Recently, the Centre launched an E-Daakhil portal across all states and the union territories of India.
The government is also moving forward with the launching of e-jagriti, a new initiative designed to further automate consumer cases' filing, tracking, and management.
|
National Consumer Dispute Redressal Commission (NSDRC) |
|
References
Recently, the Jarawa Tribe of 19 members in Andaman and Nicobar Islands was included in the electoral process for the first time, done under systematic Voters' Education & Electoral Participation program.
References
The President’s Colours were recently awarded to the 4 mechanised infantry battalions by the Army chief during a ceremony in Maharashtra.
References
Recently, the Supreme Court directed the Union government to submit the report on Tamil Nadu and Karnataka’s dispute between Pennaiyar river water.
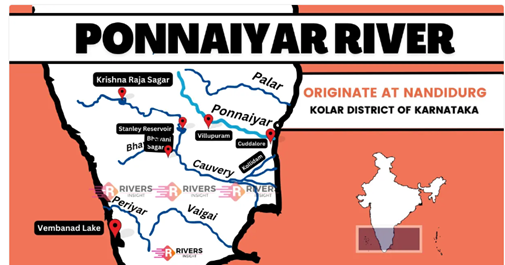
References
Recently, the Baltic Sea is at a high risk zone after a suspected sabotage attack on undersea cables.
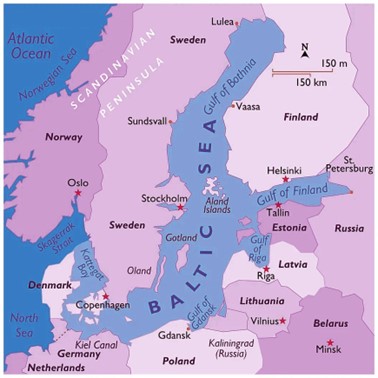
World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) doing a Baltic Programme with an aim at marine protected areas covering 30% of the sea, with 10% of the strictly protected area by 2030.
References