Bridge Inventory and Condition Rating System (BICRS)
Prelims – Current events of national and international importance; Economic and Social Development.
Mains (GS IV) – Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc.
Why in News?
- Launched by – National Highways Authority of India (NHAI).
- It is a ranking mechanism to rate NHAI’s infrastructure assets to determine their structural safety and look for remedial measures for their upkeep and regular monitoring.
National Highway Authority of India was set up NHAI Act, 1988 to provide for the constitution of an Authority for the development, maintenance and management of national highways and for matter connected therewith.
- Aim – To prepare a unified repository of all its structures, and each property will be assigned a union assessment identification number.
- Development – Based on input from its design division to ensure the systematic management and safety of infrastructure assets.
- Mandate – Comprehensive documentation, assessment, and inspection of bridges twice a year.
- Key features – Systematic evaluation of health based on predetermined rating parameters.
- Identification of structures that require immediate remedial measures, including the imposition of traffic restrictions or suspension of heavy vehicle traffic.
- Functions – It will record comprehensive structural specifications, geographical coordinates, AS-IS drawings, and other related documentation.
AS-IS is documentation of the measurements and elements of an existing building.
- This data is used in the context of renovation.
- Implementation – The engineers will record structural specifications and details of all projects, and the first inspection of structures must be completed before the monsoon.
- The project director will cross-check the data prepared by the engineers during their monthly inspections and make observations if discrepancies are found in records and the physical state.
- Importance – It ensures systematic management and safety of infrastructure assets.
Reference
The New Indian Express| Launch of Bridge Inventory and Condition Rating System (BICRS)
Navkar Mahamantra Divas
Prelims – Current events of national and international importance.
Mains (GS-I) – Indian culture will cover the salient aspects of Art Forms, literature and Architecture from ancient to modern times.
Why in News?
Recently, Navkar Mahamantra Divas was inaugurated in line with celebration of Mahavir Jayanti.
Mahavir Jayanti is celebrated on April 9the every year to commemorate the birth of Lord Mahavir, the 24th Tirthankara of Jainism.
- Navkar Mantra – It is not just a mantra but the core of our faith and the essence of life.
- It is central to Jain prayer, is more than a collection of sacred syllables, it is a rhythmic flow of energy, stability, and light.
- 9 resolutions are anchored in a commitment to knowledge, action, harmony, and rooted progress.
- Repeating the mantra 9 times, or in its multiples like 27, 54, or 108 represents spiritual completeness and intellectual clarity.
|
Navkar Mantra – Nine Resolutions for a New India
|
|
9 Resolutions
|
Description
|
|
1
Water Conservation
|
Emphasizing the need to value and save every drop of water.
|
|
2
Plant a tree in Mother’s Name
|
Planting of over 100 crore trees in recent months and urging everyone to plant a tree in their mother’s name and nurture it like her blessings.
|
|
3
Cleanliness Mission
|
Understanding the importance and contributing to cleanliness in every street, neighbourhood and city.
|
|
4
Vocal for Local
|
Promotion of locally made products, turning them global and supporting items that carry the essence of Indian soil and the sweat of Indian workers.
|
|
5
Explore India
|
To explore India’s diverse states, cultures, and regions before traveling abroad, emphasizing the uniqueness and value of every corner of the country.
|
|
6
Adopting Natural Farming-
|
The Jain principle of “One living being should not harm another”, and for freeing Mother Earth from chemicals, supporting farmers, and promoting natural farming.
|
|
7
Healthy Lifestyle
|
Following Indian dietary traditions, including millets (Shri Anna), reducing oil consumption by 10%, and maintaining health through moderation and restraint.
|
|
8
Incorporating Yoga and Sports-
|
Making yoga and sports a part of daily life, whether at home, work, school, or parks, to ensure physical health and mental peace.
|
|
9
Helping the Poor
|
Assisting the underprivileged, whether by holding a hand or filling a plate, as the true essence of service.
|
- Ecological relevance of Jainism - Lord Mahavir’s timeless teachings align beautifully with Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment), a national call for sustainable living.
- Jainism’s emblem, “Parasparopagraho Jivanam”, meaning the mutual interdependence of all life offers a deeply ecological worldview.
On Mahavir Jayanti in April 2024, a commemorative stamp and coin on the occasion of 2550th Bhagwan Mahaveer Nirvan Mahotsav.
Reference
PIB| Introduction of Navkar Mantra
Optional Practical Training program
Prelims – Current events of national and international importance.
Mains (GS II) – Bilateral relations of India
Why in News?
A Bill was introduced in the US recently to end the Optional Practical Training program for those no longer engaged in full-time study in the United States.
The F-1 Visa (Academic Student) allows you to enter the US as a full-time student at an accredited college, university, seminary, conservatory, academic high school, elementary school, or other academic institution or in a language training program.
- The OPT program allows students (who are in the US on F1 visas) to work for up to 12 months in a field related to their area of study.
- Types
- Pre-completion OPT - International students are required to be enrolled in a full-time program in the United States for a minimum of one academic year before they can finish their studies.
- Post-completion OPT - It allows the student to work after graduating.
- Eligibility - To be eligible for the OPT program, students are required to be enrolled full-time for a minimum of one academic year.
- They must submit their application through their educational institution, which has the authority to endorse them for OPT.
- The application process is managed by the United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS).
- Students who hold F-1 status are permitted to stay in the United States while participating in OPT employment.
Of the 3,31,602 Indian students in the US, around 29% or 97,556 students were on OPT in 2023-24.
- Extension for STEM students - Students in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) fields can extend their OPTs by another 24 months.
- This effectively means that a student in a STEM field can work in the US for 3 years after graduation.
References
- The Indian Express | Optional Practical Training program in US
- Economic Times | Optional Practical Training (OPT) program
PM-POSHAN Scheme
Prelims – Indian polity and Governance
Mains - GS II |Government Policies & Interventions & GS I | Social empowerment
Why in News?
The Union government recently increased the material cost for midday meals per day for those enrolled in kindergarten and primary schools and upper primary schools
- The PM-POSHAN Scheme, previously referred to as the Mid-Day Meal Scheme.
- It is a Centrally Sponsored initiative overseen by the Ministry of Education.
- Aim - To provide a hot, cooked meal each school day to 11.20 crore children enrolled in Balvatikas (pre-primary) and Classes 1 to 8 across 10.36 lakh government and government-aided schools.
- This scheme serves two main purposes
- To enhance the nutritional status of children attending school.
- To boost enrollment, retention, and attendance rates, particularly among underprivileged children.
- The updated material cost per student per day is as follows
- Rs. 6.78 for Balvatika and Primary students (an increase from Rs. 6.19).
- Rs. 10.17 for Upper Primary students (up from Rs. 9.29).
- These amounts represent the minimum required contribution; however, States and Union Territories have the option to allocate additional funds from their budgets to offer meals with improved nutritional quality.
- Nutritional standards
- For Balvatika and Primary classes - 20g of pulses, 50g of vegetables, and 5g of oil.
- For Upper Primary classes - 30g of pulses, 75g of vegetables, and 7.5g of oil.
- The Labour Bureau, under the Ministry of Labour, provides inflation data for the items included in the PM-POSHAN meal basket, which is derived from the Consumer Price Index – Rural Labourers (CPI-RL) based on 600 sample villages across 20 States.
- The POSHAN Abhiyan, managed by the Ministry of Women and Child Development, focuses on improving nutrition for adolescent girls, pregnant women, lactating mothers, and children aged 0 to 6 years.
- Mission POSHAN 2.0, launched in 2021, combines the efforts of POSHAN Abhiyan and the Supplementary Nutrition Program into a single, cohesive framework.
- Funding structure
- A 60:40 split between the Centre and States/UTs with a legislature.
- A 90:10 split for Northeastern and Himalayan States.
- Full central funding for Union Territories without a legislature.
Reference
Hindustan Times | PM Poshan Scheme
Magic of Indian Silk
Prelims – Current events of national and international importance| Economic and Social Development.
Mains (GS III) – Inclusive growth and issues arising from it.
Why in News?
According to the recent data of Ministry of Textiles, India’s silk production and exports have been raised from 2017-18 to 2023-24.
- Silk – It is a thread made from pure mulberry silk, which is woven by skilled artisans.
- Silk from silkworms – Sericulture is the process of farming silkworms, which eat mulberry leaves to make silk.
- Global production – It has accounting for only 0.2 % of world's total textile production.
- India’s production – It is the 2nd largest producer and consumer of silk globally.
- State wise production
- Mulberry silk – Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Jammu & Kashmir and West Bengal.
- Non-mulberry silk – Jharkhand, Chattisgarh, Orissa and north-eastern states.
India's total raw silk production increased during the period 2017-24 and Exports of silk and silk goods rose during the period 2017-24.
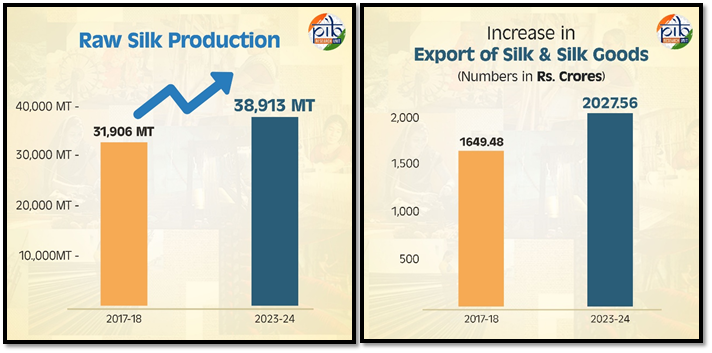
Initiatives to Silk Development
- Silk Samagra Scheme – To scale up production by improving the quality and productivity of sericulture in the country.
- Silk Samagra-2 – To improve the entire silk production process, from raising silkworms to producing quality silk fabrics.
- Raw Material Supply Scheme (RMSS) – To make available quality yarn & their blends to the eligible Handloom weavers at subsidized rates.
- National Handloom Development Programme (NHDP) – To support weavers in the handloom sector, including silk fabric producers.
- Scheme for Capacity Building in Textile Sector Scheme (SAMARTH) – To focus on entry-level training, upskilling and reskilling in Apparel & Garmenting, handloom, handicraft, silk, and jute.
|
Types of Silk in India
|
- Mulberry silk – It comes from silkworms that eat only mulberry leaves.
- Feature – It is soft, smooth, and shiny with a bright glow, making it perfect for luxury sarees and high-end fabrics.
- 92% of the country's total raw silk production comes from mulberry.
- Non-mulberry silk – It comes from wild silkworms that feed on leaves from trees like oak, castor and arjun.
- Feature – It is a natural silk with less shine but is strong, durable, and eco-friendly.
- Silk waste – It's repurposed to create lower-quality products like silk yarn or fabric, or even recycled into new silk items.
|
Reference
PIB| Magic of Indian Silk Production
|
One Liners 14-02-2025
|
|
History, Art and Culture
|
|
Khultabad Name Change to Ratnapur
Recently, Maharashtra government announced the renaming of the historic town Khultabad to its original name, Ratnapur.
- History of Ratnapur/Khultabad - Originally known as Ratnapur, the town's name was changed to Khultabad during the Mughal era.
- Location - Situated approximately 25 km from Chhatrapati Sambhaji Nagar (formerly Aurangabad)
- Tomb of Aurangazeb – The town houses the tomb of Mughal emperor Aurangzeb, along with the graves of his son Azam Shah and Asaf Jah I, the founder of the Hyderabad Nizam dynasty.
|
|
Geography
|
|
Thar Desert Greening
The Thar Desert in India saw a striking 38 per cent rise in greening annually over the last two decades, a new study showed.
- Thar Desert – It is an arid region in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent that covers an area of 200,000 km² in India and Pakistan.
- Thar desert States - Rajasthan, Gujarat, Punjab and Haryana.
- It is the world's 18th-largest desert, and the world's 9th-largest hot subtropical desert.
- Unique phenomena - Thar was the only desert in the world with the highest concurrent increase in population, precipitation and vegetation during the last few decades.
- This remarkable transformation stands in contrast to vegetation trends observed in other deserts globally.
- Thar is among only four major deserts (Thar, Arabian, Negev and Eastern Gobi) worldwide that have experienced significant precipitation increases during this period.
- Reason for greening:
- Enhanced South West Monsoon rainfall
- Groundwater pumping for irrigation.
|
|
International Relations and Issues
|
|
Country Partnership Framework (CPF)
Recently, Mauritius has signed a Country Partnership Framework (CPF) with the International Solar Alliance (ISA).
- CPF – It is a strategic document designed to facilitate medium- and long-term cooperation with ISA member countries to achieve their solar energy goals.
- Aim – To promote the deployment of solar-based applications, capacity-building on technical, regulatory, and financing needs to the country.
- To establish the Solar Technology Application Resource Centre (STAR-C), scaling of solar rooftop, projects, agrivoltaics, water pumping systems and solar Green Hydrogen.
Solar Technology Application Resource Centre (STAR-C) is a program initiated by ISA, to build a skilled solar workforce through specialized training, tools, and learning modules.
- Mauritius – It has become the 1st African nation and 4th globally to enter into this partnership with ISA.
- Duration – 3 years and renewed based on mutual consent.
|
|
Economy
|
|
GI Tags for Meghalaya's Textiles
Recently, the Geographical Indication (GI) tags to Ryndia silk and Khasi handloom, two significant traditional textile products from Meghalaya.
- Ryndia Silk – It is a hand-spun eri silk which is naturally dyed, and organically produced and ethically sourced.
- Ryndia – It is the Khasi name for eri, named after the ryndia (castor) plant that nourishes the eri silkworms.
- Peace Sik, or Ahimsa Silk - Its yarn is extracted without cruelly boiling the silkworms and killing them, unlike other silks.
- Region - It is particularly associated with the Umden-Diwon region, designated as Meghalaya’s first Eri Silk Village in 2021.
- Khasi Handloom – It is the traditional textile art of the Khasi community.
- Uniqueness - This handloom is known for its distinctive weaves and the use of natural dyes.
|
|
Environment
|
|
Vembur Sheep
Vembur sheep in Tamil Nadu faces threat from industrial plan.
- Vembur Sheep - It is one of 5 the indigenous hair sheep breeds in Tamil Nadu and locally called as Pottu aadu.
- Characteristics – It has medium-sized drooping ears, short thin tails, and tall lean bodies.
- It doesn’t require shearing and well-suited to the Tamil Nadu climate.
- Unique coating pattern – White fur adorned with irregular reddish brown patches, and in rare cases black fawn patches.
- It does not rely on commercial cattle fodder, but entirely on natural grazing grounds.
- Recognising its uniqueness, the National Bureau of Animal Genetic Resources officially registered the breed in 2007.

- Climate resilient - The breed’s natural resilience and adaptability to dry climate makes it ideal for the rain-fed agricultural regions.
- Conservation status – IUCN – Not listed.
|
|
India in Mission Innovation Annual Gathering (MIAG), 2025
Recently, India highlighted their initiatives at Mission Innovation Annual Gathering, 2025 which was held at Seoul, South Korea.
- Mission Innovation – It is a global clean energy initiative to catalyse action and investment in research, development and demonstration in clean energy.
- Launched in – It was announced at COP21 in 2015 by the then President Obama of the United States.
- Members - 23 countries including India and the European Commission (on behalf of the European Union).
- Missions

- Mission Innovation 2.0 - It was launched on 2021, is catalysing a decade of action and investment.
- India’s leadership - The Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India - co-leads the Mission Integrated Biorefinery jointly with the Netherlands as part of Mission Innovation (MI) 2.0.
- Bio E3 Policy - Biotechnology for Environment, Energy, and Economy Policy.
|
|
Security
|
|
Gaurav – Long-Range Glide Bomb (LRGB)
Recently, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully conducted the trials of Gaurav from a Su-30 MKI aircraft.
- LRGB ‘Gaurav’ – It is a 1,000 kg class glide bomb.

- Indigenous production – It is indigenously designed and developed by DRDO's Research Centre Imarat, Armament Research and Development Establishment, and Integrated Test Range, Chandipur.
- Range - The trials successfully demonstrated range close to 100 kms with pin-point accuracy.
|
|
YARD 3039- Next Generation Offshore Patrol Vessel
Recently, The Keel Laying ceremony for Yard 3039, the third Next Generation Offshore Patrol Vessel (NGOPV) was held in Kolkata.
- Yard 3039 – It is a Next Generation Offshore Patrol Vessel.
- Developed by - Goa Shipyard Ltd (GSL), Goa and Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata.
- Features of Yard 3039
- It has a tonnage capcity of around 3000T.
- Designed for coastal defence and surveillance, search and rescue, offshore asset protection, and anti-piracy missions.
|
|
Science
|
|
Black Rats: Primary Hantavirus Carriers in Madagascar
Recent research published in Ecology and Evolution has identified black rats as the primary carriers of hantavirus in rural Madagascar, highlighting a significant health risk to local populations.
- Hantavirus infection - Hantavirus is a serious viral infection transmitted to humans through contact with the excreta (urine, droppings, saliva) of infected rodents.
- Associated Syndromes
- Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS), a potentially fatal respiratory disease
- Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS), which primarily affects kidney function.
- Black rat (Rattus rattus) – It is an invasive species, introduced to Madagascar centuries ago, between the 10th and 14th centuries.
- Increased Human Contact - Deforestation and agricultural expansion in Madagascar have led to increased interaction between human communities and hantavirus-carrying black rats, elevating the potential for disease transmission.
|
|
Miscellaneous
|
|
National Safe Motherhood Day, 2025
National Safe Motherhood Day is observed annually on April 11th in India, coinciding with Kasturba Gandhi's birth anniversary, to emphasize the critical need for maternal healthcare.
- Theme - “Healthy Beginnings, Hopeful Futures,” focusing on ensuring accessible and quality maternal healthcare from the beginning of pregnancy for safe outcomes.
- Maternal death – It is the death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and site of the pregnancy.
- Maternal mortality rate in India – It is declined from 130 per 100,000 live births in 2014-16 to 97 per 100,000 live births in 2018-20.
- While some states, like Kerala, Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu, have witnessed a significant reduction in maternal deaths, others continue to struggle with large numbers.
- White Ribbon Alliance – It is an international non-profit organization that advocates for maternal health.
- Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram (JSSK) – It is one of the schemes launched by the central government to provide free and zero-expense delivery and treatment for pregnant women and sick newborns.
|
