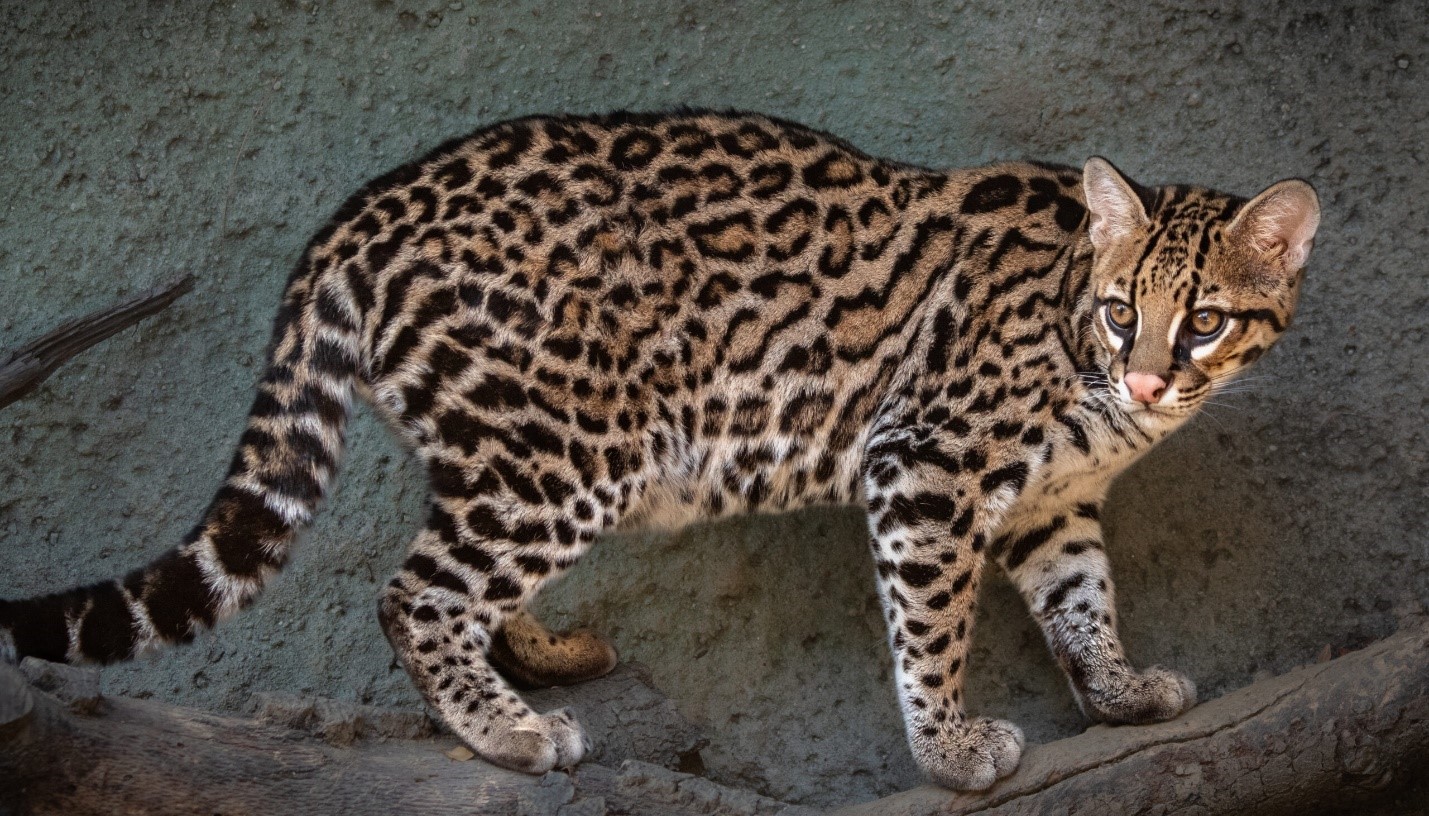

Ocelot subspecies, known as the Texas ocelot (Leopardus pardalis albescens), is endangered.
Why in News?
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways declared January 2025 as Road Safety Month, calling on all stakeholders to collaborate to make roads safer.
The Hindu | Road Safety Crises
Why in News?
Union Minister of State for Social Justice and Empowerment has recently inaugurated the Skill Training Programme under PM-DAKSH Yojana, for Persons with Disabilities (Divyangjan) in Shillong.
Why in News?
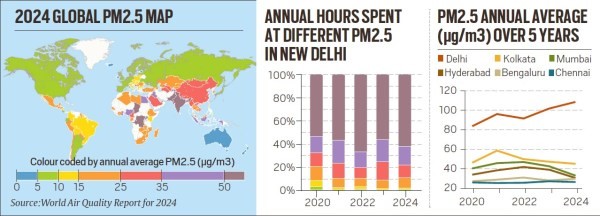
According to the recently released World Air Quality Report, 2024 13 out of world’s 20 most polluted cities are in India.
Key Findings of the Report, 2024
|
Based on WHO Annual PM2.5 Guideline |
||
|
5 Most Polluted Countries |
Countries & Regions Exceeded Guideline |
|
|
Australia Bahamas Barbados Estonia Grenada Iceland New Zealand |
Chad Bangladesh Pakistan Democratic Republic of Congo India
|
126 (91.3%)
|
|
The annual average PM2.5 concentrations of the % most polluted countries is 91.8 µg/m3, 78 µg/m3, 73.7 µg/m3, 58.2 µg/m3, and 50.6 µg/m3 respectively. |
||
|
One Liners 12-03-2025 |
|
History, Art and Culture |
|
National Archives of India (NAI) NAI celebrates its 135th Foundation Day with the inauguration of the exhibition "Indian Heritage through Architecture"
|
|
Geography |
|
Vadhavan Port on PPP Model Recently, Union Cabinet has approved the setting up of Major Port at Vadhavan, near Dahanu, in Maharashtra on PPP mode.
|
|
Polity & Governance |
|
Prime Minister Dhan Dhaanya Krishi Yojna Recently, government has launched a programme to improve farmer’s livelihood.
|
|
Rural Prosperity and Resilience Programme Recently, government has launched a comprehensive multi-sectoral rural programme.
|
|
PLI scheme for Specialty Steel Recently, government has launched the second round of PLI scheme for Specialty Steel.
|
|
Agriculture |
|
Soil Fertility Mapping
|
|
AAHAR-2025 Recently, Union Minister of Food Processing Industry inaugurated the AAHAR-2025 event.
|
|
Science |
|
Preprints Preprints were gaining popularity due to its open-access.
|
|
Polygraph
|
|
Miscellaneous |
|
75/25 Initiative Recently, government unveiled the 75/25 initiative on World Hypertension Day on May 17, 2023.
|