Project NAMAN
The Indian Army launched the first phase of Project NAMAN recently.
- Aim- It is designed to provide dedicated support and services to Defence pensioners, veterans, and their families.
- Ministry - Ministry of Defence.
- Enabled by - Tripartite Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between
- The Indian Army’s Directorate of Indian Army Veterans,
- Common Service Centre (CSC) e-Governance India Limited, and
- HDFC Bank Limited.
- SPARSH- The project is centred on SPARSH (System for Pension Administration Raksha), a digital pension system that streamlines pension-related processes for Defence Pensioners.
SPARSH is implemented by Ministry of Defence for meeting the pension sanction and disbursement requirements for Armed Forces viz. Army, Navy, Air Force and Defence Civilians.
- Beneficiaries - It extends services to the entire resident population of military stations and surrounding localities.
- Common Services Centres- In the 1st phase 14 CSCs have been established across India in key locations such as New Delhi, Jalandhar, Leh, Dehradun, Lucknow, Jodhpur, etc.
- There is a plan to establish around 200 centres nationwide over the next 2-3 years.
- Support and Management- HDFC Bank will provide IT infrastructure while local military stations contributed physical infrastructure for CSCs.
- Each CSC is managed by a Village Level Entrepreneur (VLE) selected from veterans or Next of Kin (NOKs) by Local Military Authorities.
- Significance- The project reflects the Indian Army’s commitment to the welfare of veterans and their families.
- It also creates entrepreneurial opportunities for Veterans and NOKs, empowering them to contribute to their communities.
References
- PIB | PROJECT NAMAN
- News on air | Indian Army Launches Project NAMAN
Biosensors on Metal-organic frameworks (MOF) and 2-dimensional (2D) materials
Recently Scientist have developed a bunch of electrochemical and optical biosensors-based on Metal-organic Frameworks(MOF) and 2 dimensional (2D) maetrials.
- MOFs – They are a group of chemical compounds or polymers of nano size that are formed by linking inorganic and organic units by strong bonds in a certain geometrical structure.
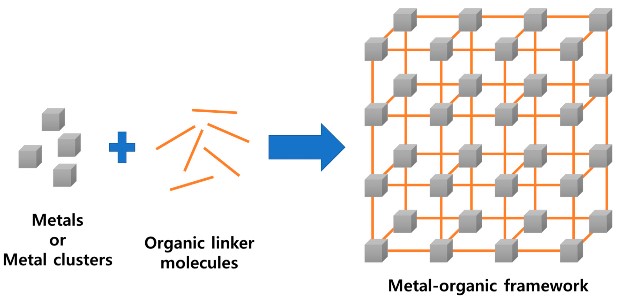
- 2D materials - They are crystalline solids consisting of a single layer of atoms with only one dimension is nano-sized, resembling a large, but very thin sheet.
- The electrochemical and optical biosensors-based on MOF and 2D materials is developed by Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali,Punjab.
- Characteristics of the Sensors – They are porus materials with large surface area, Functionality, and Optoelectronic properties.
- They can be integrated with biorecognition molecules robustly for reliable sensor performance.
- Nano to Pico Sensitivity - The bioconjugation of biorecognition elements over the MOF and 2D materials-based interfaces with a greater density facilitates nano- to pico- molar level sensitivities.
Bioconjugation is a chemical process that creates a stable covalent bond between two molecules, at least one of which is a biomolecule.
- Useability - They can be developed into disposable electrodes, optical kits, fiber optic sensors, colorimetric strips, etc.
- Application – They can be used
- To develop electrochemical and optical sensors for different analytes, such as bacteria, Aflatoxins, and heavy metals
- For rapid and convenient detection of several health, food quality, and environmental parameters.
- For analyzing food toxins such as Aflatoxins and Zearaloene in water, milk and staple food samples.
- In low-cost point of care devices for quick detection and screening of diseases such as anaemia, cancer.
- As gas and heavy metal detection tools to monitor the environmental quality.
References
PIB | Novel nano polymers pave way for low-cost, efficient sensors
Fluoxetine (Prozac) & its effects on guppy fish
A recent study has revealed that long-term exposure to fluoxetine (Prozac) can significantly disrupt the behavior and reproductive traits of the male guppy fish.
- Fluoxetine (Prozac) - Fluoxetine is an antidepressant that belongs to a group of medicines called serotonin selective reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
- It works by increasing the amount of a natural chemical called serotonin in the brain.
- Effects of Low Concentrations
- It reduced activity levels and increased refuge-seeking behaviour in male guppies.
- It altered their body condition, increased the size of their reproductive organs, and reduced sperm velocity.
- Reduced flexibility in response to environmental changes.
Refuge-seeking behaviour refers specifically to how much time the fish spend in hiding or protected areas, as opposed to open, potentially more dangerous spaces in their habitat.
- Effects of High Concentrations
- Increased variability in body condition and sperm production.
- It changed 'pace of life syndromes'.
- Larger reproductive organs are associated with lower sperm quality.
|
Guppy Fish
|
- Scientific name- Poecilia reticulate.
- They are named for Robert John Lechmere Guppy who collected these fish on the island of Trinidad in 1866.
- Native- They are native to tropical regions of South America and the Caribbean, particularly found in freshwater streams and pools.
- Lifespan- They generally live for 2 to 3 years.
- Diet- Omnivorous.
- Appearance - Guppies come in nearly every color of the rainbow. Many types have silvery scales marked with dark dots, splotches of color, or complex patterns.
- Size - A guppy’s body is little only about 1 to 2 inches long. Males are smaller and more brightly colored than females.
- Social Behavior- These fish are peaceful and thrive in groups, making them ideal for community tanks.
- Breeding- Guppies are livebearers, meaning they give birth to live young rather than laying eggs.

|
Reference
Down to Earth | Fluoxetine (Prozac) & its effects on guppy fish
Tourism & Hospitality Skill Council
The Tourism and Hospitality Skill Council recently signed a Memorandum of Understanding with Visa to train youth for the growing tourism industry.
- It is a Not-for-Profit Organization, registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860, promoted by the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII).
- Aim - It is formed by the Industry and for the industry to tackle the skilling of large manpower to fulfil the industry requirements, playing a crucial role in bridging this gap.
- Nodal ministry- Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship.
- THSC is now an approved awarding body under National Council for Vocational Education and Training (NCVET).
- Vision- To promote skill development in the Hospitality and Tourism sector to build a strong industry-aligned ecosystem, creating respectable employment opportunities in India.
- Mission- To contribute to a skilled workforce by setting
- National occupational standards,
- Establishing a labour market information system,
- Affiliating training partners,
- Certifying trainers, and
- Facilitating learner assessments and certifications.
The recent Memorandum of Understanding (MoU)
- The initiative aims to support India’s ambitions of becoming a global tourism hub by ensuring a skilled workforce.
- Objective-To up skill at least 20,000 Indian youth in tourism-relevant skills.
In 2023, tourism accounted for over $231 billion in GDP and employed more than 42 million people in India.
- Duration- 3-year partnership.
- Funding- Partnership valued at up to $1 million USD.
- States covered- Assam, Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, and West Bengal, among others (10 States in total).
- Key Areas of Training- Tour guides, customer service executives, naturalists, and paragliding tandem pilots.
- Agency- The partnership involved Tourism & Hospitality Skill Council (THSC) under the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), Visa (a global leader in digital payments).
- Significance- This partnership aims to equip Indian youth with skills for the growing tourism sector, boosting economic development and enriching the tourist experience in India.
References
- PIB | Visa partners with Skill India
- THSC | Vision & Mission
Navaratna status
The Solar Energy Corporation of India Ltd (SECI), a Central Public Sector Enterprise (CPSE) under Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, has recently been granted Navratna status by the Ministry of Finance.
- The main aim of assigning the "Ratna" statuses to various CPSEs was to give operational freedom and decision-making power to the state-run entities.
|
Criteria
|
Miniratna
|
Navratna
|
Maharatna
|
|
Introduced
in
|
1997
|
1997
|
2010
|
|
Eligibility
|
Miniratna Category-I: Profit over Rs. 30 crores in at least one of the last 3 years
Miniratna Category-II: Continuous profitability over last 3 years
Positive net worth and no defaults on loan repayments or government guarantees.
Continuous profitability and positive net worth.
|
Must be Miniratna I or Schedule ‘A’ CPSE.
‘Excellent’ or ‘Very Good’ MOU rating in 3 of the last 5 years.
Composite score of 60 or above across 6 performance indicators.
|
Must have Navratna status.
Listed on Indian stock exchange with minimum prescribed public shareholding.
Annual turnover > Rs. 25,000 crores
Net worth > Rs. 15,000 crores
Net profit > Rs. 5,000 crore (average of last 3 years)
|
|
Profit requirement
|
Category-I- Pre-tax profit of Rs. 30 crore in at least one of the last three years
Category-II- Profit for the last 3 consecutive years
|
Must be a Miniratna-I with a score of 60 or above in 6 performance parameters
|
Must have an average annual profit of over Rs.5,000 crore for the last 3 years
|
|
Investment Powers
|
Can make investments up to Rs. 500 crore or equal to their net worth, whichever is lower
|
Can invest up to Rs. 1,000 crore or 15% of their net worth, whichever is lower
|
Can invest up to Rs. 5,000 crore or 15% of their net worth, whichever is lower
|
|
Delegated Powers
|
Limited operational autonomy
|
Enhanced powers in capital expenditure, investments, mergers, etc.
|
Greater autonomy in investments and HR management
|
|
Current Count
|
57 companies
|
17 companies
|
13 companies
|
|
Examples
|
Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL)
Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL)
|
Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC)
National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC)
|
Coal India Limited
Indian Oil Corporation Limited (IOCL)
|
Reference
- PIB | Navaratna status
- CNBC | Miniratna, Navratna and Maharatna companies
